A Novel 1,4-Dihydropyridine Derivative Improves Spatial Learning and Memory and Modifies Brain Protein Expression in Wild Type and Transgenic APPSweDI Mice.
Jansone, B; Kadish, I; van Groen, T; Beitnere, U; Moore, DR; Plotniece, A; Pajuste, K; Klusa, V
PloS one
10
e0127686
2015
Show Abstract
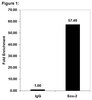
Ca2+ blockers, particularly those capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB), have been suggested as a possible treatment or disease modifying agents for neurodegenerative disorders, e.g., Alzheimer's disease. The present study investigated the effects of a novel 4-(N-dodecyl) pyridinium group-containing 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative (AP-12) on cognition and synaptic protein expression in the brain. Treatment of AP-12 was investigated in wild type C57BL/6J mice and transgenic Alzheimer's disease model mice (Tg APPSweDI) using behavioral tests and immunohistochemistry, as well as mass spectrometry to assess the blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration. The data demonstrated the ability of AP-12 to cross the BBB, improve spatial learning and memory in both mice strains, induce anxiolytic action in transgenic mice, and increase expression of hippocampal and cortical proteins (GAD67, Homer-1) related to synaptic plasticity. The compound AP-12 can be seen as a prototype molecule for use in the design of novel drugs useful to halt progression of clinical symptoms (more specifically, anxiety and decline in memory) of neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Alzheimer's disease. | | | 26042808
 |
Forebrain deletion of the dystonia protein torsinA causes dystonic-like movements and loss of striatal cholinergic neurons.
Pappas, SS; Darr, K; Holley, SM; Cepeda, C; Mabrouk, OS; Wong, JM; LeWitt, TM; Paudel, R; Houlden, H; Kennedy, RT; Levine, MS; Dauer, WT
eLife
4
e08352
2015
Show Abstract
Striatal dysfunction plays an important role in dystonia, but the striatal cell types that contribute to abnormal movements are poorly defined. We demonstrate that conditional deletion of the DYT1 dystonia protein torsinA in embryonic progenitors of forebrain cholinergic and GABAergic neurons causes dystonic-like twisting movements that emerge during juvenile CNS maturation. The onset of these movements coincides with selective degeneration of dorsal striatal large cholinergic interneurons (LCI), and surviving LCI exhibit morphological, electrophysiological, and connectivity abnormalities. Consistent with the importance of this LCI pathology, murine dystonic-like movements are reduced significantly with an antimuscarinic agent used clinically, and we identify cholinergic abnormalities in postmortem striatal tissue from DYT1 dystonia patients. These findings demonstrate that dorsal LCI have a unique requirement for torsinA function during striatal maturation, and link abnormalities of these cells to dystonic-like movements in an overtly symptomatic animal model. | | | 26052670
 |
TWIK-Related Spinal Cord K⁺ Channel Expression Is Increased in the Spinal Dorsal Horn after Spinal Nerve Ligation.
Hwang, HY; Zhang, E; Park, S; Chung, W; Lee, S; Kim, DW; Ko, Y; Lee, W
Yonsei medical journal
56
1307-15
2015
Show Abstract
The TWIK-related spinal cord K⁺ channel (TRESK) has recently been discovered and plays an important role in nociceptor excitability in the pain pathway. Because there have been no reports on the TRESK expression or its function in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord in neuropathic pain, we analyzed TRESK expression in the spinal dorsal horn in a spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model.We established a SNL mouse model by using the L5-6 spinal nerves ligation. We used real-time polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry to investigate TRESK expression in the dorsal horn and L5 dorsal rot ganglion (DRG).The SNL group showed significantly higher expression of TRESK in the ipsilateral dorsal horn under pain, but low expression in L5 DRG. Double immunofluorescence staining revealed that immunoreactivity of TRESK was mostly restricted in neuronal cells, and that synapse markers GAD67 and VGlut2 appeared to be associated with TRESK expression. We were unable to find a significant association between TRESK and calcineurin by double immunofluorescence.TRESK in spinal cord neurons may contribute to the development of neuropathic pain following injury. | | | 26256973
 |
Altered activity of the medial prefrontal cortex and amygdala during acquisition and extinction of an active avoidance task.
Jiao, X; Beck, KD; Myers, CE; Servatius, RJ; Pang, KC
Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience
9
249
2015
Show Abstract
Altered medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and amygdala function is associated with anxiety-related disorders. While the mPFC-amygdala pathway has a clear role in fear conditioning, these structures are also involved in active avoidance. Given that avoidance perseveration represents a core symptom of anxiety disorders, the neural substrate of avoidance, especially its extinction, requires better understanding. The present study was designed to investigate the activity, particularly, inhibitory neuronal activity in mPFC and amygdala during acquisition and extinction of lever-press avoidance in rats. Neural activity was examined in the mPFC, intercalated cell clusters (ITCs) lateral (LA), basal (BA) and central (CeA) amygdala, at various time points during acquisition and extinction, using induction of the immediate early gene product, c-Fos. Neural activity was greater in the mPFC, LA, BA, and ITC during the extinction phase as compared to the acquisition phase. In contrast, the CeA was the only region that was more activated during acquisition than during extinction. Our results indicate inhibitory neurons are more activated during late phase of acquisition and extinction in the mPFC and LA, suggesting the dynamic involvement of inhibitory circuits in the development and extinction of avoidance response. Together, these data start to identify the key brain regions important in active avoidance behavior, areas that could be associated with avoidance perseveration in anxiety disorders. | | | 26441578
 |
An anterograde rabies virus vector for high-resolution large-scale reconstruction of 3D neuron morphology.
Haberl, MG; Viana da Silva, S; Guest, JM; Ginger, M; Ghanem, A; Mulle, C; Oberlaender, M; Conzelmann, KK; Frick, A
Brain structure & function
220
1369-79
2015
Show Abstract
Glycoprotein-deleted rabies virus (RABV ∆G) is a powerful tool for the analysis of neural circuits. Here, we demonstrate the utility of an anterograde RABV ∆G variant for novel neuroanatomical approaches involving either bulk or sparse neuronal populations. This technology exploits the unique features of RABV ∆G vectors, namely autonomous, rapid high-level expression of transgenes, and limited cytotoxicity. Our vector permits the unambiguous long-range and fine-scale tracing of the entire axonal arbor of individual neurons throughout the brain. Notably, this level of labeling can be achieved following infection with a single viral particle. The vector is effective over a range of ages (greater than 14 months) aiding the studies of neurodegenerative disorders or aging, and infects numerous cell types in all brain regions tested. Lastly, it can also be readily combined with retrograde RABV ∆G variants. Together with other modern technologies, this tool provides new possibilities for the investigation of the anatomy and physiology of neural circuits. | | | 24723034
 |
Processing of visually evoked innate fear by a non-canonical thalamic pathway.
Wei, P; Liu, N; Zhang, Z; Liu, X; Tang, Y; He, X; Wu, B; Zhou, Z; Liu, Y; Li, J; Zhang, Y; Zhou, X; Xu, L; Chen, L; Bi, G; Hu, X; Xu, F; Wang, L
Nature communications
6
6756
2015
Show Abstract
The ability of animals to respond to life-threatening stimuli is essential for survival. Although vision provides one of the major sensory inputs for detecting threats across animal species, the circuitry underlying defensive responses to visual stimuli remains poorly defined. Here, we investigate the circuitry underlying innate defensive behaviours elicited by predator-like visual stimuli in mice. Our results demonstrate that neurons in the superior colliculus (SC) are essential for a variety of acute and persistent defensive responses to overhead looming stimuli. Optogenetic mapping revealed that SC projections to the lateral posterior nucleus (LP) of the thalamus, a non-canonical polymodal sensory relay, are sufficient to mimic visually evoked fear responses. In vivo electrophysiology experiments identified a di-synaptic circuit from SC through LP to the lateral amygdale (Amg), and lesions of the Amg blocked the full range of visually evoked defensive responses. Our results reveal a novel collicular-thalamic-Amg circuit important for innate defensive responses to visual threats. | | | 25854147
 |
Chronic nicotine activates stress/reward-related brain regions and facilitates the transition to compulsive alcohol drinking.
Leão, RM; Cruz, FC; Vendruscolo, LF; de Guglielmo, G; Logrip, ML; Planeta, CS; Hope, BT; Koob, GF; George, O
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
35
6241-53
2015
Show Abstract
Alcohol and nicotine are the two most co-abused drugs in the world. Previous studies have shown that nicotine can increase alcohol drinking in nondependent rats, yet it is unknown whether nicotine facilitates the transition to alcohol dependence. We tested the hypothesis that chronic nicotine will speed up the escalation of alcohol drinking in rats and that this effect will be accompanied by activation of sparsely distributed neurons (neuronal ensembles) throughout the brain that are specifically recruited by the combination of nicotine and alcohol. Rats were trained to respond for alcohol and made dependent using chronic, intermittent exposure to alcohol vapor, while receiving daily nicotine (0.8 mg/kg) injections. Identification of neuronal ensembles was performed after the last operant session, using immunohistochemistry. Nicotine produced an early escalation of alcohol drinking associated with compulsive alcohol drinking in dependent, but not in nondependent rats (air exposed), as measured by increased progressive-ratio responding and increased responding despite adverse consequences. The combination of nicotine and alcohol produced the recruitment of discrete and phenotype-specific neuronal ensembles (∼4-13% of total neuronal population) in the nucleus accumbens core, dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, central nucleus of the amygdala, bed nucleus of stria terminalis, and posterior ventral tegmental area. Blockade of nicotinic receptors using mecamylamine (1 mg/kg) prevented both the behavioral and neuronal effects of nicotine in dependent rats. These results demonstrate that nicotine and activation of nicotinic receptors are critical factors in the development of alcohol dependence through the dysregulation of a set of interconnected neuronal ensembles throughout the brain. | | | 25878294
 |
Tfap2a and 2b act downstream of Ptf1a to promote amacrine cell differentiation during retinogenesis.
Jin, K; Jiang, H; Xiao, D; Zou, M; Zhu, J; Xiang, M
Molecular brain
8
28
2015
Show Abstract
Retinogenesis is a precisely controlled developmental process during which different types of neurons and glial cells are generated under the influence of intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Three transcription factors, Foxn4, RORβ1 and their downstream effector Ptf1a, have been shown to be indispensable intrinsic regulators for the differentiation of amacrine and horizontal cells. At present, however, it is unclear how Ptf1a specifies these two cell fates from competent retinal precursors. Here, through combined bioinformatic, molecular and genetic approaches in mouse retinas, we identify the Tfap2a and Tfap2b transcription factors as two major downstream effectors of Ptf1a. RNA-seq and immunolabeling analyses show that the expression of Tfap2a and 2b transcripts and proteins is dramatically downregulated in the Ptf1a null mutant retina. Their overexpression is capable of promoting the differentiation of glycinergic and GABAergic amacrine cells at the expense of photoreceptors much as misexpressed Ptf1a is, whereas their simultaneous knockdown has the opposite effect. Given the demonstrated requirement for Tfap2a and 2b in horizontal cell differentiation, our study thus defines a Foxn4/RORβ1-Ptf1a-Tfap2a/2b transcriptional regulatory cascade that underlies the competence, specification and differentiation of amacrine and horizontal cells during retinal development. | | | 25966682
 |
Neuronal BDNF signaling is necessary for the effects of treadmill exercise on synaptic stripping of axotomized motoneurons.
Krakowiak, J; Liu, C; Papudesu, C; Ward, PJ; Wilhelm, JC; English, AW
Neural plasticity
2015
392591
2015
Show Abstract
The withdrawal of synaptic inputs from the somata and proximal dendrites of spinal motoneurons following peripheral nerve injury could contribute to poor functional recovery. Decreased availability of neurotrophins to afferent terminals on axotomized motoneurons has been implicated as one cause of the withdrawal. No reduction in contacts made by synaptic inputs immunoreactive to the vesicular glutamate transporter 1 and glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 is noted on axotomized motoneurons if modest treadmill exercise, which stimulates the production of neurotrophins by spinal motoneurons, is applied after nerve injury. In conditional, neuron-specific brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) knockout mice, a reduction in synaptic contacts onto motoneurons was noted in intact animals which was similar in magnitude to that observed after nerve transection in wild-type controls. No further reduction in coverage was found if nerves were cut in knockout mice. Two weeks of moderate daily treadmill exercise following nerve injury in these BDNF knockout mice did not affect synaptic inputs onto motoneurons. Treadmill exercise has a profound effect on synaptic inputs to motoneurons after peripheral nerve injury which requires BDNF production by those postsynaptic cells. | | | 25918648
 |
Glucocorticoid receptors in the locus coeruleus mediate sleep disorders caused by repeated corticosterone treatment.
Wang, ZJ; Zhang, XQ; Cui, XY; Cui, SY; Yu, B; Sheng, ZF; Li, SJ; Cao, Q; Huang, YL; Xu, YP; Zhang, YH
Scientific reports
5
9442
2015
Show Abstract
Stress induced constant increase of cortisol level may lead to sleep disorder, but the mechanism remains unclear. Here we described a novel model to investigate stress mimicked sleep disorders induced by repetitive administration of corticosterone (CORT). After 7 days treatment of CORT, rats showed significant sleep disturbance, meanwhile, the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) level was notably lowered in locus coeruleus (LC). We further discovered the activation of noradrenergic neuron in LC, the suppression of GABAergic neuron in ventrolateral preoptic area (VLPO), the remarkable elevation of norepinephrine in LC, VLPO and hypothalamus, as well as increase of tyrosine hydroxylase in LC and decrease of glutamic acid decarboxylase in VLPO after CORT treatment. Microinjection of GR antagonist RU486 into LC reversed the CORT-induced sleep changes. These results suggest that GR in LC may play a key role in stress-related sleep disorders and support the hypothesis that repeated CORT treatment may decrease GR levels and induce the activation of noradrenergic neurons in LC, consequently inhibit GABAergic neurons in VLPO and result in sleep disorders. Our findings provide novel insights into the effect of stress-inducing agent CORT on sleep and GRs' role in sleep regulation. | Immunohistochemistry | | 25801728
 |