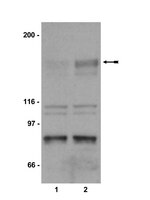
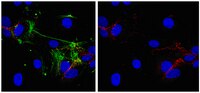
Phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2 is required for VEGF-A/VEGFR2-induced proliferation and migration of lymphatic endothelium.
Dellinger, MT; Brekken, RA
PloS one
6
e28947
2010
Show Abstract
There is growing evidence that vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A), a ligand of the receptor tyrosine kinases VEGFR1 and VEGFR2, promotes lymphangiogenesis. However, the underlying mechanisms by which VEGF-A induces the growth of lymphatic vessels remain poorly defined. Here we report that VEGFR2, not VEGFR1, is the primary receptor regulating VEGF-A-induced lymphangiogenesis. We show that specific inhibition of VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signaling with the fully human monoclonal antibody r84 significantly inhibits lymphangiogenesis in MDA-MB-231 tumors. In vitro experiments with primary human dermal lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) demonstrate that blocking VEGF-A activation of VEGFR2, not VEGFR1, significantly inhibits VEGF-A-induced proliferation and migration of LECs. We show that VEGF-A stimulation of LECs leads to the phosphorylation of VEGFR2 (Tyr 951, 1054, 1059, 1175, and 1214) which subsequently triggers PKC dependent phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and PI3-K dependent phosphorylation of Akt. Additionally, we demonstrate that inhibitors that suppress the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and Akt significantly block VEGF-A- induced proliferation and migration of LECs. Together, these results shed light on the mechanisms regulating VEGF-A-induced proliferation and migration of LECs, reveal that VEGFR2 is the primary signaling VEGF-A receptor on lymphatic endothelium, and suggest that therapeutic agents targeting the VEGF-A/VEGFR2 axis could be useful in blocking the pathological formation of lymphatic vessels. Full Text Article | | 22174934
 |
A systems pathology model for predicting overall survival in patients with refractory, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with gefitinib.
Michael J Donovan,Angeliki Kotsianti,Valentina Bayer-Zubek,David Verbel,Mikhail Teverovskiy,Carlos Cordon-Cardo,Jose Costa,F Anthony Greco,John D Hainsworth,Dinah V Parums
European journal of cancer (Oxford, England : 1990)
45
2009
Show Abstract
To identify clinical and biometric features associated with overall survival of patients with advanced refractory non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with gefitinib. | | 19272767
 |
Preclinical activity of ABT-869, a multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Albert, DH; Tapang, P; Magoc, TJ; Pease, LJ; Reuter, DR; Wei, RQ; Li, J; Guo, J; Bousquet, PF; Ghoreishi-Haack, NS; Wang, B; Bukofzer, GT; Wang, YC; Stavropoulos, JA; Hartandi, K; Niquette, AL; Soni, N; Johnson, EF; McCall, JO; Bouska, JJ; Luo, Y; Donawho, CK; Dai, Y; Marcotte, PA; Glaser, KB; Michaelides, MR; Davidsen, SK
Molecular cancer therapeutics
5
995-1006
2005
Show Abstract
ABT-869 is a structurally novel, receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor that is a potent inhibitor of members of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor families (e.g., KDR IC50 = 4 nmol/L) but has much less activity (IC50s greater than 1 micromol/L) against unrelated RTKs, soluble tyrosine kinases, or serine/threonine kinases. The inhibition profile of ABT-869 is evident in cellular assays of RTK phosphorylation (IC50 = 2, 4, and 7 nmol/L for PDGFR-beta, KDR, and CSF-1R, respectively) and VEGF-stimulated proliferation (IC50 = 0.2 nmol/L for human endothelial cells). ABT-869 is not a general antiproliferative agent because, in most cancer cells, greater than 1,000-fold higher concentrations of ABT-869 are required for inhibition of proliferation. However, ABT-869 exhibits potent antiproliferative and apoptotic effects on cancer cells whose proliferation is dependent on mutant kinases, such as FLT3. In vivo ABT-869 is effective orally in the mechanism-based murine models of VEGF-induced uterine edema (ED50 = 0.5 mg/kg) and corneal angiogenesis (greater than 50% inhibition, 15 mg/kg). In tumor growth studies, ABT-869 exhibits efficacy in human fibrosarcoma and breast, colon, and small cell lung carcinoma xenograft models (ED50 = 1.5-5 mg/kg, twice daily) and is also effective (greater than 50% inhibition) in orthotopic breast and glioma models. Reduction in tumor size and tumor regression was observed in epidermoid carcinoma and leukemia xenograft models, respectively. In combination, ABT-869 produced at least additive effects when given with cytotoxic therapies. Based on pharmacokinetic analysis from tumor growth studies, efficacy correlated more strongly with time over a threshold value (cellular KDR IC50 corrected for plasma protein binding = 0.08 microg/mL, greater than or=7 hours) than with plasma area under the curve or Cmax. These results support clinical assessment of ABT-869 as a therapeutic agent for cancer. | Western Blotting | 16648571
 |
Substitution of C-terminus of VEGFR-2 with VEGFR-1 promotes VEGFR-1 activation and endothelial cell proliferation.
Meyer, Rosana D, et al.
Oncogene, 23: 5523-31 (2004)
2004
Show Abstract
VEGFR-1 is devoid of ligand-dependent tyrosine autophosphorylation and its activation is not associated with proliferation of endothelial cells. The molecular mechanism responsible for this characteristic of VEGFR-1 is not known. In this study, we show that VEGFR-1 is devoid of ligand-dependent downregulation and failed to stimulate intracellular calcium release, cell migration and angiogenesis in vitro. To understand the molecular mechanisms responsible for the poor tyrosine autophosphorylation of VEGFR-1, we have either deleted the carboxyl terminus of VEGFR-1 or exchanged it with the carboxyl terminus of VEGFR-2. The deletion of carboxyl terminus of VEGFR-1 did not reverse its defective ligand-dependent autophosphorylation. The carboxyl terminus-swapped VEGFR-1, however, displayed ligand-dependent autophosphorylation, downregulation and also conveyed strong mitogenic responses. Thus, the carboxyl tail of VEGFR-1 restrains the ligand-dependent kinase activation and downregulation of VEGFR-1 and its ability to convey the angiogenic responses in endothelial cells. | | 15107818
 |
The presence of a single tyrosine residue at the carboxyl domain of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2/FLK-1 regulates its autophosphorylation and activation of signaling molecules.
Meyer, Rosana D, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 277: 27081-7 (2002)
2002
Show Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-2 plays a critical role in vasculogenesis during embryonic development and pathological angiogenesis, but little is known about the molecular mechanisms governing its functions. Here we investigated the role of tyrosine 1212 on mouse VEGFR-2 autophosphorylation and its signal transduction relay in endothelial cells. Mutation of tyrosine 1212 on VEGFR-2 to phenylalanine severely impaired the ligand-dependent autophosphorylation of VEGFR-2 and its ability to associate with and activate Src. This mutation also reduced the VEGFR-2 ability to phosphorylate phospholipase Cgamma1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Unlike mutation of tyrosine 1212 to phenylalanine, replacement of tyrosine 1212 with glutamic acid preserved the ligand-dependent activation of VEGFR-2 and activation of VEGFR-2-associated signaling proteins including Src, phospholipase Cgamma1, and MAPK. Further analysis showed that Src activation is not required for activation of VEGFR-2, since cells co-expressing wild type receptor with kinase dead Src or wild type Src displayed no apparent effect in the ligand-dependent autophosphorylation of VEGFR-2. Similarly, expression of wild type VEGFR-2 in fibroblast (SYF) cells obtained from the triple knockout Src family kinases showed normal ligand-dependent autophosphorylation. Collectively, these results suggest that phosphorylation of tyrosine 1212 of VEGFR-2 plays a crucial role in the activation of VEGFR-2 and subsequently VEGFR-2-mediated angiogenesis. | | 12023952
 |
Identification of tyrosine residues in vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2/FLK-1 involved in activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and cell proliferation.
Dayanir, V, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 276: 17686-92 (2001)
2001
Show Abstract
Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) plays a critical role in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. However, the mechanism by which VEGFR-2 activation elicits these cellular events is not fully understood. We recently constructed a chimeric receptor containing the extracellular domain of human CSF-1R/c-fms, fused with the entire transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of murine VEGFR-2 (Rahimi, N., Dayanir, V., and Lashkari, K. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 16986-16992). In this study we used VEGFR-2 chimera (herein named CKR) to elucidate the signal transduction relay of VEGFR-2 in porcine aortic endothelial (PAE) cells. Mutation of tyrosines 799 and 1173 individually on CKR resulted in partial loss of CKR's ability to stimulate cell growth. Double mutation of these sites caused total loss of CKR's ability to stimulate cell growth. Interestingly, mutation of these sites had no effect on the ability of CKR to stimulate cell migration. Further analysis revealed that tyrosines 799 and 1173 are docking sites for p85 of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). Pretreatment of cells with wortmannin, an inhibitor of PI3K, and rapamycin, a potent inhibitor of S6 kinase, abrogated CKR-mediated cell growth. However, expression of a dominant negative form of ras (N(17)ras) and inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway by PD98059 did not attenuate CKR-stimulated cell growth. Altogether, these results demonstrate that activation of VEGFR-2 results in activation of PI3K and that activation of PI3K/S6kinase pathway, but not Ras/MAPK, is responsible for VEGFR-2-mediated cell growth. | | 11278468
 |
Receptor chimeras indicate that the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) modulates mitogenic activity of VEGFR-2 in endothelial cells.
Rahimi, N, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 275: 16986-92 (2000)
1999
Show Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) provokes angiogenesis in vivo and stimulates growth and differentiation of endothelial cells in vitro. Although VEGF receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) and VEGFR-2 are known to be high affinity receptors for VEGF, it is not clear which of the VEGFRs are responsible for the transmission of the diverse biological responses of VEGF. For this purpose we have constructed a chimeric receptor for VEGFR-1 (CTR) and VEGFR-2 (CKR) in which the extracellular domain of each receptor was replaced with the extracellular domain of human colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R), and these receptors were expressed in pig aortic endothelial (PAE) cells. We show that CKR individually expressed in PAE cells is readily tyrosine-phosphorylated in vivo, autophosphorylated in vitro, and stimulates cell proliferation in a CSF-1-dependent manner. In contrast, CTR individually expressed in PAE cells showed no significant in vivo, in vitro tyrosine phosphorylation and cell growth in response to CSF-1 stimulation. The kinase activity of CKR was essential for its biological activity, since mutation of lysine 866 to arginine abolished its in vivo, in vitro tyrosine phosphorylation and mitogenic signals. Remarkably, activation of CTR repressed CKR-mediated mitogen-activate protein kinase activation and cell proliferation. Similar effects were observed for VEGFR-2 co-expressed with VEGFR-1. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that VEGFR-2 activation plays a positive role in angiogenesis by promoting endothelial cell proliferation. In contrast, activation of VEGFR-1 plays a stationary role in angiogenesis by antagonizing VEGFR-2 responses. | | 10747927
 |