533572 Sigma-AldrichHECT Ligase Inhibitor, Heclin - Calbiochem
HECT Ligase Inhibitor, Heclin, is a cell-permeable reversible, broadly specific inhibitor of HECT ligases (IC₅₀ = 6.8, 6.3, 6.9 mM for Smurf2, Nedd4, and WWP, respectively).
More>> HECT Ligase Inhibitor, Heclin, is a cell-permeable reversible, broadly specific inhibitor of HECT ligases (IC₅₀ = 6.8, 6.3, 6.9 mM for Smurf2, Nedd4, and WWP, respectively). Less<<Synonyms: HECT Ligase Inhibitor, Compound III
Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| Empirical Formula |
|---|
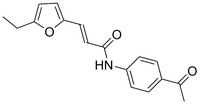
| C₁₇H₁₇NO₃ |
| References | |
|---|---|
| References | Mund, T., et al. 2014. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 111, 16736. |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Form | Off-white solid |
| Hill Formula | C₁₇H₁₇NO₃ |
| Chemical formula | C₁₇H₁₇NO₃ |
| Reversible | Y |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Applications |
|---|
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Primary Target | HECT ligases |
| Primary Target IC<sub>50</sub> | 6.8, 6.3 and 6.9 µ |
| Purity | ≥98% by HPLC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
|---|---|
| Cell permeable | Y |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Product Usage Statements |
|---|
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Packaged under inert gas | Packaged under inert gas |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | GTIN |
| 533572 | 0 |
Documentation
HECT Ligase Inhibitor, Heclin - Calbiochem SDS
| Title |
|---|
References
| Reference overview |
|---|
| Mund, T., et al. 2014. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 111, 16736. |