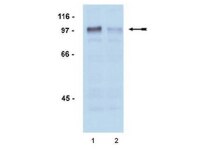
04-078 Sigma-AldrichAnti-phospho-Androgen Receptor (Ser81) Antibody, rabbit monoclonal
Anti-phospho-Androgen Receptor (Ser81) Antibody detects level of phospho-Androgen Receptor (Ser81) & has been published & validated for use in WB.
More>> Anti-phospho-Androgen Receptor (Ser81) Antibody detects level of phospho-Androgen Receptor (Ser81) & has been published & validated for use in WB. Less<<Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | WB | Rb | Culture Supernatant | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | 04-078 |
| Brand Family | Upstate |
| Trade Name |
|
| Description | Anti-phospho-Androgen Receptor (Ser81) Antibody, rabbit monoclonal |
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Culture Supernatant |
| Presentation | 100μl of cell culture supernatant with 0.1% sodium azide |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Storage and Shipping Information | |
|---|---|
| Storage Conditions | 2 years at -20°C from date of shipment |
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 100 µL |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | GTIN |
| 04-078 | 04053252329401 |
Documentation
Anti-phospho-Androgen Receptor (Ser81) Antibody, rabbit monoclonal MSDS
| Title |
|---|
Anti-phospho-Androgen Receptor (Ser81) Antibody, rabbit monoclonal Certificates of Analysis
References
| Reference overview | Pub Med ID |
|---|---|
| Androgen receptor and prostate apoptosis response factor-4 target the c-FLIP gene to determine survival and apoptosis in the prostate gland Gao, Shen, et al J Mol Endocrinol, 36:463-83 (2006) 2006 | 16720717
 |
| Elevated E2F1 inhibits transcription of the androgen receptor in metastatic hormone-resistant prostate cancer Davis, Joanne N, et al Cancer Res, 66:11897-906 (2006) 2006 | 17178887
 |