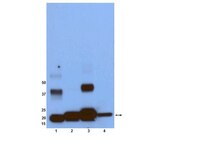
Site-specific processing of Ras and Rap1 Switch I by a MARTX toxin effector domain.
Antic, I; Biancucci, M; Zhu, Y; Gius, DR; Satchell, KJ
Nature communications
6
7396
2015
Show Abstract
Ras (Rat sarcoma) protein is a central regulator of cell growth and proliferation. Mutations in the RAS gene are known to occur in human cancers and have been shown to contribute to carcinogenesis. In this study, we show that the multifunctional-autoprocessing repeats-in-toxin (MARTX) toxin-effector domain DUF5(Vv) from Vibrio vulnificus to be a site-specific endopeptidase that cleaves within the Switch 1 region of Ras and Rap1. DUF5(Vv) processing of Ras, which occurs both biochemically and in mammalian cell culture, inactivates ERK1/2, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation. The ability to cleave Ras and Rap1 is shared by DUF5(Vv) homologues found in other bacteria. In addition, DUF5(Vv )can cleave all Ras isoforms and KRas with mutations commonly implicated in malignancies. Therefore, we speculate that this new family of Ras/Rap1-specific endopeptidases (RRSPs) has potential to inactivate both wild-type and mutant Ras proteins expressed in malignancies. | | 26051945
 |
EGF-Induced Acetylation of Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins Is Dependent on KRAS Mutational Status in Colorectal Cancer Cells.
Roda, D; Castillo, J; Telechea-Fernández, M; Gil, A; López-Rodas, G; Franco, L; González-Rodríguez, P; Roselló, S; Pérez-Fidalgo, JA; García-Trevijano, ER; Cervantes, A; Zaragozá, R
PloS one
10
e0130543
2015
Show Abstract
KRAS mutational status is considered a negative predictive marker of the response to anti-EGFR therapies in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. However, conflicting data exist regarding the variable response to EGFR-targeted therapy. The effects of oncogenic KRAS on downstream targets were studied in cell lines with different KRAS mutations. Cells harboring a single KRASG13D allele showed the most tumorigenic profile, with constitutive activation of the downstream pathway, rendering them EGF-unresponsive. Conversely, KRASA146T cells showed a full EGF-response in terms of signal transduction pathways, cell proliferation, migration or adhesion. Moreover, the global acetylome of CRC cells was also dependent on KRAS mutational status. Several hnRNP family members were identified within the 36 acetylated-proteins. Acetylation status is known to be involved in the modulation of EGF-response. In agreement with results presented herein, hnRNPA1 and L acetylation was induced in response to EGF in KRASA146T cells, whereas acetyl-hnRNPA1 and L levels remained unchanged after growth factor treatment in KRASG13D unresponsive cells. Our results showed that hnRNPs induced-acetylation is dependent on KRAS mutational status. Nevertheless hnRNPs acetylation might also be the point where different oncogenic pathways converge. | | 26110767
 |
MEK-dependent negative feedback underlies BCR-ABL-mediated oncogene addiction.
Asmussen, J; Lasater, EA; Tajon, C; Oses-Prieto, J; Jun, YW; Taylor, BS; Burlingame, A; Craik, CS; Shah, NP
Cancer discovery
4
200-15
2014
Show Abstract
The clinical experience with BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) provides compelling evidence for oncogene addiction. Yet, the molecular basis of oncogene addiction remains elusive. Through unbiased quantitative phosphoproteomic analyses of CML cells transiently exposed to BCR-ABL TKI, we identified persistent downregulation of growth factor receptor (GF-R) signaling pathways. We then established and validated a tissue-relevant isogenic model of BCR-ABL-mediated addiction, and found evidence for myeloid GF-R signaling pathway rewiring that profoundly and persistently dampens physiologic pathway activation. We demonstrate that eventual restoration of ligand-mediated GF-R pathway activation is insufficient to fully rescue cells from a competing apoptotic fate. In contrast to previous work with BRAF(V600E) in melanoma cells, feedback inhibition following BCR-ABL TKI treatment is markedly prolonged, extending beyond the time required to initiate apoptosis. Mechanistically, BCR-ABL-mediated oncogene addiction is facilitated by persistent high levels of MAP-ERK kinase (MEK)-dependent negative feedback.We found that BCR–ABL can confer addiction in vitro by rewiring myeloid GF-R signaling through establishment of MEK-dependent negative feedback. Our findings predict that deeper, more durable responses to targeted agents across a range of malignancies may be facilitated by maintaining negative feedback concurrently with oncoprotein inhibition. | | 24362263
 |
MicroRNA-5p and -3p co-expression and cross-targeting in colon cancer cells.
Choo, KB; Soon, YL; Nguyen, PN; Hiew, MS; Huang, CJ
Journal of biomedical science
21
95
2014
Show Abstract
Two mature miRNA species may be generated from the 5' and 3' arms of a pre-miRNA precursor. In most cases, only one species remains while the complementary species is degraded. However, co-existence of miRNA-5p and -3p species is increasingly being reported. In this work, we aimed to systematically investigate co-expression of miRNA-5p/3p in colon cancer cells in a genome-wide analysis, and to examine cross-targeting of the dysregulated miRNAs and 5p/3p species.Four colon cancer cell lines were examined relative to two normal colon tissues. Of the 1,190 miRNAs analyzed, 92 and 36 were found to be up- or down-regulated, respectively, in cancer cells. Nineteen co-expressed miRNA-5p/3p pairs were further identified suggesting frequent 5p/3p co-accumulation in colon cancer cells. Of these, 14 pairs were co-up-regulated and 3 pairs were co-down-regulated indicating concerted 5p/3p dysregulation. Nine dysregulated miRNA pairs fell into three miRNA gene families, namely let-7, mir-8/200 and mir-17, which showed frequent cross-targeting in the metastasis process. Focusing on the let-7d-5p/3p pair, the respectively targeted IGF1R and KRAS were shown to be in a reverse relationship with expression of the respective miRNA, which was confirmed in transient transfection assays using let-7d mimic or inhibitor. Targeting of KRAS by let-7d was previous reported; targeting of IGF1R by let-7d-5p was confirmed in luciferase assays in this study. The findings of let-7d-5p/3p and multiple other miRNAs targeting IGF1R, KRAS and other metastasis-related factors suggest that 5p/3p miRNAs contribute to cross-targeting of multiple cancer-associated factors and processes possibly to evade functional abolishment when any one of the crucial factors are inactivated.miRNA-5p/3p species are frequently co-expressed and are coordinately regulated in colon cancer cells. In cancer cells, multiple cross-targeting by the miRNAs, including the co-existing 5p/3p species, frequently occurs in an apparent safe-proof scheme of miRNA regulation of important tumorigenesis processes. Further systematic analysis of co-existing miRNA-5p/3p pairs in clinical tissues is important in elucidating 5p/3p contributions to cancer pathogenesis. | Western Blotting | 25287248
 |
PLC-γ and PI3K link cytokines to ERK activation in hematopoietic cells with normal and oncogenic Kras.
Diaz-Flores, E; Goldschmidt, H; Depeille, P; Ng, V; Akutagawa, J; Krisman, K; Crone, M; Burgess, MR; Williams, O; Houseman, B; Shokat, K; Sampath, D; Bollag, G; Roose, JP; Braun, BS; Shannon, K
Science signaling
6
ra105
2013
Show Abstract
Oncogenic K-Ras proteins, such as K-Ras(G12D), accumulate in the active, guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-bound conformation and stimulate signaling through effector kinases. The presence of the K-Ras(G12D) oncoprotein at a similar abundance to that of endogenous wild-type K-Ras results in only minimal phosphorylation and activation of the canonical Raf-mitogen-activated or extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase kinase (MEK)-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling cascades in primary hematopoietic cells, and these pathways remain dependent on growth factors for efficient activation. We showed that phospholipase C-γ (PLC-γ), PI3K, and their generated second messengers link activated cytokine receptors to Ras and ERK signaling in differentiated bone marrow cells and in a cell population enriched for leukemia stem cells. Cells expressing endogenous oncogenic K-Ras(G12D) remained dependent on the second messenger diacylglycerol for the efficient activation of Ras-ERK signaling. These data raise the unexpected possibility of therapeutically targeting proteins that function upstream of oncogenic Ras in cancer. | | 24300897
 |
Reversible, interrelated mRNA and miRNA expression patterns in the transcriptome of Rasless fibroblasts: functional and mechanistic implications.
Azrak, SS; Ginel-Picardo, A; Drosten, M; Barbacid, M; Santos, E
BMC genomics
14
731
2013
Show Abstract
4-Hydroxy-tamoxifen (4OHT) triggers Cre-mediated K-Ras removal in [H-Ras-/-; N-Ras-/-; K-Ras lox/lox; RERT ert/ert] fibroblasts, generating growth-arrested "Rasless" MEFs which are able to recover their proliferative ability after ectopic expression of Ras oncoproteins or constitutively active BRAF or MEK1.Comparison of the transcriptional profiles of Rasless fibroblasts with those of MEFs lacking only H-Ras and N-Ras identified a series of differentially expressed mRNAs and microRNAs specifically linked to the disappearance of K-Ras from these cells. The rescue of cell cycle progression in Rasless cells by activated BRAF or MEK1 resulted in the reversal of most such transcriptional mRNA and microRNA alterations.Functional analysis of the differentially expressed mRNAs uncovered a significant enrichment in the components of pathways regulating cell division, DNA/RNA processing and response to DNA damage. Consistent with G1/S blockade, Rasless cells displayed repression of a series of cell cycle-related genes, including Cyclins, Cyclin-dependent kinases, Myc and E2F transcription targets, and upregulation of Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. The profile of differentially expressed microRNAs included a specific set of oncomiR families and clusters (repressed miR-17 ~ 92, miR-106a ~ 363, miR-106b ~ 25, miR-212 ~ 132, miR-183 ~ 182, and upregulated miR-335) known for their ability to target a specific set of cellular regulators and checkpoint sensors (including Rb, E2F and Cdkns) able to modulate the interplay between the pro- and anti-proliferative or stress-response pathways that are reversibly altered in Rasless cells.Our data suggest that the reversible proliferation phenotype of Rasless cells is the pleiotropic result of interplay among distinct pro- and anti-proliferative, and stress-response pathways modulated by a regulatory circuitry constituted by a specific set of differentially expressed mRNAs and microRNAs and preferentially targeting two cross-talking signalling axes: Myc-Rb-E2F-dependent and Cdkns-p53-dependent pathways. | Western Blotting | 24156637
 |
A phospholipase C-γ1-independent, RasGRP1-ERK-dependent pathway drives lymphoproliferative disease in linker for activation of T cells-Y136F mutant mice.
Kortum, RL; Rouquette-Jazdanian, AK; Miyaji, M; Merrill, RK; Markegard, E; Pinski, JM; Wesselink, A; Nath, NN; Alexander, CP; Li, W; Kedei, N; Roose, JP; Blumberg, PM; Samelson, LE; Sommers, CL
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950)
190
147-58
2013
Show Abstract
Mice expressing a germline mutation in the phospholipase C-γ1-binding site of linker for activation of T cells (LAT) show progressive lymphoproliferation and ultimately die at 4-6 mo age. The hyperactivated T cells in these mice show defective TCR-induced calcium flux but enhanced Ras/ERK activation, which is critical for disease progression. Despite the loss of LAT-dependent phospholipase C-γ1 binding and activation, genetic analysis revealed RasGRP1, and not Sos1 or Sos2, to be the major Ras guanine exchange factor responsible for ERK activation and the lymphoproliferative phenotype in these mice. Analysis of isolated CD4(+) T cells from LAT-Y136F mice showed altered proximal TCR-dependent kinase signaling, which activated a Zap70- and LAT-independent pathway. Moreover, LAT-Y136F T cells showed ERK activation that was dependent on Lck and/or Fyn, protein kinase C-θ, and RasGRP1. These data demonstrate a novel route to Ras activation in vivo in a pathological setting. | | 23209318
 |
A high-fat diet activates oncogenic Kras and COX2 to induce development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice.
Philip, B; Roland, CL; Daniluk, J; Liu, Y; Chatterjee, D; Gomez, SB; Ji, B; Huang, H; Wang, H; Fleming, JB; Logsdon, CD; Cruz-Monserrate, Z
Gastroenterology
145
1449-58
2013
Show Abstract
Obesity is a risk factor for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), but it is not clear how obesity contributes to pancreatic carcinogenesis. The oncogenic form of KRAS is expressed during early stages of PDAC development and is detected in almost all of these tumors. However, there is evidence that mutant KRAS requires an additional stimulus to activate its full oncogenic activity and that this stimulus involves the inflammatory response. We investigated whether the inflammation induced by a high-fat diet, and the accompanying up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2), increases Kras activity during pancreatic carcinogenesis in mice.We studied mice with acinar cell-specific expression of KrasG12D (LSL-Kras/Ela-CreERT mice) alone or crossed with COX2 conditional knockout mice (COXKO/LSL-Kras/Ela-CreERT). We also studied LSL-Kras/PDX1-Cre mice. All mice were fed isocaloric diets with different amounts of fat, and a COX2 inhibitor was administered to some LSL-Kras/Ela-CreERT mice. Pancreata were collected from mice and analyzed for Kras activity, levels of phosphorylated extracellular-regulated kinase, inflammation, fibrosis, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN), and PDACs.Pancreatic tissues from LSL-Kras/Ela-CreERT mice fed high-fat diets (HFDs) had increased Kras activity, fibrotic stroma, and numbers of PanINs and PDACs than LSL-Kras/Ela-CreERT mice fed control diets; the mice fed the HFDs also had shorter survival times than mice fed control diets. Administration of a COX2 inhibitor to LSL-Kras/Ela-CreERT mice prevented these effects of HFDs. We also observed a significant reduction in survival times of mice fed HFDs. COXKO/LSL-Kras/Ela-CreERT mice fed HFDs had no evidence for increased numbers of PanIN lesions, inflammation, or fibrosis, as opposed to the increases observed in LSL-Kras/Ela-CreERT mice fed HFDs.In mice, an HFD can activate oncogenic Kras via COX2, leading to pancreatic inflammation and fibrosis and development of PanINs and PDAC. This mechanism might be involved in the association between risk for PDAC and HFDs. | Western Blotting | 23958541
 |
Endomembrane H-Ras controls vascular endothelial growth factor-induced nitric-oxide synthase-mediated endothelial cell migration.
Haeussler, DJ; Pimentel, DR; Hou, X; Burgoyne, JR; Cohen, RA; Bachschmid, MM
The Journal of biological chemistry
288
15380-9
2013
Show Abstract
We demonstrate for the first time that endomembrane-delimited H-Ras mediates VEGF-induced activation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) and migratory response of human endothelial cells. Using thiol labeling strategies and immunofluorescent cell staining, we found that only 31% of total H-Ras is S-palmitoylated, tethering the small GTPase to the plasma membrane but leaving the function of the large majority of endomembrane-localized H-Ras unexplained. Knockdown of H-Ras blocked VEGF-induced PI3K-dependent Akt (Ser-473) and eNOS (Ser-1177) phosphorylation and nitric oxide-dependent cell migration, demonstrating the essential role of H-Ras. Activation of endogenous H-Ras led to recruitment and phosphorylation of eNOS at endomembranes. The loss of migratory response in cells lacking endogenous H-Ras was fully restored by modest overexpression of an endomembrane-delimited H-Ras palmitoylation mutant. These studies define a newly recognized role for endomembrane-localized H-Ras in mediating nitric oxide-dependent proangiogenic signaling. | Western Blotting | 23548900
 |
Elucidating distinct roles for NF1 in melanomagenesis.
Maertens, O; Johnson, B; Hollstein, P; Frederick, DT; Cooper, ZA; Messiaen, L; Bronson, RT; McMahon, M; Granter, S; Flaherty, K; Wargo, JA; Marais, R; Cichowski, K
Cancer discovery
3
338-49
2013
Show Abstract
BRAF mutations play a well-established role in melanomagenesis; however, without additional genetic alterations, tumor development is restricted by oncogene-induced senescence (OIS). Here, we show that mutations in the NF1 tumor suppressor gene cooperate with BRAF mutations in melanomagenesis by preventing OIS. In a genetically engineered mouse model, Nf1 mutations suppress Braf-induced senescence, promote melanocyte hyperproliferation, and enhance melanoma development. Nf1 mutations function by deregulating both phosphoinositide 3-kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. As such, Nf1/Braf-mutant tumors are resistant to BRAF inhibitors but are sensitive to combined inhibition of mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase and mTOR. Importantly, NF1 is mutated or suppressed in human melanomas that harbor concurrent BRAF mutations, NF1 ablation decreases the sensitivity of melanoma cell lines to BRAF inhibitors, and NF1 is lost in tumors from patients following treatment with these agents. Collectively, these studies provide mechanistic insight into how NF1 cooperates with BRAF mutations in melanoma and show that NF1/neurofibromin inactivation may have an impact on responses to targeted therapies. | Western Blotting | 23171796
 |