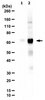
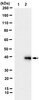
Upregulation and secretion of kallikrein-related peptidase 6 (KLK6) in gastric cancer.
Jin Ju Kim,Jong-Tae Kim,Hyo Ran Yoon,Min Ah Kang,Joo Heon Kim,Young-Ha Lee,Jae Wha Kim,Seon-Jin Lee,Eun Young Song,Pyung Keun Myung,Hee Gu Lee
Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine
33
2011
Show Abstract
KLK6 encoding kallikrein-related peptidase 6, a trypsin-like serine protease, has been shown to be upregulated in several cancers, although the tumorigenic role of KLK6 has not been elucidated. In this study, KLK6 was identified as a highly upregulated gene in gastric cancer; therefore, the possibility that KLK6 might be a suitable candidate tumor marker was examined. RT-PCR and immunohistochemical analysis showed overexpression of KLK6 in gastric cancer tissues compared to nontumor regions. Sera from gastric cancer patients had a 1.7-fold increase in KLK6 (373.1 μg/L, P = 0.048) compared to healthy individuals (214.2 μg/L), although there was no significant difference among patients with various tumor stages. Cellular invasiveness decreased by 45% in cells transfected with KLK6-specific small interfering RNA. Exogenous overexpression of KLK6 led to decreased activity of the E-cadherin promoter. This study shows that KLK6 is significantly upregulated and secreted in gastric cancer tissues and sera, suggesting that KLK6 might be used as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for gastric cancer. | | 22373580
 |
ANGPTL4 modulates vascular junction integrity by integrin signaling and disruption of intercellular VE-cadherin and claudin-5 clusters.
Huang, RL; Teo, Z; Chong, HC; Zhu, P; Tan, MJ; Tan, CK; Lam, CR; Sng, MK; Leong, DT; Tan, SM; Kersten, S; Ding, JL; Li, HY; Tan, NS
Blood
118
3990-4002
2010
Show Abstract
Vascular disruption induced by interactions between tumor-secreted permeability factors and adhesive proteins on endothelial cells facilitates metastasis. The role of tumor-secreted C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain of angiopoietin-like 4 (cANGPTL4) in vascular leakiness and metastasis is controversial because of the lack of understanding of how cANGPTL4 modulates vascular integrity. Here, we show that cANGPTL4 instigated the disruption of endothelial continuity by directly interacting with 3 novel binding partners, integrin α5β1, VE-cadherin, and claudin-5, in a temporally sequential manner, thus facilitating metastasis. We showed that cANGPTL4 binds and activates integrin α5β1-mediated Rac1/PAK signaling to weaken cell-cell contacts. cANGPTL4 subsequently associated with and declustered VE-cadherin and claudin-5, leading to endothelial disruption. Interfering with the formation of these cANGPTL4 complexes delayed vascular disruption. In vivo vascular permeability and metastatic assays performed using ANGPTL4-knockout and wild-type mice injected with either control or ANGPTL4-knockdown tumors confirmed that cANGPTL4 induced vascular leakiness and facilitated lung metastasis in mice. Thus, our findings elucidate how cANGPTL4 induces endothelial disruption. Our findings have direct implications for targeting cANGPTL4 to treat cancer and other vascular pathologies. | | 21841165
 |
Infertile women with isolated polycystic ovaries are deficient in endometrial expression of osteopontin but not alphavbeta3 integrin during the implantation window.
Renée DuQuesnay, Corrina Wright, Anita Abdul Aziz, Gordon W H Stamp, Geoffrey H Trew, Raul A Margara, John O White, Renée DuQuesnay, Corrina Wright, Anita Abdul Aziz, Gordon W H Stamp, Geoffrey H Trew, Raul A Margara, John O White, Renée DuQuesnay, Corrina Wright, Anita Abdul Aziz, Gordon W H Stamp, Geoffrey H Trew, Raul A Margara, John O White
Fertility and sterility
91
489-99
2009
Show Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To characterize possible endometrial defects in infertile women with isolated PCO morphology. DESIGN: Prospective study. SETTING: An academic hospital with an IVF unit. PATIENT(S): Women with primary unexplained infertility and isolated PCO, fertile women, and women with infertility secondary to male factor. INTERVENTION(S): Thirty-one women (fertile and with male factor infertility) had endometrial sampling across the menstrual cycle. Nine fertile women and 10 infertile women with isolated PCO had sampling on day LH +7, adjusted for histologic dating. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE(S): Expression of alphavbeta3 and its ligand, osteopontin, were determined using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. In vitro regulation of osteopontin was assessed using the Ishikawa cell line. RESULT(S): Cyclic variations revealed a fall in integrin alphavbeta3 mRNA during the secretory phase with concomitant up-regulation of osteopontin mRNA. Immunohistochemistry on day LH +7 demonstrated a significant reduction in expression of osteopontin in the isolated PCO group with no difference in expression of alphavbeta3. In vitro studies confirmed up-regulation of osteopontin by estrogen with no apparent effect of androgen. CONCLUSION(S): These results demonstrate an apparent reduction of osteopontin expression, important in cell-cell adhesion, during the window of implantation in infertile women with isolated PCO morphology. | | 18353318
 |
Expression and activation of alpha v beta 3 integrins by SDF-1/CXC12 increases the aggressiveness of prostate cancer cells.
Yan-Xi Sun,Ming Fang,Jianhua Wang,Carlton R Cooper,Kenneth J Pienta,Russell S Taichman
The Prostate
67
2007
Show Abstract
Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1 or CXCL12) and CXCR4 are key elements in the metastasis of prostate cancer cells to bone--but the mechanisms as to how it localizes to the marrow remains unclear. | | 17034033
 |
Correlation between the tumoral expression of beta3-integrin and outcome in cervical cancer patients who had undergone radiotherapy.
Gruber, G; Hess, J; Stiefel, C; Aebersold, DM; Zimmer, Y; Greiner, RH; Studer, U; Altermatt, HJ; Hlushchuk, R; Djonov, V
British journal of cancer
92
41-6
2004
Show Abstract
Integrins are cell-surface receptors, which mediate cell-to-cell and cell-to-extracellular matrix adhesion. Besides playing an important role in tumour angiogenesis, beta3-integrin is also expressed in several types of epithelial cancer cells. It was the purpose of the present study to evaluate the prognostic value of beta3-integrin expression in patients with cervical cancer. Biopsies were taken from 82 patients with squamous cell or adenocarcinomas of the uterine cervix who had undergone external-beam radiotherapy with or without brachytherapy. These tissue samples were analysed immunohistochemically for the expression of beta3-integrin. The impact of immunoreactivity for beta3-integrin on survival end points was assessed by univariate and multivariate analyses, and its correlation with clinicopathological characteristics evaluated by crosstabulations. beta3-integrin was expressed in 61% (50 of 82) of the patients. Kaplan-Meier curves revealed local progression-free survival, distant metastasis-free survival and cause-specific survival to be significantly shorter (P-values according to the log-rank test: 0.002, 0.04 and 0.01, respectively) in patients with beta3-integrin expression. The prognostic impact of this parameter was even higher than for other well-known prognostic parameters and remained statistically significant in the multivariate analyses. beta3-integrin, which is expressed in the majority of patients with advanced cervical cancer, has a significant prognostic impact on outcome according to univariate and multivariate analyses. | | 15597101
 |
Osteonectin/SPARC induction by ectopic beta(3) integrin in human radial growth phase primary melanoma cells
Sturm, Richard A, et al
Cancer Res, 62:226-32 (2002)
2002
| Flow Cytometry | 11782382
 |
Progression-related expression of beta3 integrin in melanomas and nevi.
Van Belle, P A, et al.
Hum. Pathol., 30: 562-7 (1999)
1998
Show Abstract
The expression of the beta3 integrin subunit was investigated in 130 fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens of human melanomas and nevi using two different monoclonal antibodies. Expression was not observed in melanocytes and was absent or low in most nevi. In primary melanomas, expression was absent or low in the nontumorigenic radial growth phase, which includes the classes of in situ and microinvasive melanomas. In contrast, expression was high in the tumorigenic or vertical growth phase compartment of many primary melanomas and in most metastatic melanomas. Expression patterns were similar with the two antibodies, SSA6 and SAP, and was membrane-related as well as cytoplasmically expressed. In those nevi that reacted focally, the reactivity tended to occur in the dermal component of neurotized nevi, and in Spitz nevi, where the reactivity was stronger and more diffuse. A few dysplastic nevi showed focal reactivity of the junctional component. These results are consistent with tumor progression-related expression of the beta3 integrin, which is expressed in melanocytic tumors as the alphavbeta3 integrin, having affinity for matrix molecules, including vitronectin and fibronectin. In all melanomas, and in the subset of tumorigenic vertical growth phase melanomas, expression increased with thickness (P < .01). For this reason, and because ligation of this integrin has been shown in vitro to have several properties that may be related to the malignant phenotype, it is likely that expression of this marker may have prognostic value. However, because of its consistent and strong expression in Spitz nevi, the diagnostic utility of this marker will likely be limited. | Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | 10333228
 |