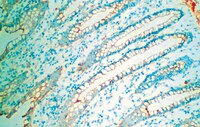
Long-term characterization of axon regeneration and matrix changes using multiple channel bridges for spinal cord regeneration.
Tuinstra, HM; Margul, DJ; Goodman, AG; Boehler, RM; Holland, SJ; Zelivyanskaya, ML; Cummings, BJ; Anderson, AJ; Shea, LD
Tissue engineering. Part A
20
1027-37
2014
Show Abstract
Spinal cord injury (SCI) results in loss of sensory and motor function below the level of injury and has limited available therapies. The host response to SCI is typified by limited endogenous repair, and biomaterial bridges offer the potential to alter the microenvironment to promote regeneration. Porous multiple channel bridges implanted into the injury provide stability to limit secondary damage and support cell infiltration that limits cavity formation. At the same time, the channels provide a path that physically directs axon growth across the injury. Using a rat spinal cord hemisection injury model, we investigated the dynamics of axon growth, myelination, and scar formation within and around the bridge in vivo for 6 months, at which time the bridge has fully degraded. Axons grew into and through the channels, and the density increased overtime, resulting in the greatest axon density at 6 months postimplantation, despite complete degradation of the bridge by that time point. Furthermore, the persistence of these axons contrasts with reports of axonal dieback in other models and is consistent with axon stability resulting from some degree of connectivity. Immunostaining of axons revealed both motor and sensory origins of the axons found in the channels of the bridge. Extensive myelination was observed throughout the bridge at 6 months, with centrally located and peripheral channels seemingly myelinated by oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells, respectively. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan deposition was restricted to the edges of the bridge, was greatest at 1 week, and significantly decreased by 6 weeks. The dynamics of collagen I and IV, laminin, and fibronectin deposition varied with time. These studies demonstrate that the bridge structure can support substantial long-term axon growth and myelination with limited scar formation. | Immunofluorescence | 24168314
 |
Phage-based molecular probes that discriminate force-induced structural states of fibronectin in vivo.
Cao, L; Zeller, MK; Fiore, VF; Strane, P; Bermudez, H; Barker, TH
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
109
7251-6
2011
Show Abstract
Applied forces and the biophysical nature of the cellular microenvironment play a central role in determining cellular behavior. Specifically, forces due to cell contraction are transmitted into structural ECM proteins and these forces are presumed to activate integrin "switches." The mechanism of such switches is thought to be the partial unfolding of integrin-binding domains within fibronectin (Fn). However, integrin switches remain largely hypothetical due to a dearth of evidence for their existence, and relevance, in vivo. By using phage display in combination with the controlled deposition and extension of Fn fibers, we report the discovery of peptide-based molecular probes capable of selectively discriminating Fn fibers under different strain states. Importantly, we show that the probes are functional in both in vitro and ex vivo tissue contexts. The development of such tools represents a critical step in establishing the relevance of theoretical mechanotransduction events within the cellular microenvironment. | | 22529344
 |
Development of an esophagus acellular matrix tissue scaffold.
Amit D Bhrany, Benjamin L Beckstead, Tess C Lang, D Gregory Farwell, Cecilia M Giachelli, Buddy D Ratner
Tissue engineering
12
319-30
2005
Show Abstract
A cell-extraction protocol yielding an esophagus acellular matrix (EAM) scaffold for use in tissue engineering of an esophagus, including hypotonic lysis, multiple detergent cell extraction steps, and nucleic acid digestion, was developed in a rat model. Histological techniques, burst pressure studies, in vitro esophageal epithelial cell seeding, and in vivo implantation were used to assess cell extraction, extracellular matrix (ECM) preservation, and biocompatibility. Microscopy demonstrated that cell extraction protocols using sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (0.5%, wt/vol) as a detergent resulted in cell-free EAM with retained ECM protein collagen, elastin, laminin, and fibronectin. Burst pressure studies indicated a loss of tensile strength in EAMs, but at intraluminal pressures that were unlikely to affect in vivo application. In vitro cell seeding studies exhibited epithelial cell proliferation with stratification similar to native esophagi after 11 days, and subcutaneously implanted EAMs displayed neovascularization and a minimal inflammatory response after 30 days of implantation. This study presents an esophagus acellular matrix tissue scaffold with preserved ECM proteins, biomechanical properties, and the ability to support esophageal cell proliferation to serve as the foundation for a tissue-engineered esophagus. | | 16548690
 |