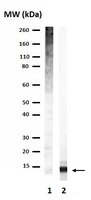
A specific E3 ligase/deubiquitinase pair modulates TBP protein levels during muscle differentiation.
Li, L; Martinez, SS; Hu, W; Liu, Z; Tjian, R
eLife
4
e08536
2015
Show Abstract
TFIID-a complex of TATA-binding protein (TBP) and TBP-associated factors (TAFs)-is a central component of the Pol II promoter recognition apparatus. Recent studies have revealed significant downregulation of TFIID subunits in terminally differentiated myocytes, hepatocytes and adipocytes. Here, we report that TBP protein levels are tightly regulated by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Using an in vitro ubiquitination assay coupled with biochemical fractionation, we identified Huwe1 as an E3 ligase targeting TBP for K48-linked ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation. Upregulation of Huwe1 expression during myogenesis induces TBP degradation and myotube differentiation. We found that Huwe1 activity on TBP is antagonized by the deubiquitinase USP10, which protects TBP from degradation. Thus, modulating the levels of both Huwe1 and USP10 appears to fine-tune the requisite degradation of TBP during myogenesis. Together, our study unmasks a previously unknown interplay between an E3 ligase and a deubiquitinating enzyme regulating TBP levels during cellular differentiation. | | 26393420
 |
Alanine scan of core positions in ubiquitin reveals links between dynamics, stability, and function.
Lee, SY; Pullen, L; Virgil, DJ; Castañeda, CA; Abeykoon, D; Bolon, DN; Fushman, D
Journal of molecular biology
426
1377-89
2014
Show Abstract
Mutations at solvent-inaccessible core positions in proteins can impact function through many biophysical mechanisms including alterations to thermodynamic stability and protein dynamics. As these properties of proteins are difficult to investigate, the impacts of core mutations on protein function are poorly understood for most systems. Here, we determined the effects of alanine mutations at all 15 core positions in ubiquitin on function in yeast. The majority (13 of 15) of alanine substitutions supported yeast growth as the sole ubiquitin. Both the two null mutants (I30A and L43A) were less stable to temperature-induced unfolding in vitro than wild type (WT) but were well folded at physiological temperatures. Heteronuclear NMR studies indicated that the L43A mutation reduces temperature stability while retaining a ground-state structure similar to WT. This structure enables L43A to bind to common ubiquitin receptors in vitro. Many of the core alanine ubiquitin mutants, including one of the null variants (I30A), exhibited an increased accumulation of high-molecular-weight species, suggesting that these mutants caused a defect in the processing of ubiquitin-substrate conjugates. In contrast, L43A exhibited a unique accumulation pattern with reduced levels of high-molecular-weight species and undetectable levels of free ubiquitin. When conjugation to other proteins was blocked, L43A ubiquitin accumulated as free ubiquitin in yeast. Based on these findings, we speculate that ubiquitin's stability to unfolding may be required for efficient recycling during proteasome-mediated substrate degradation. | | 24361330
 |
Miz1 is required to maintain autophagic flux.
Wolf, E; Gebhardt, A; Kawauchi, D; Walz, S; von Eyss, B; Wagner, N; Renninger, C; Krohne, G; Asan, E; Roussel, MF; Eilers, M
Nature communications
4
2535
2013
Show Abstract
Miz1 is a zinc finger protein that regulates the expression of cell cycle inhibitors as part of a complex with Myc. Cell cycle-independent functions of Miz1 are poorly understood. Here we use a Nestin-Cre transgene to delete an essential domain of Miz1 in the central nervous system (Miz1(ΔPOZNes)). Miz1(ΔPOZNes) mice display cerebellar neurodegeneration characterized by the progressive loss of Purkinje cells. Chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing and biochemical analyses show that Miz1 activates transcription upon binding to a non-palindromic sequence present in core promoters. Target genes of Miz1 encode regulators of autophagy and proteins involved in vesicular transport that are required for autophagy. Miz1(ΔPOZ) neuronal progenitors and fibroblasts show reduced autophagic flux. Consistently, polyubiquitinated proteins and p62/Sqtm1 accumulate in the cerebella of Miz1(ΔPOZNes) mice, characteristic features of defective autophagy. Our data suggest that Miz1 may link cell growth and ribosome biogenesis to the transcriptional regulation of vesicular transport and autophagy. | Western Blotting | 24088869
 |
The SUVR4 histone lysine methyltransferase binds ubiquitin and converts H3K9me1 to H3K9me3 on transposon chromatin in Arabidopsis.
Veiseth, SV; Rahman, MA; Yap, KL; Fischer, A; Egge-Jacobsen, W; Reuter, G; Zhou, MM; Aalen, RB; Thorstensen, T
PLoS genetics
7
e1001325
2010
Show Abstract
Chromatin structure and gene expression are regulated by posttranslational modifications (PTMs) on the N-terminal tails of histones. Mono-, di-, or trimethylation of lysine residues by histone lysine methyltransferases (HKMTases) can have activating or repressive functions depending on the position and context of the modified lysine. In Arabidopsis, trimethylation of lysine 9 on histone H3 (H3K9me3) is mainly associated with euchromatin and transcribed genes, although low levels of this mark are also detected at transposons and repeat sequences. Besides the evolutionarily conserved SET domain which is responsible for enzyme activity, most HKMTases also contain additional domains which enable them to respond to other PTMs or cellular signals. Here we show that the N-terminal WIYLD domain of the Arabidopsis SUVR4 HKMTase binds ubiquitin and that the SUVR4 product specificity shifts from di- to trimethylation in the presence of free ubiquitin, enabling conversion of H3K9me1 to H3K9me3 in vitro. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and immunocytological analysis showed that SUVR4 in vivo specifically converts H3K9me1 to H3K9me3 at transposons and pseudogenes and has a locus-specific repressive effect on the expression of such elements. Bisulfite sequencing indicates that this repression involves both DNA methylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Transcribed genes with high endogenous levels of H3K4me3, H3K9me3, and H2Bub1, but low H3K9me1, are generally unaffected by SUVR4 activity. Our results imply that SUVR4 is involved in the epigenetic defense mechanism by trimethylating H3K9 to suppress potentially harmful transposon activity. | Western Blotting | 21423664
 |
Ubiquitin over-expression phenotypes and ubiquitin gene molecular misreading during aging in Drosophila melanogaster.
Hoe, N; Huang, CM; Landis, G; Verhage, M; Ford, D; Yang, J; van Leeuwen, FW; Tower, J
Aging
3
237-61
2010
Show Abstract
Molecular Misreading (MM) is the inaccurate conversion of genomic information into aberrant proteins. For example, when RNA polymerase II transcribes a GAGAG motif it synthesizes at low frequency RNA with a two-base deletion. If the deletion occurs in a coding region, translation will result in production of misframed proteins. During mammalian aging, misframed versions of human amyloid precursor protein (hApp) and ubiquitin (hUbb) accumulate in the aggregates characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases, suggesting dysfunctional degradation or clearance. Here cDNA clones encoding wild-type hUbb and the frame-shifted version hUbb(+1) were expressed in transgenic Drosophila using the doxycycline-regulated system. Misframed proteins were abundantly produced, both from the transgenes and from endogenous Drosophila ubiquitin-encoding genes, and their abundance increased during aging in whole-fly extracts. Over-expression of wild-type hUbb, but not hUbb(+1), was toxic during fly development. In contrast, when over-expressed specifically in adult flies, hUbb(+1) caused small decreases in life span, whereas hUbb was associated with small increases, preferentially in males. The data suggest that MM occurs in Drosophila and that the resultant misframed proteins accumulate with age. MM of the ubiquitin gene can produce alternative ubiquitin gene products with different and sometimes opposing phenotypic effects. | | 21415465
 |
Constitutive fusion of ubiquitin to PCNA provides DNA damage tolerance independent of translesion polymerase activities.
Pastushok, L; Hanna, M; Xiao, W
Nucleic acids research
38
5047-58
2009
Show Abstract
In response to replication-blocking DNA lesions, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) can be conjugated with a single ubiquitin (Ub) or Lys63-linked Ub chains at the Lys164 residue, leading to two modes of DNA damage tolerance (DDT), namely translesion synthesis (TLS) and error-free DDT, respectively. Several reports suggest a model whereby monoubiquitylated PCNA recruits TLS polymerases through an enhanced physical association. We sought to examine this model in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through artificial fusions of Ub to PCNA in vivo. We created N- and C- terminal gene fusions of Ub to PCNA-K164R (collectively called PCNA.Ub) and found that both conferred tolerance to DNA damage. The creation of viable PCNA.Ub strains lacking endogenous PCNA enabled a thorough analysis of roles for PCNA mono-Ub in DDT. As expected, the DNA damage resistance provided by PCNA.Ub is not dependent on RAD18 or UBC13. Surprisingly, inactivation of TLS polymerases did not abolish PCNA.Ub resistance to DNA damage, nor did PCNA.Ub cause elevated spontaneous mutagenesis, which is a defining characteristic of REV3-dependent TLS activity. Taken together, our data suggest that either the monoubiquitylation of PCNA does not promote TLS activity in all cases or PCNA.Ub reveals a currently undiscovered role for monoubiquitylated PCNA in DNA damage tolerance. Full Text Article | | 20385585
 |
BRCA1/BARD1 E3 ubiquitin ligase can modify histones H2A and H2B in the nucleosome particle.
Amit Thakar,Jeffrey D Parvin,Jordanka Zlatanova
Journal of biomolecular structure & dynamics
27
2009
Show Abstract
BRCA1, the protein product of the Breast Cancer Susceptibility Gene (BRCA1) has been implicated in multiple pathways that preserve genome stability, including cell cycle control, DNA repair, transcription, and chromatin remodeling. BRCA1, in complex with another RING-domain protein BARD1, possesses ubiquitin-ligase activity. Only a few targets for this activity have been identified in vivo. Nucleosomal histones may also be targets in vivo since they can be modified by the BRCA1/BARD1 complex in vitro. Here we demonstrate that the BRCA1/BARD1 complex can ubiquitylate both free H2A and H2B histones and histones in the context of nucleosomal particles. These results raise the possibility that BRCA1/BARD1 can directly affect nucleosomal structure, dynamics, and function through its ability to modify nucleosomal histones. | | 19916563
 |
Molecular discrimination of structurally equivalent Lys 63-linked and linear polyubiquitin chains.
David Komander,Francisca Reyes-Turcu,Julien D F Licchesi,Peter Odenwaelder,Keith D Wilkinson,David Barford
EMBO reports
10
2009
Show Abstract
At least eight types of ubiquitin chain exist, and individual linkages affect distinct cellular processes. The only distinguishing feature of differently linked ubiquitin chains is their structure, as polymers of the same unit are chemically identical. Here, we have crystallized Lys 63-linked and linear ubiquitin dimers, revealing that both adopt equivalent open conformations, forming no contacts between ubiquitin molecules and thereby differing significantly from Lys 48-linked ubiquitin chains. We also examined the specificity of various deubiquitinases (DUBs) and ubiquitin-binding domains (UBDs). All analysed DUBs, except CYLD, cleave linear chains less efficiently compared with other chain types, or not at all. Likewise, UBDs can show chain specificity, and are able to select distinct linkages from a ubiquitin chain mixture. We found that the UBAN (ubiquitin binding in ABIN and NEMO) motif of NEMO (NF-kappaB essential modifier) binds to linear chains exclusively, whereas the NZF (Npl4 zinc finger) domain of TAB2 (TAK1 binding protein 2) is Lys 63 specific. Our results highlight remarkable specificity determinants within the ubiquitin system. Full Text Article | | 19373254
 |
Mutations in the hydrophobic core of ubiquitin differentially affect its recognition by receptor proteins.
Haririnia, A; Verma, R; Purohit, N; Twarog, MZ; Deshaies, RJ; Bolon, D; Fushman, D
Journal of molecular biology
375
979-96
2008
Show Abstract
Ubiquitin (Ub) is one of the most highly conserved signaling proteins in eukaryotes. In carrying out its myriad functions, Ub conjugated to substrate proteins interacts with dozens of receptor proteins that link the Ub signal to various biological outcomes. Here we report mutations in conserved residues of Ub's hydrophobic core that have surprisingly potent and specific effects on molecular recognition. Mutant Ubs bind tightly to the Ub-associated domain of the receptor proteins Rad23 and hHR23A but fail to bind the Ub-interacting motif present in the receptors Rpn10 and S5a. Moreover, chains assembled on target substrates with mutant Ubs are unable to support substrate degradation by the proteasome in vitro or sustain viability of yeast cells. The mutations have relatively little effect on Ub's overall structure but reduce its rigidity and cause a slight displacement of the C-terminal beta-sheet, thereby compromising association with Ub-interacting motif but not with Ub-associated domains. These studies emphasize an unexpected role for Ub's core in molecular recognition and suggest that the diversity of protein-protein interactions in which Ub engages placed enormous constraints on its evolvability. | Western Blotting | 18054791
 |
The role of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in oncogenic signaling.
Fuchs, Serge Y
Cancer Biol. Ther., 1: 337-41 (2002)
2002
Show Abstract
Oncogenic activation of genes that regulate cell proliferation and survival plays a central role in the development of human cancer. This activation is frequently achieved by the aberrant expression of oncogene products due to the gene amplification, enhanced transcription or stabilization of their mRNA or protein. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway(UPP) is the key player in the intracellular degradation of regulatory proteins in eukaryotes. UPP controls the abundance and activity of important protein regulators of cellular signal transduction including a variety of cellular proto-oncogenes. Alteration of ubiquitination and degradation of these proto-oncogene proteins often occurs during tumorigenesis and critically contributes to cell decisions as per proliferation/differentiation and survival/death.This article attempts to briefly overview the role of UPP in the regulation of several signal transduction pathways that contribute to development of cancer. | | 12432242
 |