658552 Sigma-AldrichAG 1478 - CAS 175178-82-2 - Calbiochem
AG 1478, CAS 175178-82-2, is a cell-permeable, potent, selective, reversible & ATP-competitive inhibitor of EGF receptor kinase (IC50 = 3 nM vs 100 µM for HER2-neu and PDGF receptor kinase).
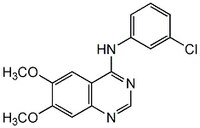
More>> AG 1478, CAS 175178-82-2, is a cell-permeable, potent, selective, reversible & ATP-competitive inhibitor of EGF receptor kinase (IC50 = 3 nM vs 100 µM for HER2-neu and PDGF receptor kinase). Less<<Synonyms: 4-(3-Chloroanilino)-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline
Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| CAS # | Empirical Formula |
|---|---|
| 175178-82-2 | C₁₆H₁₄ClN₃O₂ |
Products
| Catalogue Number | Packaging | Qty/Pack | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 658552-5MG | Plastic ampoule | 5 mg |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Overview | A cell-permeable, reversible, ATP-competitive, highly potent and selective inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase (IC50 = 3 nM) versus HER2-neu (IC50 >100 µM) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor kinase (IC50 >100 µM). Abolishes MAP kinase (ERK) activation induced by Angiotensin II (Cat. No. 05-23-0101). Also inhibits the activation of EGFR kinase and MAP kinase by 4-hydroxynonenal. Downregulates ARF1 activity and disperses Golgi structure. A 10 mM (1 mg/317 µl) solution of AG 1478 (Cat. No. 658548) in DMSO is also available. |
| Catalogue Number | 658552 |
| Brand Family | Calbiochem® |
| Synonyms | 4-(3-Chloroanilino)-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| CAS number | 175178-82-2 |
| ATP Competitive | Y |
| Declaration | Sold under license of U.S. Patent 5,457,105 and European Patent 0,566,266. |
| Form | Pale yellow solid |
| Hill Formula | C₁₆H₁₄ClN₃O₂ |
| Chemical formula | C₁₆H₁₄ClN₃O₂ |
| Reversible | Y |
| Structure formula Image | |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Primary Target | Epidermal growth factor receptor kinase |
| Primary Target IC<sub>50</sub> | 3 nM against epidermal growth factor receptor kinase |
| Purity | ≥98% by HPLC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
|---|---|
| Cell permeable | Y |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Product Usage Statements |
|---|
| Packaging Information |
|---|
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | GTIN |
| 658552-5MG | 07790788052232 |
Documentation
AG 1478 - CAS 175178-82-2 - Calbiochem SDS
| Title |
|---|
AG 1478 - CAS 175178-82-2 - Calbiochem Certificates of Analysis
| Title | Lot Number |
|---|---|
| 658552 |
References
| Reference overview |
|---|
| Pan, H., et al. 2008. J. Biol. Chem. 283, In press. Liu, W., et al. 1999. J. Cell Sci. 112, 2409. Eguchi, S., et al. 1998. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8890. Levitzki, A., and Gazit, A. 1995. Science 267, 1782. Fry, D.W., et al. 1994. Science 265, 1093. Osherov, N., and Levitski, A. 1994. Eur. J. Biochem. 225, 1047. Ward, W.H., et al. 1994. Biochem. Pharmacol. 48, 659. |
Citations
| Title | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Data Sheet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Note that this data sheet is not lot-specific and is representative of the current specifications for this product. Please consult the vial label and the certificate of analysis for information on specific lots. Also note that shipping conditions may differ from storage conditions.
|