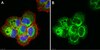
Activation of ERα signaling differentially modulates IFN-γ induced HLA-class II expression in breast cancer cells.
Mostafa, AA; Codner, D; Hirasawa, K; Komatsu, Y; Young, MN; Steimle, V; Drover, S
PloS one
9
e87377
2014
Show Abstract
The coordinate regulation of HLA class II (HLA-II) is controlled by the class II transactivator, CIITA, and is crucial for the development of anti-tumor immunity. HLA-II in breast carcinoma is associated with increased IFN-γ levels, reduced expression of the estrogen receptor (ER) and reduced age at diagnosis. Here, we tested the hypothesis that estradiol (E₂) and ERα signaling contribute to the regulation of IFN-γ inducible HLA-II in breast cancer cells. Using a panel of established ER⁻ and ER⁺ breast cancer cell lines, we showed that E₂ attenuated HLA-DR in two ER⁺ lines (MCF-7 and BT-474), but not in T47D, while it augmented expression in ER⁻ lines, SK-BR-3 and MDA-MB-231. To further study the mechanism(s), we used paired transfectants: ERα⁺ MC2 (MDA-MB-231 c10A transfected with the wild type ERα gene) and ERα⁻ VC5 (MDA-MB-231 c10A transfected with the empty vector), treated or not with E₂ and IFN-γ. HLA-II and CIITA were severely reduced in MC2 compared to VC5 and were further exacerbated by E₂ treatment. Reduced expression occurred at the level of the IFN-γ inducible CIITA promoter IV. The anti-estrogen ICI 182,780 and gene silencing with ESR1 siRNA reversed the E2 inhibitory effects, signifying an antagonistic role for activated ERα on CIITA pIV activity. Moreover, STAT1 signaling, necessary for CIITA pIV activation, and selected STAT1 regulated genes were variably downregulated by E₂ in transfected and endogenous ERα positive breast cancer cells, whereas STAT1 signaling was noticeably augmented in ERα⁻ breast cancer cells. Collectively, these results imply immune escape mechanisms in ERα⁺ breast cancer may be facilitated through an ERα suppressive mechanism on IFN-γ signaling. | Western Blotting | 24475282
 |
IL-4 suppresses the responses to TLR7 and TLR9 stimulation and increases the permissiveness to retroviral infection of murine conventional dendritic cells.
Sriram, U; Xu, J; Chain, RW; Varghese, L; Chakhtoura, M; Bennett, HL; Zoltick, PW; Gallucci, S
PloS one
9
e87668
2014
Show Abstract
Th2-inducing pathological conditions such as parasitic diseases increase susceptibility to viral infections through yet unclear mechanisms. We have previously reported that IL-4, a pivotal Th2 cytokine, suppresses the response of murine bone-marrow-derived conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) and splenic DCs to Type I interferons (IFNs). Here, we analyzed cDC responses to TLR7 and TLR9 ligands, R848 and CpGs, respectively. We found that IL-4 suppressed the gene expression of IFNβ and IFN-responsive genes (IRGs) upon TLR7 and TLR9 stimulation. IL-4 also inhibited IFN-dependent MHC Class I expression and amplification of IFN signaling pathways triggered upon TLR stimulation, as indicated by the suppression of IRF7 and STAT2. Moreover, IL-4 suppressed TLR7- and TLR9-induced cDC production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα, IL-12p70 and IL-6 by inhibiting IFN-dependent and NFκB-dependent responses. IL-4 similarly suppressed TLR responses in splenic DCs. IL-4 inhibition of IRGs and pro-inflammatory cytokine production upon TLR7 and TLR9 stimulation was STAT6-dependent, since DCs from STAT6-KO mice were resistant to the IL-4 suppression. Analysis of SOCS molecules (SOCS1, -2 and -3) showed that IL-4 induces SOCS1 and SOCS2 in a STAT6 dependent manner and suggest that IL-4 suppression could be mediated by SOCS molecules, in particular SOCS2. IL-4 also decreased the IFN response and increased permissiveness to viral infection of cDCs exposed to a HIV-based lentivirus. Our results indicate that IL-4 modulates and counteracts pro-inflammatory stimulation induced by TLR7 and TLR9 and it may negatively affect responses against viruses and intracellular parasites. | | 24489947
 |
Dual modulation of type I interferon response by bluetongue virus.
Doceul, V; Chauveau, E; Lara, E; Bréard, E; Sailleau, C; Zientara, S; Vitour, D
Journal of virology
88
10792-802
2014
Show Abstract
Bluetongue virus (BTV) is a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) virus that causes an economically important disease in ruminants. BTV infection is a strong inducer of type I interferon (IFN-I) in multiple cell types. It has been shown recently that BTV and, more specifically, the nonstructural protein NS3 of BTV are able to modulate the IFN-I synthesis pathway. However, nothing is known about the ability of BTV to counteract IFN-I signaling. Here, we investigated the effect of BTV on the IFN-I response pathway and, more particularly, the Janus tyrosine kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription protein (STAT) signaling pathway. We found that BTV infection triggered the expression of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) in A549 cells. However, when BTV-infected cells were stimulated with external IFN-I, we showed that activation of the IFN-stimulated response element (ISRE) promoter and expression of ISGs were inhibited. We found that this inhibition involved two different mechanisms that were dependent on the time of infection. After overnight infection, BTV blocked specifically the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of STAT1. This inhibition correlated with the redistribution of STAT1 in regions adjacent to the nucleus. At a later time point of infection, BTV was found to interfere with the activation of other key components of the JAK/STAT pathway and to induce the downregulation of JAK1 and TYK2 protein expression. Overall, our study indicates for the first time that BTV is able to interfere with the JAK/STAT pathway to modulate the IFN-I response.Bluetongue virus (BTV) causes a severe disease in ruminants and has an important impact on the livestock economy in areas of endemicity such as Africa. The emergence of strains, such as serotype 8 in Europe in 2006, can lead to important economic losses due to commercial restrictions and prophylactic measures. It has been known for many years that BTV is a strong inducer of type I interferon (IFN-I) in vitro and in vivo in multiple cell types. However, the ability of BTV to interact with the IFN-I system remains unclear. Here, we report that BTV is able to modulate the IFN-I response by interfering with the Janus tyrosine kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription protein (STAT) signaling pathway. These findings contribute to knowledge of how BTV infection interferes with the host's innate immune response and becomes pathogenic. This will also be important for the design of efficacious vaccine candidates. | | 25008919
 |
JAK2/STAT2/STAT3 are required for myogenic differentiation.
Wang, K; Wang, C; Xiao, F; Wang, H; Wu, Z
The Journal of biological chemistry
283
34029-36
2008
Show Abstract
Skeletal muscle satellite cell-derived myoblasts are mainly responsible for postnatal muscle growth and injury-induced regeneration. However, the cellular signaling pathways that control proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts remain poorly defined. Recently, we found that JAK1/STAT1/STAT3 not only participate in myoblast proliferation but also actively prevent them from premature differentiation. Unexpectedly, we found that a related pathway consisting of JAK2, STAT2, and STAT3 is required for early myogenic differentiation. Interference of this pathway by either a small molecule inhibitor or small interfering RNA inhibits myogenic differentiation. Consistently, all three molecules are activated upon differentiation. The pro-differentiation effect of JAK2/STAT2/STAT3 is partially mediated by MyoD and MEF2. Interestingly, the expression of the IGF2 gene and the HGF gene is also regulated by JAK2/STAT2/STAT3, suggesting that this pathway could also promote differentiation by regulating signaling molecules known to be involved in myogenic differentiation. In summary, our current study reveals a novel role for the JAK2/STAT2/STAT3 pathway in myogenic differentiation. Full Text Article | | 18835816
 |
Developmental changes in the human GH receptor and its signal transduction pathways.
Kenth, G; Mergelas, JA; Goodyer, CG
The Journal of endocrinology
198
71-82
2008
Show Abstract
We previously reported the presence of functional human GH receptors (hGHRs) in the human fetal hepatocyte (FH) as early as the first trimester. Interestingly, fetal serum levels of hGH are in the acromegalic range, yet certain hGH-dependent factors are expressed at very low levels (IGF-I, IGF-binding protein-3), suggesting that fetal liver has limited responsiveness to hGH. To determine whether this is due to the fetal tissue levels of hGHR or factors in the hGH/hGHR axis that might influence hGHR function, we compared hGHR isoforms and downstream signaling proteins in FH versus human adult liver (HAL). Immunoprecipitation/immunoblotting (IB) analyses found similar precursor and mature hGHR forms while RT-PCR assays of truncated (T) hGHR(1-279), dominant negative for the full-length (FL) receptor, showed similar T/FL mRNA ratios in FH and HAL. IB demonstrated that Janus kinase (JAK) 2, signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT(1, 3, 5A/B)), and suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS(1, 2, 3, cytokine-inducible SH2-containing protein (CIS))) proteins were detectable in all FH and HAL tested (12 weeks of fetal age to 60 years); the levels were similar (STAT5B) or lower (JAK2/STAT1/STAT3/STAT5A: 38-53%, SOCS/CIS: 58-76%) in FH compared with HAL. Our studies to date demonstrate that, during hepatocyte development, hGHR levels are lower in the fetal cells but the hGHR isoforms, including the relative amount of truncated versus FL, remain unchanged. The JAK2/STAT/SOCS signaling molecules are present in the FH as early as the first trimester. However, they are generally at less than 50% level in postnatal liver. These data suggest that low expression of both hGHR and major hGHR signaling components may explain the limited responsiveness of the fetal cells to the high circulating levels of hGH. | | 18420710
 |
Brahma-related gene 1-dependent STAT3 recruitment at IL-6-inducible genes.
Zuyao Ni, Rod Bremner
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950)
178
345-51
2007
Show Abstract
IL-6 is an immunoregulatory cytokine with multiple functions in hemopoiesis, proliferation, and tumorigenesis. IL-6 triggers phosphorylation, dimerization, and nuclear translocation of STAT3, which binds to target promoters and activates transcription. Brahma-related gene 1 (BRG1), the enzymatic engine of the yeast-mating type-switching and sucrose-nonfermenting chromatin-remodeling complex, is essential for recruitment of STAT1 or STAT1/STAT2-containing complexes to IFN targets. We hypothesized that BRG1 might also be required for STAT3 recruitment. In this study, we show that induction of a subset of human IL-6-responsive genes is BRG1 dependent. BRG1 is constitutively present at these targets and is required for STAT3 recruitment, downstream histone modifications, and IL-6-induced chromatin remodeling. IL-6-induced recruitment of STAT3 to the IFN regulatory factor 1 promoter and subsequent mRNA synthesis is BRG1 dependent, even though IFN-gamma-mediated STAT1 recruitment to this locus is BRG1 independent. BRG1 also increased basal expression of IFN-induced transmembrane protein 3 and IFN-gamma-induced protein 16, and the basal chromatin accessibility at the promoter of IFN regulatory factor 1. The effect on basal expression was STAT3 independent, as revealed by small interfering RNA knockdown. Together with prior observations, these data reveal that BRG1 has a broad role in mediating STAT accessibility at multiple cytokine-responsive promoters and exposes promoter specific differences in both the effect of BRG1 on basal chromatin accessibility and on access of different STAT proteins to the same target. | | 17182572
 |
Interferon-gamma-activated STAT-1alpha suppresses MMP-9 gene transcription by sequestration of the coactivators CBP/p300.
Ma, Z; Chang, MJ; Shah, RC; Benveniste, EN
Journal of leukocyte biology
78
515-23
2005
Show Abstract
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) is a pleiotropic cytokine involved in aspects of immune regulation, cell proliferation, and host defense mechanisms directed toward various cancers. Some of the biological functions of IFN-gamma are achieved through inhibition of gene expression, although the mechanisms by which IFN-gamma suppresses gene transcription are poorly understood. Herein, we demonstrate the molecular basis by which IFN-gamma mediates suppression of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) gene. IFN-gamma-activated signal transducer and activator of transcription-1alpha (STAT-1alpha) suppresses MMP-9 gene transcription, which is dependent on phosphorylation of tyrosine 701 but not phosphorylation of serine 727. The coactivator cyclic AMP response element-binding protein-binding protein (CBP) is an important component of induction of MMP-9 gene transcription. IFN-gamma induces the in vivo association of STAT-1alpha and CBP and decreases the association of CBP to the MMP-9 promoter. IFN-gamma does not influence the stability of CBP nor does IFN-gamma affect chromatin-remodeling events on the MMP-9 promoter. IFN-gamma inhibits the assembly of the MMP-9 transcription complex by suppressing H3/H4 acetylation and inhibiting recruitment of Pol II to the MMP-9 promoter. These findings indicate that IFN-gamma/STAT-1alpha exert their inhibitory effects by affecting multiple aspects of MMP-9 gene transcription. | | 15894584
 |
Nipah virus V protein evades alpha and gamma interferons by preventing STAT1 and STAT2 activation and nuclear accumulation.
Rodriguez, JJ; Parisien, JP; Horvath, CM
Journal of virology
76
11476-83
2002
Show Abstract
Characterization of recent outbreaks of fatal encephalitis in southeast Asia identified the causative agent to be a previously unrecognized enveloped negative-strand RNA virus of the Paramyxoviridae family, Nipah virus. One feature linking Nipah virus to this family is a conserved cysteine-rich domain that is the hallmark of paramyxovirus V proteins. The V proteins of other paramyxovirus species have been linked with evasion of host cell interferon (IFN) signal transduction and subsequent antiviral responses by inducing proteasomal degradation of the IFN-responsive transcription factors, STAT1 or STAT2. Here we demonstrate that Nipah virus V protein escapes IFN by a distinct mechanism involving direct inhibition of STAT protein function. Nipah virus V protein differs from other paramyxovirus V proteins in its subcellular distribution but not in its ability to inhibit cellular IFN responses. Nipah virus V protein does not induce STAT degradation but instead inhibits IFN responses by forming high-molecular-weight complexes with both STAT1 and STAT2. We demonstrate that Nipah virus V protein accumulates in the cytoplasm by a Crm1-dependent mechanism, alters the STAT protein subcellular distribution in the steady state, and prevents IFN-stimulated STAT redistribution. Consistent with the formation of complexes, STAT protein tyrosine phosphorylation is inhibited in cells expressing the Nipah virus V protein. As a result, Nipah virus V protein efficiently prevents STAT1 and STAT2 nuclear translocation in response to IFN, inhibiting cellular responses to both IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma. | | 12388709
 |
Interferon consensus sequence-binding protein is constitutively expressed and differentially regulated in the ocular lens
Li, W., et al
J Biol Chem, 274:9686-91 (1999)
1999
| Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay | 10092656
 |
Erythropoietin and Friend virus gp55 activate different JAK/STAT pathways through the erythropoietin receptor in erythroid cells
Yamamura, Y., et al
Mol Cell Biol, 18:1172-80 (1998)
1998
| Immunoblotting (Western), Immunoprecipitation | 9488432
 |