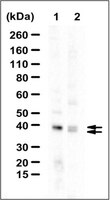
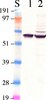
Association with endoplasmic reticulum promotes proteasomal degradation of GADD34 protein.
Zhou, W; Brush, MH; Choy, MS; Shenolikar, S
The Journal of biological chemistry
286
21687-96
2011
Show Abstract
Stress-induced endogenous and ectopically expressed GADD34 proteins were present both in the cytoplasm and in membranes, with their membrane association showing similar biochemical properties. Deletion of N-terminal sequences in GADD34-GFP proteins highlighted an amphipathic helix, whose hydrophobic surface, specifically valine 25 and leucine 29, mediated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) localization. Substitution of leucines for three arginines on the polar surface indicated that the same helix also mediated the association of GADD34 with mitochondria. Fluorescence protease protection and chemical modification of cysteines substituted in the membrane-binding domain pointed to a monotopic insertion of GADD34 into the outer layer of the ER membrane. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching showed that ER association retards the mobility of GADD34 in living cells. Both WT GADD34 and the mutant, V25R, effectively scaffolded the α-isoform of protein phosphatase-1 (PP1α) and enabled eIF2α dephosphorylation. However, the largely cytosolic V25R protein displayed a reduced rate of proteasomal degradation, and unlike WT GADD34, whose ectopic expression resulted in a dilated or distended ER, V25R did not modify ER morphology. These studies suggested that the association of with ER modulates intracellular trafficking and proteasomal degradation of GADD34, and in turn, its ability to modify ER morphology. | 21518769
 |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa vesicles associate with and are internalized by human lung epithelial cells.
Bauman, SJ; Kuehn, MJ
BMC microbiology
9
26
2009
Show Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the major pathogen associated with chronic and ultimately fatal lung infections in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF). To investigate how P. aeruginosa-derived vesicles may contribute to lung disease, we explored their ability to associate with human lung cells.Purified vesicles associated with lung cells and were internalized in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Vesicles from a CF isolate exhibited a 3- to 4-fold greater association with lung cells than vesicles from the lab strain PAO1. Vesicle internalization was temperature-dependent and was inhibited by hypertonic sucrose and cyclodextrins. Surface-bound vesicles rarely colocalized with clathrin. Internalized vesicles colocalized with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) marker, TRAPalpha, as well as with ER-localized pools of cholera toxin and transferrin. CF isolates of P. aeruginosa abundantly secrete PaAP (PA2939), an aminopeptidase that associates with the surface of vesicles. Vesicles from a PaAP knockout strain exhibited a 40% decrease in cell association. Likewise, vesicles from PAO1 overexpressing PaAP displayed a significant increase in cell association.These data reveal that PaAP promotes the association of vesicles with lung cells. Taken together, these results suggest that P. aeruginosa vesicles can interact with and be internalized by lung epithelial cells and contribute to the inflammatory response during infection. | 19192306
 |
A functional equivalent of endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi in axons for secretion of locally synthesized proteins.
Merianda, TT; Lin, AC; Lam, JS; Vuppalanchi, D; Willis, DE; Karin, N; Holt, CE; Twiss, JL
Molecular and cellular neurosciences
40
128-42
2009
Show Abstract
Subcellular localization of protein synthesis provides a means to regulate the protein composition in far reaches of a cell. This localized protein synthesis gives neuronal processes autonomy to rapidly respond to extracellular stimuli. Locally synthesized axonal proteins enable neurons to respond to guidance cues and can help to initiate regeneration after injury. Most studies of axonal mRNA translation have concentrated on cytoplasmic proteins. While ultrastructural studies suggest that axons do not have rough endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi apparatus, mRNAs for transmembrane and secreted proteins localize to axons. Here, we show that growing axons with protein synthetic activity contain ER and Golgi components needed for classical protein synthesis and secretion. Isolated axons have the capacity to traffic locally synthesized proteins into secretory pathways and inhibition of Golgi function attenuates translation-dependent axonal growth responses. Finally, the capacity for secreting locally synthesized proteins in axons appears to be increased by injury. | 19022387
 |
Partitioning and translation of mRNAs encoding soluble proteins on membrane-bound ribosomes.
Lerner, RS; Seiser, RM; Zheng, T; Lager, PJ; Reedy, MC; Keene, JD; Nicchitta, CV
RNA (New York, N.Y.)
9
1123-37
2003
Show Abstract
In eukaryotic cells, it is generally accepted that protein synthesis is compartmentalized; soluble proteins are synthesized on free ribosomes, whereas secretory and membrane proteins are synthesized on endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-bound ribosomes. The partitioning of mRNAs that accompanies such compartmentalization arises early in protein synthesis, when ribosomes engaged in the translation of mRNAs encoding signal-sequence-bearing proteins are targeted to the ER. In this report, we use multiple cell fractionation protocols, in combination with cDNA microarray, nuclease protection, and Northern blot analyses, to assess the distribution of mRNAs between free and ER-bound ribosomes. We find a broad representation of mRNAs encoding soluble proteins in the ER fraction, with a subset of such mRNAs displaying substantial ER partitioning. In addition, we present evidence that membrane-bound ribosomes engage in the translation of mRNAs encoding soluble proteins. Single-cell in situ hybridization analysis of the subcellular distribution of mRNAs encoding ER-localized and soluble proteins identify two overall patterns of mRNA distribution in the cell-endoplasmic reticular and cytosolic. However, both partitioning patterns include a distinct perinuclear component. These results identify previously unappreciated roles for membrane-bound ribosomes in the subcellular compartmentalization of protein synthesis and indicate possible functions for the perinuclear membrane domain in mRNA sorting in the cell. | 12923260
 |
The signal sequence receptor, unlike the signal recognition particle receptor, is not essential for protein translocation.
Migliaccio, G; Nicchitta, CV; Blobel, G
The Journal of cell biology
117
15-25
1992
Show Abstract
Detergent extracts of canine pancreas rough microsomal membranes were depleted of either the signal recognition particle receptor (SR), which mediates the signal recognition particle (SRP)-dependent targeting of the ribosome/nascent chain complex to the membrane, or the signal sequence receptor (SSR), which has been proposed to function as a membrane bound receptor for the newly targeted nascent chain and/or as a component of a multi-protein translocation complex responsible for transfer of the nascent chain across the membrane. Depletion of the two components was performed by chromatography of detergent extracts on immunoaffinity supports. Detergent extracts lacking either SR or SSR were reconstituted and assayed for activity with respect to SR dependent elongation arrest release, nascent chain targeting, ribosome binding, secretory precursor translocation, and membrane protein integration. Depletion of SR resulted in the loss of elongation arrest release activity, nascent chain targeting, secretory protein translocation, and membrane protein integration, although ribosome binding was unaffected. Full activity was restored by addition of immunoaffinity purified SR before reconstitution of the detergent extract. Surprisingly, depletion of SSR was without effect on any of the assayed activities, indicating that SSR is either not required for translocation or is one of a family of functionally redundant components. | 1313437
 |