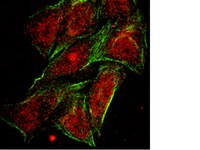
Peptide inhibitors disrupt the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor interaction with phosphatase and tensin homolog to allosterically modulate cellular signaling and behavior.
Anastasio, NC; Gilbertson, SR; Bubar, MJ; Agarkov, A; Stutz, SJ; Jeng, Y; Bremer, NM; Smith, TD; Fox, RG; Swinford, SE; Seitz, PK; Charendoff, MN; Craft, JW; Laezza, FM; Watson, CS; Briggs, JM; Cunningham, KA
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
33
1615-30
2013
Show Abstract
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) signaling through the 5-HT(2C) receptor (5-HT(2C)R) is essential in normal physiology, whereas aberrant 5-HT(2C)R function is thought to contribute to the pathogenesis of multiple neural disorders. The 5-HT(2C)R interacts with specific protein partners, but the impact of such interactions on 5-HT(2C)R function is poorly understood. Here, we report convergent cellular and behavioral data that the interaction between the 5-HT(2C)R and protein phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) serves as a regulatory mechanism to control 5-HT(2C)R-mediated biology but not that of the closely homologous 5-HT(2A)R. A peptide derived from the third intracellular loop of the human 5-HT(2C)R [3L4F (third loop, fourth fragment)] disrupted the association, allosterically augmented 5-HT(2C)R-mediated signaling in live cells, and acted as a positive allosteric modulator in rats in vivo. We identified the critical residues within an 8 aa fragment of the 3L4F peptide that maintained efficacy (within the picomolar range) in live cells similar to that of the 3L4F peptide. Last, molecular modeling identified key structural features and potential interaction sites of the active 3L4F peptides against PTEN. These compelling data demonstrate the specificity and importance of this protein assembly in cellular events and behaviors mediated by 5-HT(2C)R signaling and provide a chemical guidepost to the future development of drug-like peptide or small-molecule inhibitors as neuroprobes to study 5-HT(2C)R allostery and therapeutics for 5-HT(2C)R-mediated disorders. | 23345234
 |
Meiotic functions of RAD18.
Inagaki, A; Sleddens-Linkels, E; Wassenaar, E; Ooms, M; van Cappellen, WA; Hoeijmakers, JH; Seibler, J; Vogt, TF; Shin, MK; Grootegoed, JA; Baarends, WM
Journal of cell science
124
2837-50
2010
Show Abstract
RAD18 is an ubiquitin ligase that is involved in replication damage bypass and DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair processes in mitotic cells. Here, we investigated the testicular phenotype of Rad18-knockdown mice to determine the function of RAD18 in meiosis, and in particular, in the repair of meiotic DSBs induced by the meiosis-specific topoisomerase-like enzyme SPO11. We found that RAD18 is recruited to a specific subfraction of persistent meiotic DSBs. In addition, RAD18 is recruited to the chromatin of the XY chromosome pair, which forms the transcriptionally silent XY body. At the XY body, RAD18 mediates the chromatin association of its interaction partners, the ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes HR6A and HR6B. Moreover, RAD18 was found to regulate the level of dimethylation of histone H3 at Lys4 and maintain meiotic sex chromosome inactivation, in a manner similar to that previously observed for HR6B. Finally, we show that RAD18 and HR6B have a role in the efficient repair of a small subset of meiotic DSBs. | 21807948
 |
Cyclic GMP signaling in rat urinary bladder, prostate, and epididymis: tissue-specific changes with aging and in response to Leydig cell depletion.
Müller, D; Mukhopadhyay, AK; Davidoff, MS; Middendorff, R
Reproduction (Cambridge, England)
142
333-43
2010
Show Abstract
Aging of the male reproductive system leads to changes in endocrine signaling and is frequently associated with the emergence of prostate hyperplasia and bladder dysfunctions. Recent reports highlight prostate and bladder as promising targets for therapeutic interventions with inhibitors of the cyclic GMP (cGMP)-degrading phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5). However, the cGMP signaling system in these organs is as yet poorly characterized, and the possibility of age-related alterations has not been addressed. This study investigates key proteins of cGMP pathways in bladder, prostate, and epididymis of young (3 months) and old (23-24 months) Wistar rats. Local differences in the abundance of PDE5, soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) and particulate guanylyl cyclases (GC-A, GC-B), endothelial nitric oxide synthase, and cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (PRKG1 (cGKI)) revealed pronounced tissue-specific peculiarities. Although cGMP-generating enzymes were not affected by age in all organs, we recognized age-related decreases of PDE5 expression in bladder and a selective diminishment of membrane-associated PRKG1 in epididymis. In disagreement with published data, all cGMP pathway proteins including PDE5 are poorly expressed in prostate. However, prostatic PRKG1 expression increases with aging. Androgen withdrawal during temporary Leydig cell elimination induced a massive (greater than 12-fold) upregulation of PRKG1 in prostate but not in other (penis and epididymis) androgen-dependent organs. These findings identify PRKG1 as a key androgen-sensitive signaling protein in prostate of possible importance for growth regulation. The elucidated effects may have significance for age-associated pathologies in the male lower-urinary tract. | 21511885
 |