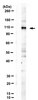
AB9676 Sigma-AldrichAnti-Tau phospho Threonine 205 Antibody
This Anti-Tau phospho Threonine 205 Antibody is validated for use in WB for the detection of Tau phospho Threonine 205.
More>> This Anti-Tau phospho Threonine 205 Antibody is validated for use in WB for the detection of Tau phospho Threonine 205. Less<<Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | WB | Rb | Affinity Purified | Polyclonal Antibody |
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Affinity Purified |
| Presentation | Affinity purified immunoglobulin. Liquid in Dulbecco's PBS (without Mg2+ and Ca2+), pH 7.3, 50% glycerol with 1.0 mg/mL BSA and 0.05% sodium azide. |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 100 µL |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | GTIN |
| AB9676 | 04053252333675 |
Documentation
Anti-Tau phospho Threonine 205 Antibody MSDS
| Title |
|---|
Anti-Tau phospho Threonine 205 Antibody Certificates of Analysis
References
| Reference overview | Pub Med ID |
|---|---|
| The retinoic acid and brain-derived neurotrophic factor differentiated SH-SY5Y cell line as a model for Alzheimer's disease-like tau phosphorylation. Jämsä, A., et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm., 319:993-1000 (2004) 2004 | 15184080
 |
| Involvement of aberrant glycosylation in phosphorylation of tau by cdk5 and GSK-3beta. Liu, F., et al. FEBS Lett., 530(1-3):209-214 (2002) 2002 | 12387894
 |
| Interaction of tau isoforms with Alzheimer's disease abnormally hyperphosphorylated tau and in vitro phosphorylation into the disease-like protein. Alonso, A.D., et al. J. Biol. Chem., 276(41):37967-37973 (2001) 2001 | 11495914
 |
| Distribution of tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta, phosphatases 2A and 2B, and phosphorylated tau in the developing rat brain. Takahashi, M., et al. Brain Res., 857(1-2):193-206 (2000) 1999 | 10700568
 |
| Tau is phosphorylated by GSK-3 at several sites found in Alzheimer disease and its biological activity markedly inhibited only after it is prephosphorylated by A-kinase. Wang, J.Z., et al. FEBS Lett., 436(1):28-34 (1998) 1998 | 9771888
 |
| Stress-activated protein kinase/c-jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylates tau protein. Reynolds, C H, et al. J. Neurochem., 68: 1736-44 (1997) 1997 Show Abstract | 9084448
 |
| Physiology and pathology of tau protein kinases in relation to Alzheimer's disease. Imahori, K. and T. Uchida J. Biochem., 121:179-188 (1997) 1997 | 9089387
 |
| Reactivating kinase/p38 phosphorylates tau protein in vitro. Reynolds, C.H., et al. J. Neurochem., 69(1):191-198 (1997) 1997 | 9202310
 |
| Regulation of the phosphorylation state and microtubule-binding activity of tau by protein phosphatase 2A. Sontag, E., et al. Neuron , 17:1201-1207 (1996) 1996 | 8982166
 |
Newsletters / Publications
| Title |
|---|
| Research Focus - Volume 2, 2013 |