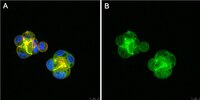
Antagonistic and agonistic effects of an extracellular fragment of nectin on formation of E-cadherin-based cell-cell adhesion.
Honda T, Shimizu K, Kawakatsu T, Yasumi M, Shingai T, Fukuhara A, Ozaki-Kuroda K, Irie K, Nakanishi H, Takai Y.
Genes Cells
8(1)
51-63
2003
Show Abstract
Nectin is a Ca2+-independent immunoglobulin-like cell-cell adhesion molecule at the E-cadherin-based cell-cell adherens junctions (AJs), and comprises a family consisting of four members, nectin-1, -2, -3, and -4. Nectin and E-cadherin are associated with afadin and alpha-catenin, actin filament (F-actin)-binding proteins connecting respective adhesion molecules to the actin cytoskeleton, but the role of nectin in the formation of the E-cadherin-based cell-cell AJs has not yet been fully understood. To obtain evidence for this role of nectin, we attempted to develop an antagonist and/or agonist of nectin. | 12558799
 |
Different behavior of l-afadin and neurabin-II during the formation and destruction of cell-cell adherens junction.
Sakisaka T, Nakanishi H, Takahashi K, Mandai K, Miyahara M, Satoh A, Takaishi K, Takai Y.
Oncogene
18(8)
1609-17
1998
Show Abstract
We have recently isolated two novel actin filament-binding proteins, l-afadin and neurabin-II and shown that they are localized at cell-cell adherens junction (AJ) in epithelial cells. We found here that l-afadin, neurabin-II, ZO-1, and E-cadherin showed similar and different behavior during the formation and destruction of cell-cell AJ in MDCK cells. In MDCK cells, the accumulation of both l-afadin and E-cadherin, but not that of ZO-1, changed in parallel depending on Rac small G protein activity. Dissociation of MDCK cells by culturing the cells at 2 microM Ca2+ caused rapid endocytosis of E-cadherin, but not that of l-afadin or ZO-1. Addition of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate to these dissociated cells formed a tight junction-like structure where ZO-1 and l-afadin, but not neurabin-II or E-cadherin, accumulated. We furthermore found that, in non-epithelial EL cells, which expressed E-cadherin and attached to each other, l-afadin, neurabin-II, ZO-1 and E-cadherin were all localized at AJ. In cadherin-deficient L cells, I-afadin was mainly localized at cell-cell contact sites, but ZO-1 was mainly localized at the tip area of cell processes. Neurabin-II did not accumulate at the plasma membrane area. Neither l-afadin nor neurabin-II significantly interacted with alpha-, beta-catenin, E-cadherin, ZO-1 or occludin. | 10102631
 |
Nectin/PRR: an immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecule recruited to cadherin-based adherens junctions through interaction with Afadin, a PDZ domain-containing protein.
Takahashi K, Nakanishi H, Miyahara M, Mandai K, Satoh K, Satoh A, Nishioka H, Aoki J, Nomoto A, Mizoguchi A, Takai Y.
J Cell Biol
145(3)
539-49
1998
Show Abstract
We have isolated a novel actin filament-binding protein, named afadin, localized at cadherin-based cell-cell adherens junctions (AJs) in various tissues and cell lines. Afadin has one PDZ domain, three proline-rich regions, and one actin filament-binding domain. We found here that afadin directly interacted with a family of the immunoglobulin superfamily, which was isolated originally as the poliovirus receptor-related protein (PRR) family consisting of PRR1 and -2, and has been identified recently to be the alphaherpes virus receptor. PRR has a COOH-terminal consensus motif to which the PDZ domain of afadin binds. PRR and afadin were colocalized at cadherin-based cell-cell AJs in various tissues and cell lines. In E-cadherin-expressing EL cells, PRR was recruited to cadherin-based cell-cell AJs through interaction with afadin. PRR showed Ca2+-independent cell-cell adhesion activity. These results indicate that PRR is a cell-cell adhesion molecule of the immunoglobulin superfamily which is recruited to cadherin-based cell-cell AJs through interaction with afadin. We rename PRR as nectin (taken from the Latin word "necto" meaning "to connect"). | 10225955
 |