420107 Sigma-AldrichJasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni - CAS 102396-24-7 - Calbiochem
Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni, CAS 102396-24-7, is a cell-permeable F-actin probe. Induces actin polymerization and stabilization. Blocks activation of store-mediated Ca2+ entry into cells.
More>> Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni, CAS 102396-24-7, is a cell-permeable F-actin probe. Induces actin polymerization and stabilization. Blocks activation of store-mediated Ca2+ entry into cells. Less<<Produits recommandés
Aperçu
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Tableau de caractéristiques principal
| CAS # | Empirical Formula |
|---|---|
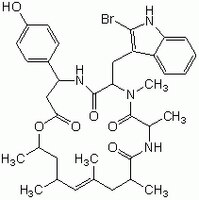
| 102396-24-7 | C₃₆H₄₅BrN₄O₆ |
Prix & Disponibilité
| Référence | Disponibilité | Conditionnement | Qté | Prix | Quantité | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 420107-50UG |
|
Flacon en verre | 50 μg |
|
— |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Overview | A cell-permeable F-actin probe. A cyclodepsipeptide with antifungal and antitumor properties. A potent inducer of actin polymerization and stabilization in vitro. Prevents activation of store-mediated Ca2+ entry into cells. It competes with Phalloidin (Cat. No. 516640) for actin binding (Kd = 15 nM) and enhances apoptosis induced by interleukin 2 (IL-2) deprivation. A 1 mM (50 µg/71 µl) solution of Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni (Cat. No. 420127) in DMSO is also available. |
| Catalogue Number | 420107 |
| Brand Family | Calbiochem® |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| CAS number | 102396-24-7 |
| ATP Competitive | N |
| Form | Off-white solid |
| Hill Formula | C₃₆H₄₅BrN₄O₆ |
| Chemical formula | C₃₆H₄₅BrN₄O₆ |
| Reversible | N |
| Structure formula Image | |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Primary Target | Inducer of actin polymerization and stabilization in vitro |
| Primary Target IC<sub>50</sub> | Kd = 15 nM for actin binding |
| Purity | ≥95% by HPLC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
|---|---|
| Cell permeable | Y |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information | |
|---|---|
| R Phrase | R: 20/21/22 Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| S Phrase | S: 36 Wear suitable protective clothing. |
| Product Usage Statements |
|---|
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Packaged under inert gas | Packaged under inert gas |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Référence | GTIN |
| 420107-50UG | 07790788050085 |
Documentation
Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni - CAS 102396-24-7 - Calbiochem FDS
| Titre |
|---|
Jasplakinolide, Jaspis johnstoni - CAS 102396-24-7 - Calbiochem Certificats d'analyse
| Titre | Numéro de lot |
|---|---|
| 420107 |
Références bibliographiques
| Aperçu de la référence bibliographique |
|---|
| Rosado, J.A., et al. 2000. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 7527. Posey, S.C., and Bierer, B.E. 1999. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 4259. Senderowicz, A.M., et al. 1995. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 87, 46. Bubb, M.R., et al. 1994. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 14869. Scott, V.R., et al. 1988. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32, 1154. |
Citations
| Titre | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Fiche technique | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Note that this data sheet is not lot-specific and is representative of the current specifications for this product. Please consult the vial label and the certificate of analysis for information on specific lots. Also note that shipping conditions may differ from storage conditions.
|