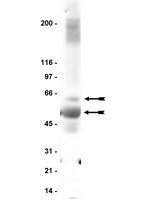
Cellular plasticity induced by anti-α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor encephalitis antibodies.
Peng, X; Hughes, EG; Moscato, EH; Parsons, TD; Dalmau, J; Balice-Gordon, RJ
Annals of neurology
77
381-98
2015
Show Abstract
Autoimmune-mediated anti-α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR) encephalitis is a severe but treatment-responsive disorder with prominent short-term memory loss and seizures. The mechanisms by which patient antibodies affect synapses and neurons leading to symptoms are poorly understood.The effects of patient antibodies on cultures of live rat hippocampal neurons were determined with immunostaining, Western blot, and electrophysiological analyses.We show that patient antibodies cause a selective decrease in the total surface amount and synaptic localization of GluA1- and GluA2-containing AMPARs, regardless of receptor subunit binding specificity, through increased internalization and degradation of surface AMPAR clusters. In contrast, patient antibodies do not alter the density of excitatory synapses, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) clusters, or cell viability. Commercially available AMPAR antibodies directed against extracellular epitopes do not result in a loss of surface and synaptic receptor clusters, suggesting specific effects of patient antibodies. Whole-cell patch clamp recordings of spontaneous miniature postsynaptic currents show that patient antibodies decrease AMPAR-mediated currents, but not NMDAR-mediated currents. Interestingly, several functional properties of neurons are also altered: inhibitory synaptic currents and vesicular γ-aminobutyric acid transporter (vGAT) staining intensity decrease, whereas the intrinsic excitability of neurons and short-interval firing increase.These results establish that antibodies from patients with anti-AMPAR encephalitis selectively eliminate surface and synaptic AMPARs, resulting in a homeostatic decrease in inhibitory synaptic transmission and increased intrinsic excitability, which may contribute to the memory deficits and epilepsy that are prominent in patients with this disorder. | | | 25369168
 |
Acute mechanisms underlying antibody effects in anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis.
Moscato, EH; Peng, X; Jain, A; Parsons, TD; Dalmau, J; Balice-Gordon, RJ
Annals of neurology
76
108-19
2014
Show Abstract
A severe but treatable form of immune-mediated encephalitis is associated with antibodies in serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) against the GluN1 subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). Prolonged exposure of hippocampal neurons to antibodies from patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis caused a reversible decrease in the synaptic localization and function of NMDARs. However, acute effects of the antibodies, fate of the internalized receptors, type of neurons affected, and whether neurons develop compensatory homeostatic mechanisms were unknown and are the focus of this study.Dissociated hippocampal neuron cultures and rodent brain sections were used for immunocytochemical, physiological, and molecular studies.Patient antibodies bind to NMDARs throughout the rodent brain, and decrease NMDAR cluster density in both excitatory and inhibitory hippocampal neurons. They rapidly increase the internalization rate of surface NMDAR clusters, independent of receptor activity. This internalization likely accounts for the observed decrease in NMDAR-mediated currents, as no evidence of direct blockade was detected. Once internalized, antibody-bound NMDARs traffic through both recycling endosomes and lysosomes, similar to pharmacologically induced NMDAR endocytosis. The antibodies are responsible for receptor internalization, as their depletion from CSF abrogates these effects in hippocampal neurons. We find that although anti-NMDAR antibodies do not induce compensatory changes in glutamate receptor gene expression, they cause a decrease in inhibitory synapse density onto excitatory hippocampal neurons.Our data support an antibody-mediated mechanism of disease pathogenesis driven by immunoglobulin-induced receptor internalization. Antibody-mediated downregulation of surface NMDARs engages homeostatic synaptic plasticity mechanisms, which may inadvertently contribute to disease progression. | | | 24916964
 |
Decreased intracellular GABA levels contribute to spinal cord stimulation-induced analgesia in rats suffering from painful peripheral neuropathy: the role of KCC2 and GABA(A) receptor-mediated inhibition.
S P Janssen,S Gerard,M E Raijmakers,M Truin,M Van Kleef,E A Joosten
Neurochemistry international
60
2011
Show Abstract
Elevated spinal extracellular γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels have been described during spinal cord stimulation (SCS)-induced analgesia in experimental chronic peripheral neuropathy. Interestingly, these increased GABA levels strongly exceeded the time frame of SCS-induced analgesia. In line with the former, pharmacologically-enhanced extracellular GABA levels by GABA(B) receptor agonists in combination with SCS in non-responders to SCS solely could convert these non-responders into responders. However, similar treatment with GABA(A) receptor agonists and SCS is known to be less efficient. Since K⁺ Cl⁻ cotransporter 2 (KCC2) functionality strongly determines proper GABA(A) receptor-mediated inhibition, both decreased numbers of GABA(A) receptors as well as reduced KCC2 protein expression might play a pivotal role in this loss of GABA(A) receptor-mediated inhibition in non-responders. Here, we explored the mechanisms underlying both changes in extracellular GABA levels and impaired GABA(A) receptor-mediated inhibition after 30 min of SCS in rats suffering from partial sciatic nerve ligation (PSNL). Immediately after cessation of SCS, a decreased spinal intracellular dorsal horn GABA-immunoreactivity was observed in responders when compared to non-responders or sham SCS rats. One hour later however, GABA-immunoreactivity was already increased to similar levels as those observed in non-responder or sham SCS rats. These changes did not coincide with alterations in the number of GABA-immunoreactive cells. C-Fos/GABA double-fluorescence clearly confirmed a SCS-induced activation of GABA-immunoreactive cells in responders immediately after SCS. Differences in spinal dorsal horn GABA(A) receptor-immunoreactivity and KCC2 protein levels were absent between all SCS groups. However, KCC2 protein levels were significantly decreased compared to sham PSNL animals. In conclusion, reduced intracellular GABA levels are only present during the time frame of SCS in responders and strongly point to a SCS-mediated on/off GABAergic release mechanism. Furthermore, a KCC2-dependent impaired GABA(A) receptor-mediated inhibition seems to be present both in responders and non-responders to SCS due to similar KCC2 and GABA(A) receptor levels. | | | 22107704
 |
Estrous cycle variations in GABA(A) receptor phosphorylation enable rapid modulation by anabolic androgenic steroids in the medial preoptic area.
Oberlander, JG; Porter, DM; Onakomaiya, MM; Penatti, CA; Vithlani, M; Moss, SJ; Clark, AS; Henderson, LP
Neuroscience
226
397-410
2011
Show Abstract
Anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS), synthetic testosterone derivatives that are used for ergogenic purposes, alter neurotransmission and behaviors mediated by GABA(A) receptors. Some of these effects may reflect direct and rapid action of these synthetic steroids at the receptor. The ability of other natural allosteric steroid modulators to alter GABA(A) receptor-mediated currents is dependent upon the phosphorylation state of the receptor complex. Here we show that phosphorylation of the GABA(A) receptor complex immunoprecipitated by β(2)/β(3) subunit-specific antibodies from the medial preoptic area (mPOA) of the mouse varies across the estrous cycle; with levels being significantly lower in estrus. Acute exposure to the AAS, 17α-methyltestosterone (17α-MeT), had no effect on the amplitude or kinetics of inhibitory postsynaptic currents in the mPOA of estrous mice when phosphorylation was low, but increased the amplitude of these currents from mice in diestrus, when it was high. Inclusion of the protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor, calphostin, in the recording pipette eliminated the ability of 17α-MeT to enhance currents from diestrous animals, suggesting that PKC-receptor phosphorylation is critical for the allosteric modulation elicited by AAS during this phase. In addition, a single injection of 17α-MeT was found to impair an mPOA-mediated behavior (nest building) in diestrus, but not in estrus. PKC is known to target specific serine residues in the β(3) subunit of the GABA(A) receptor. Although phosphorylation of these β(3) serine residues showed a similar profile across the cycle, as did phosphoserine in mPOA lysates immunoprecipitated with β2/β3 antibody (lower in estrus than in diestrus or proestrus), the differences were not significant. These data suggest that the phosphorylation state of the receptor complex regulates both the ability of AAS to modulate receptor function in the mPOA and the expression of a simple mPOA-dependent behavior through a PKC-dependent mechanism that involves the β(3) subunit and other sites within the GABA(A) receptor complex. | | | 22989919
 |
Inflammation-induced shift in spinal GABA(A) signaling is associated with a tyrosine kinase-dependent increase in GABA(A) current density in nociceptive afferents.
Zhu, Y; Dua, S; Gold, MS
Journal of neurophysiology
108
2581-93
2011
Show Abstract
To account for benzodiazepine-induced spinal analgesia observed in association with an inflammation-induced shift in the influence of the GABA(A) receptor antagonist gabazine on nociceptive threshold, the present study was designed to determine whether persistent inflammation is associated with the upregulation of high-affinity GABA(A) receptors in primary afferents. The cell bodies of afferents innervating the glabrous skin of the rat hind paw were retrogradely labeled, acutely dissociated, and studied before and after the induction of persistent inflammation. A time-dependent increase in GABA(A) current density was observed that was more than twofold by 72 h after the initiation of inflammation. This increase in current density included both high- and low-affinity currents and was restricted to neurons in which GABA increased intracellular Ca(2+). No increases in GABA(A) receptor subunit mRNA or protein were detected in whole ganglia. In contrast, the increased current density was completely reversed by 20-min preincubation with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein and partially reversed with the Src kinase inhibitor PP2. Genistein reversal was partially blocked by the dynamin inhibitor peptide P4. Changes in nociceptive threshold following spinal administration of genistein and muscimol to inflamed rats indicated that the pronociceptive actions of muscimol observed in the presence of inflammation were reversed by genistein. These results suggest that persistent changes in relative levels of tyrosine kinase activity following inflammation provide not only a sensitive way to dynamically regulate spinal nociceptive signaling but a viable target for the development of novel therapeutic interventions for the treatment of inflammatory pain. | | | 22914654
 |
The ly-6 protein, lynx1, is an endogenous inhibitor of nicotinic signaling in airway epithelium.
Fu, XW; Rekow, SS; Spindel, ER
American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology
303
L661-8
2011
Show Abstract
Our laboratory has previously reported that bronchial epithelial cells (BEC) express a regulatory cascade of classic neurotransmitters and receptors that communicate in an almost neuronal-like manner to achieve physiological regulation. In this paper we show that the similarity between neurotransmitter signaling in neurons and BEC extends to the level of transmitter receptor allosteric modulators. Lynx1 is a member of the ly-6/three-finger superfamily of proteins, many of which modulate receptor signaling activity. Lynx1 specifically has been shown to modulate nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) function in neurons by altering receptor sensitivity and desensitization. We now report that lynx1 forms a complex with α7 nAChR in BEC and serves to negatively regulate α7 downstream signaling events. Treatment of primary cultures of BEC with nicotine increased levels of nAChR subunits and that increase was potentiated by lynx1 knockdown. Lynx1 knockdown also potentiated the nicotine-induced increase in GABA(A) receptors (GABA(A)R) and MUC5AC mRNA expression, and that effect was blocked by α7 antagonists and α7 knockdown. In parallel with the increases in nAChR, GABA(A)R, and mucin mRNA levels, lynx1 knockdown also increased levels of p-Src. Consistent with this, inhibition of Src signaling blocked the ability of the lynx1 knockdown to increase basal and nicotine-stimulated GABA(A)R and mucin mRNA expression. Thus lynx1 appears to act as a negative modulator of α7 nAChR-induced events by inhibiting Src activation. This suggests that lynx1 agonists or mimetics are a potentially important therapeutic target to develop new therapies for smoking-related diseases characterized by increased mucin expression. | | | 22923641
 |
Mixed GABA-glycine synapses delineate a specific topography in the nucleus tractus solitarii of adult rat.
Dufour, A; Tell, F; Kessler, JP; Baude, A
The Journal of physiology
588
1097-115
2009
Show Abstract
Using combined morphological and electrophysiological approaches, we have determined the composition of inhibitory synapses of the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS), a brainstem structure that is a gateway for many visceral sensory afferent fibres. Immunohistochemical experiments demonstrate that, in adult rat, GABA axon terminals are present throughout the NTS while mixed GABA-glycine axon terminals are strictly located to the lateral part of the NTS within subnuclei surrounding the tractus solitarius. Purely glycine axon terminals are rare in the lateral part of the NTS and hardly detected in its medial part. Electrophysiological experiments confirm the predominance of GABA inhibition throughout the NTS and demonstrate the existence of a dual inhibition involving the co-release of GABA and glycine restricted to the lateral part of NTS. Since GABA(A) and glycine receptors are co-expressed postsynaptically in virtually all the inhibitory axon terminals throughout the NTS, it suggests that the inhibition phenotype relies on the characteristics of the axon terminals. Our results also demonstrate that glycine is mostly associated with GABA within axon terminals and raise the possibility of a dynamic regulation of GABA/glycine release at the presynaptic level. Our data provide new information for understanding the mechanisms involved in the processing of visceral information by the central nervous system in adult animals. Full Text Article | Immunohistochemistry | Rat | 20156844
 |
Development of gamma-aminobutyric acidergic synapses in cultured hippocampal neurons.
Swanwick, CC; Murthy, NR; Mtchedlishvili, Z; Sieghart, W; Kapur, J
The Journal of comparative neurology
495
497-510
2005
Show Abstract
The formation and maturation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic synapses was studied in cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons by both performing immunocytochemistry for GABAergic markers and recording miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs). Nascent GABAergic synapses appeared between 3 and 8 days in vitro (DIV), with GABAA receptor subunit clusters appearing first, followed by GAD-65 puncta, then functional synapses. The number of GABAergic synapses increased from 7 to 14 DIV, with a corresponding increase in frequency of mIPSCs. Moreover, these new GABAergic synapses formed on neuronal processes farther from the soma, contributing to decreased mIPSC amplitude and slowed mIPSC 19-90% rise time. The mIPSC decay quickened from 7 to 14 DIV, with a parallel change in the distribution of the alpha5 subunit from diffuse expression at 7 DIV to clustered expression at 14 DIV. These alpha5 clusters were mostly extrasynaptic. The alpha1 subunit was expressed as clusters in none of the neurons at 7 DIV, in 20% at 14 DIV, and in 80% at 21 DIV. Most of these alpha1 clusters were expressed at GABAergic synapses. In addition, puncta of GABA transporter 1 (GAT-1) were localized to GABAergic synapses at 14 DIV but were not expressed at 7 DIV. These studies demonstrate that mIPSCs appear after pre- and postsynaptic elements are in place. Furthermore, the process of maturation of GABAergic synapses involves increased synapse formation at distal processes, expression of new GABAA receptor subunits, and GAT-1 expression at synapses; these changes are reflected in altered frequency, kinetics, and drug sensitivity of mIPSCs. | | | 16498682
 |
Synaptic targeting of PSD-Zip45 (Homer 1c) and its involvement in the synaptic accumulation of F-actin.
Usui, Shinichi, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 278: 10619-28 (2003)
2003
Show Abstract
PSD-Zip45/Homer1c, which contains an enabled/VASP homology 1 (EVH1) domain and leucine zipper motifs, is a postsynaptic density (PSD) scaffold protein that interacts with metabotropic glutamate receptors and the shank family. We studied the molecular mechanism underlying the synaptic targeting of PSD-Zip45 in cultured hippocampal neurons. The EVH1 domain and the extreme C-terminal leucine zipper motif were molecular determinants for its synaptic targeting. The overexpression of the mutant of the EVH1 domain or deletion of the extreme C-terminal leucine zipper motif markedly suppressed the synaptic localization of endogenous shank but not PSD-95 or GKAP. In contrast, an overexpressed GKAP mutant lacking shank binding activity had no effect on the synaptic localization of shank. Actin depolymerization by latrunculin A reduced the synaptic localization of PSD-Zip45, shank, and F-actin but not of PSD-95 or GKAP. Overexpression of PSD-Zip45 enhanced the accumulation of synaptic F-actin. Additionally, overexpression of PSD-Zip45 and an isoform of shank induced synaptic enlargement in association with the further accumulation of synaptic F-actin. The EVH1 domain and extreme C-terminal leucine zipper motif of PSD-Zip45 were also critical for these events. Thus, these data suggest that the PSD-Zip45-shank and PSD-95-GKAP complexes form different synaptic compartments, and PSD-Zip45 alone or PSD-Zip45-shank is involved in the synaptic accumulation of F-actin. | Immunocytochemistry | | 12524440
 |
Analgesia and hyperalgesia from GABA-mediated modulation of the cerebral cortex.
Luc Jasmin, Samuel D Rabkin, Alberto Granato, Abdennacer Boudah, Peter T Ohara
Nature
424
316-20
2003
Show Abstract
It is known that pain perception can be altered by mood, attention and cognition, or by direct stimulation of the cerebral cortex, but we know little of the neural mechanisms underlying the cortical modulation of pain. One of the few cortical areas consistently activated by painful stimuli is the rostral agranular insular cortex (RAIC) where, as in other parts of the cortex, the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) robustly inhibits neuronal activity. Here we show that changes in GABA neurotransmission in the RAIC can raise or lower the pain threshold--producing analgesia or hyperalgesia, respectively--in freely moving rats. Locally increasing GABA, by using an enzyme inhibitor or gene transfer mediated by a viral vector, produces lasting analgesia by enhancing the descending inhibition of spinal nociceptive neurons. Selectively activating GABA(B)-receptor-bearing RAIC neurons produces hyperalgesia through projections to the amygdala, an area involved in pain and fear. Whereas most studies focus on the role of the cerebral cortex as the end point of nociceptive processing, we suggest that cerebral cortex activity can change the set-point of pain threshold in a top-down manner. | | | 12867983
 |