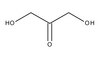
Differential properties of human ACL and MCL stem cells may be responsible for their differential healing capacity.
Zhang, J; Pan, T; Im, HJ; Fu, FH; Wang, JH
BMC medicine
9
68
2010
Show Abstract
The human anterior cruciate ligament (hACL) and medial collateral ligament (hMCL) of the knee joint are frequently injured, especially in athletic settings. It has been known that, while injuries to the MCL typically heal with conservative treatment, ACL injuries usually do not heal. As adult stem cells repair injured tissues through proliferation and differentiation, we hypothesized that the hACL and hMCL contain stem cells exhibiting unique properties that could be responsible for the differential healing capacity of the two ligaments.To test the above hypothesis, we derived ligament stem cells from normal hACL and hMCL samples from the same adult donors using tissue culture techniques and characterized their properties using immunocytochemistry, RT-PCR, and flow cytometry.We found that both hACL stem cells (hACL-SCs) and hMCL stem cells (hMCL-SCs) formed colonies in culture and expressed stem cell markers nucleostemin and stage-specific embryonic antigen-4 (SSEA-4). Moreover, both hACL-SCs and hMCL-SCs expressed CD surface markers for mesenchymal stem cells, including CD44 and CD90, but not those markers for vascular cells, CD31, CD34, CD45, and CD146. However, hACL-SCs differed from hMCL-SCs in that the size and number of hACL-SC colonies in culture were much smaller and grew more slowly than hMCL-SC colonies. Moreover, fewer hACL-SCs in cell colonies expressed stem cell markers STRO-1 and octamer-binding transcription factor-4 (Oct-4) than hMCL-SCs. Finally, hACL-SCs had less multi-differentiation potential than hMCL-SCs, evidenced by differing extents of adipogenesis, chondrogenesis, and osteogenesis in the respective induction media.This study shows for the first time that hACL-SCs are intrinsically different from hMCL-SCs. We suggest that the differences in their properties contribute to the known disparity in healing capabilities between the two ligaments. Full Text Article | 21635735
 |
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells modulate BV2 microglia responses to lipopolysaccharide.
Yin Yin Ooi,Rajesh Ramasamy,Zul'atfi Rahmat,Hemavathy Subramaiam,Shi Wei Tan,Maha Abdullah,Daud Ahmad Israf,Sharmili Vidyadaran
International immunopharmacology
10
2009
Show Abstract
The immunoregulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have been demonstrated on a wide range of cells. Here, we describe the modulatory effects of mouse bone marrow-derived MSC on BV2 microglia proliferation rate, nitric oxide (NO) production and CD40 expression. Mouse bone marrow MSC were co-cultured with BV2 cells at various seeding density ratios and activated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We show that MSC exert an anti-proliferative effect on microglia and are potent producers of NO when stimulated by soluble factors released by LPS-activated BV2. MSC suppressed proliferation of both untreated and LPS-treated microglia in a dose-dependent manner, significantly reducing BV2 proliferation at seeding density ratios of 1:0.2 and 1:0.1 (p<.05). Co-culturing MSC with BV2 cells at different ratios revealed interesting dynamics in NO production. A high number of MSC significantly increases NO in co-cultures whilst a lower number reduces NO. The increased NO levels in co-cultures may be MSC-derived, as we also show that activated BV2 cells stimulate MSC to produce NO. Cell-cell interaction is not a requirement for this effect as soluble factors released by activated BV2 cells alone do stimulate MSC to produce high levels of NO. Although NO is implicated as a mediator for T cell proliferation, it does not appear to play a major role in the suppression of microglia proliferation. Additionally, MSC reduced the expression of the microglial co-stimulator molecule, CD40. Collectively, these regulatory effects of MSC on microglia offer insight into the potential moderating properties of MSC on inflammatory responses within the CNS. | 20850581
 |
Multipotent adult progenitor cells from swine bone marrow.
Lepeng Zeng, Eric Rahrmann, Qingsong Hu, Troy Lund, Lee Sandquist, Mike Felten, Timothy D O'Brien, Jianyi Zhang, Catherine Verfaillie
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio)
24
2355-66
2005
Show Abstract
We show that multipotent adult progenitor cells (MAPCs) can be derived from both postnatal and fetal swine bone marrow (BM). Although swine MAPC (swMAPC) cultures are initially mixed, cultures are phenotypically homogenous by 50 population doublings (PDs) and can be maintained as such for more than 100 PDs. swMAPCs are negative for CD44, CD45, and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) classes I and II; express octamer binding transcription factor 3a (Oct3a) mRNA and protein at levels close to those seen in human ESCs (hESCs); and have telomerase activity preventing telomere shortening even after 100 PDs. Using quantitative-reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (Q-RT-PCR), immunofluorescence, and functional assays, we demonstrate that swMAPCs differentiate into chondrocytes, adipocytes, osteoblasts, smooth muscle cells, endothelium, hepatocyte-like cells, and neuron-like cells. Consistent with what we have shown for human and rodent MAPCs, Q-RT-PCR demonstrated a significant upregulation of transcription factors and other lineage-specific transcripts in a time-dependent fashion similar to development. When swMAPCs were passaged for 3-6 passages at high density (2,000-8,000 cells per cm(2)), Oct3a mRNA levels were no longer detectable, cells acquired the phenotype of mesenchymal stem cells (CD44(+), MHC class I(+)), and could differentiate into typical mesenchymal lineages (adipocytes, osteoblasts, and chondroblasts), but not endothelium, hepatocyte-like cells, or neuron-like cells. Even if cultures were subsequently replated at low density (approximately 100-500 cells per cm(2)) for >20 PDs, Oct3a was not re-expressed, nor were cells capable of differentiating to cells other than mesenchymal-type cells. This suggests that the phenotype and functional characteristics of swMAPCs may not be an in vitro culture phenomenon. | 16931778
 |
Genetically-modified pig mesenchymal stromal cells: xenoantigenicity and effect on human T-cell xenoresponses.
Mohamed Ezzelarab,Corin Ezzelarab,Tyler Wilhite,Goutham Kumar,Hidetaka Hara,David Ayares,David K C Cooper
Xenotransplantation
18
2001
Show Abstract
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) are being investigated as immunomodulatory therapy in the field of transplantation, particularly islet transplantation. While MSC can regenerate across species barriers, the immunoregulatory influence of genetically modified pig MSC (pMSC) on the human and non-human primate T-cell responses has not been studied. | 21696448
 |