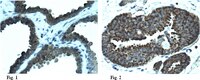
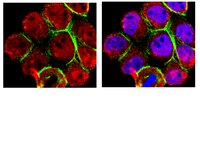
AB9985 Sigma-AldrichAnti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) Antibody
Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) Antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody for detection of glutathione p53 (Cys141) also known as Antigen NY-CO-13, Phosphoprotein p53, Tumor suppressor p53 & has been validated in WB, IP, IHC, ICC.
More>> Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) Antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody for detection of glutathione p53 (Cys141) also known as Antigen NY-CO-13, Phosphoprotein p53, Tumor suppressor p53 & has been validated in WB, IP, IHC, ICC. Less<<Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H, Chp, Rhesus Macaque, Gs, Mk, Ht | WB, IP, IHC, ICC | Rb | Affinity Purified | Polyclonal Antibody |
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Affinity Purified |
| Control |
|
| Presentation | Purified rabbit polyclonal in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide. |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Storage and Shipping Information | |
|---|---|
| Storage Conditions | Stable for 1 year at 2-8°C from date of receipt. |
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 100 µL |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | GTIN |
| AB9985 | 04053252297144 |
Documentation
Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) Antibody MSDS
| Title |
|---|
Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) Antibody Certificates of Analysis
| Title | Lot Number |
|---|---|
| Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) - 2363029 | 2363029 |
| Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) - 3552710 | 3552710 |
| Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) - NG1837353 | NG1837353 |
| Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) - NRG1810084 | NRG1810084 |
| Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) -2767030 | 2767030 |
| Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) Polyclonal Antibody | 2949191 |
| Anti-glutathione p53 (Cys141) Polyclonal Antibody | 2868352 |