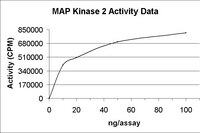
ERKs and p38 kinases mediate ultraviolet B-induced phosphorylation of histone H3 at serine 10.
Zhong, S P, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 275: 20980-4 (2000)
2000
Show Abstract
Histone H3 is the core protein of the nucleosome. Phosphorylation of H3 involves immediate early gene expression, chromatin remodeling, and chromosome condensation during mitosis. Very recently, Rsk2 or MSK1 kinase-mediated phosphorylation of H3 at serine 10 was reported. In the present study, we show that both ERKs and p38 kinase may mediate ultraviolet B-induced phosphorylation of H3 at serine 10. PD 98059, a MEK1 inhibitor, and SB 202190, a p38 kinase inhibitor, efficiently inhibited ultraviolet B-induced phosphorylation of H3. Phosphorylation of H3 was also inhibited in cells expressing dominant negative mutant (DNM) ERK2 and DNM p38 kinase. In contrast, no inhibition of H3 phosphorylation in Jnk1 or Jnk2 knockout cells (Jnk1(-/-) or Jnk2(-/-)) and cells expressing DNM JNK1 was observed. More importantly, incubation of active ERK2 or p38 kinase with H3 protein resulted in phosphorylation of H3 at serine 10 in vitro. These results suggest that ERK and p38 kinase are at least two important mediators of phosphorylation of H3 at serine 10. | Immunoblotting (Western) | 10806218
 |
Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors.
Davies, S P, et al.
Biochem. J., 351: 95-105 (2000)
2000
Show Abstract
The specificities of 28 commercially available compounds reported to be relatively selective inhibitors of particular serine/threonine-specific protein kinases have been examined against a large panel of protein kinases. The compounds KT 5720, Rottlerin and quercetin were found to inhibit many protein kinases, sometimes much more potently than their presumed targets, and conclusions drawn from their use in cell-based experiments are likely to be erroneous. Ro 318220 and related bisindoylmaleimides, as well as H89, HA1077 and Y 27632, were more selective inhibitors, but still inhibited two or more protein kinases with similar potency. LY 294002 was found to inhibit casein kinase-2 with similar potency to phosphoinositide (phosphatidylinositol) 3-kinase. The compounds with the most impressive selectivity profiles were KN62, PD 98059, U0126, PD 184352, rapamycin, wortmannin, SB 203580 and SB 202190. U0126 and PD 184352, like PD 98059, were found to block the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade in cell-based assays by preventing the activation of MAPK kinase (MKK1), and not by inhibiting MKK1 activity directly. Apart from rapamycin and PD 184352, even the most selective inhibitors affected at least one additional protein kinase. Our results demonstrate that the specificities of protein kinase inhibitors cannot be assessed simply by studying their effect on kinases that are closely related in primary structure. We propose guidelines for the use of protein kinase inhibitors in cell-based assays. | Kinase Assay | 10998351
 |
Identification of insulin-stimulated protein kinase-1 as the rabbit equivalent of rskmo-2. Identification of two threonines phosphorylated during activation by mitogen-activated protein kinase.
Sutherland, C, et al.
Eur. J. Biochem., 212: 581-8 (1993)
1993
Show Abstract
An improved procedure has been developed for the isolation of insulin-stimulated protein kinase-1 (ISPK-1), an S6 kinase-II homologue, by which 0.5 mg highly purified enzyme can be obtained within four days. The sequences of tryptic peptides from ISPK-1 (100 residues) revealed 100% identity with the predicted protein product of rskmo-2, a cDNA clone isolated from a mouse F2 cell line library [Alcorta, D. A., Crews, C. M., Sweet, L. J., Bankston, L., Jones, S. W. and Erikson, R. L. (1989) Mol. Cell. Biol. 9, 3850-3859], demonstrating that rskmo-2 encodes an S6 kinase-II. Two isoforms of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase (p42mapk and p44mapk) were the only ISPK-1-reactivating enzymes detected after Mono Q chromatography of extracts prepared from rabbit skeletal muscle or phaeochromocytoma 12 cells stimulated by nerve or epidermal growth factors. One of the residues on ISPK-1 phosphorylated by p42mapk was a threonine located nine residues N-terminal to the conserved Ala-Pro-Glu motif in the C-terminal protein kinase domain, an analogous location to phosphorylation sites essential for the activity of cAMP-dependent protein kinase, MAP kinase and p34cdc2. A further threonine located five residues N-terminal to the same Ala-Pro-Glu motif was also phosphorylated, probably via autophosphorylation catalysed by ISPK-1 itself. | | 8444194
 |