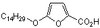
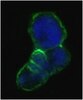
Inhibition of collagen XVI expression reduces glioma cell invasiveness.
Bauer, R; Ratzinger, S; Wales, L; Bosserhoff, A; Senner, V; Grifka, J; Grässel, S
Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology
27
217-26
2010
Show Abstract
Glioblastomas are characterized by an intense local invasiveness that limits surgical resection. One mechanism by which glioma cells enforce their migration into brain tissue is reorganization of tumour associated extracellular matrix (ECM). Collagen XVI is a minor component of connective tissues. However, in glioblastoma tissue it is dramatically upregulated compared to the ECM of normal cortex. The aim of this study is to delineate tumour cell invasion and underlying mechanisms involving collagen XVI by using a siRNA mediated collagen XVI knockdown model in U87MG human glioblastoma cells. Knockdown of collagen XVI resulted in decreased invasiveness in Boyden chamber assays, and in a reduction of focal adhesion contact numbers per cell. Gene expression was upregulated for protocadherin 18 and downregulated for kindlin-1 and -2. Proliferation was not affected while flow cytometric analysis demonstrated reduced β1-integrin activation in collagen XVI knockdown cells. We suggest that in glioblastoma tissue collagen XVI may impair the cell-cell interaction in favour of enhancement of invasion. The modification of the β1-integrin activation pattern through collagen XVI might be a molecular mechanism to further augment the invasive phenotype of glioma cells. Elucidating the underlying mechanisms of glioma cell invasion promoted by collagen XVI may provide novel cancer therapeutic approaches in neurooncology. | 21471710
 |
Induction of type XVI collagen expression facilitates proliferation of oral cancer cells.
Sabine Ratzinger,Susanne Grässel,Albert Dowejko,Torsten E Reichert,Richard J Bauer
Matrix biology : journal of the International Society for Matrix Biology
30
2010
Show Abstract
Type XVI collagen belongs to the family of fibril-associated collagens with interrupted triple helices (FACIT). Recently, high affinity to integrin alpha1beta1 has been shown allowing cells expressing those integrins to attach and spread on recombinant type XVI collagen. Here, we show that type XVI collagen is overexpressed in dysplastic areas of mucosal epithelium from oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) patients. Induction of its expression in OSCC cell lines (COLXVI cells) leads to an increased expression of Kindlin-1. Moreover, we demonstrate a significantly increased Kindlin-1/beta1-integrin interaction. Additionally, we detected a higher number of activated beta1-integrins in COLXVI cells and found a neo-expression of alpha1 integrin subunit on these cells. FACS analysis revealed a significantly higher amount of COLXVI cells in S-phase and G2/M-phase 6h after synchronisation leading to a markedly higher proliferation activity. Blocking beta1-integrins with a specific antibody resulted in reduced proliferation of COLXVI cells. In summary, we demonstrate that overexpression of type XVI collagen in aberrant oral keratinocytes leads to Kindlin-1 induction, increased Kindlin-1/beta1-integrin interaction, integrin activation and subsequently to a proliferative cellular phenotype. | 21251976
 |
Integrin activation by dithiothreitol or Mn2+ induces a ligand-occupied conformation and exposure of a novel NH2-terminal regulatory site on the beta1 integrin chain.
Ni, H, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 273: 7981-7 (1998)
1998
Show Abstract
Integrins can be expressed in at least three functional states (i.e. latent, active, and ligand-occupied). However, the molecular bases for the transitions between these states are unknown. In the present study, changes in the accessibility of several beta1 epitopes (e.g. N29, B44, and B3B11) were used to probe activation-related conformational changes. Dithiothreitol or Mn2+ activation of integrin-mediated adhesion in the human B cell line, IM9, resulted in a marked increase in the exposure of the B44 epitope, while N29 expression levels were most sensitive to dithiothreitol treatment. These results contrasted with the epitope expression patterns of spontaneously adherent K562 cells, where N29 was almost fully accessible and B44 was low. Addition of a soluble ligand resulted in a marked increase in B44 levels, suggesting that this antibody detected a ligand-induced binding site. The N29 epitope was mapped to a cysteine-rich region near the NH2 terminus of the integrin chain, thus defining a novel regulatory site. These studies indicate that the activation of integrin function by different stimuli may involve related but nonidentical conformations. Both Mn2+ and dithiothreitol appear to induce localized conformational changes that mimic a ligand-occupied receptor. This differs from the "physiologically" activated integrins on K562 cells that display a marked increase in overall epitope accessibility without exposure of the ligand-induced binding site epitopes. The increased exposure of the N29 site on K562 cells may indicate a role for this region in the regulation of integrin function. | 9525896
 |
Control of beta1 integrin function. Localization of stimulatory epitopes.
Wilkins, J A, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 271: 3046-51 (1996)
1996
Show Abstract
The beta1 integrins can be expressed on the surface of cells in a latent form, which is activated by a variety of stimuli. As an approach to examining the transition to an active receptor, a panel of stimulatory antibodies to beta1 were produced and characterized. These antibodies induced adherence of the T-leukemic cell line Jurkat to collagen and fibronectin. Competitive antibody binding assays indicated the existence of at least three distinct epitope clusters A (B3B11, JB1B, 21C8), B (B44, 13B9), and C(N29) defined by the indicated antibodies. Two antibodies to the A site, JB1B and B3B11, were shown to localize to positions 671-703 and 657-670, respectively, of the beta1. This region is located in an area encompassing a predicted disulfide bond between linearly distant cysteines in beta1 (Cys415-Cys671). The homologous region of the beta3 integrin (490 690 and 602 690) has been shown to be one of the sites recognized by stimulatory antibodies to ligand-induced binding sites. The present results indicate the existence of multiple stimulatory regions and suggest considerable homology between the locations of beta1 and beta3 regulatory sites. | 8621699
 |