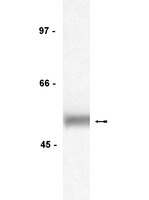
Association of SRC-related kinase Lyn with the interleukin-2 receptor and its role in maintaining constitutive phosphorylation of JAK/STAT in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-transformed T cells.
Shuh, M; Morse, BA; Heidecker, G; Derse, D
Journal of virology
85
4623-7
2010
Pokaż streszczenie
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infection and transformation are associated with an incremental switch in the expression of the Src-related protein tyrosine kinases Lck and Lyn. We examined the physical and functional interactions of Lyn with receptors and signal transduction proteins in HTLV-1-infected T cells. Lyn coimmunoprecipitates with the interleukin-2 beta receptor (IL-2Rβ) and JAK3 proteins; however, the association of Lyn with the IL-2Rβ and Lyn kinase activity was independent of IL-2 stimulation. Phosphorylation of Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) and signal transducers and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) proteins was reduced by treatment of cells with the Src kinase inhibitor PP2 or by ectopic expression of a dominant negative Lyn kinase protein. | Western Blotting | 21345943
 |
The differential expression of LCK and BAFF-receptor and their role in apoptosis in human lymphomas.
Jennifer C Paterson, Sara Tedoldi, Andrew Craxton, Margaret Jones, Martin-Leo Hansmann, Graham Collins, Helen Roberton, Yasodha Natkunam, Stefano Pileri, Elias Campo, Edward A Clark, David Y Mason, Teresa Marafioti
Haematologica
91
772-80
2005
Pokaż streszczenie
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: We explored the expression of LCK and BAFF-R (B-cell activating factor receptor) both of which are known to play a role in signaling and apoptosis, in routine tissue biopsies. It was hypothesized that their expression patterns might yield information on apoptosis as it occurs in normal and reactive lymphoid cells, and also be of value for the detection of lymphoma subtypes. DESIGN AND METHODS: Both molecules were studied in paraffin-embedded tissue sections and cell lines by immunoperoxidase staining, and were also studied by western blotting. Human tonsillar B-cell subsets were analyzed by flow cytometry for LCK expression. RESULTS: LCK was detected for the first time in germinal centers and, at lower levels, in mantle zone B cells. The presence of LCK in B cells was confirmed by western blotting. Cross-linking surface IgM reduced LCK expression whereas cross-linking surface CD40 appeared to have the opposite effect. BAFF-R was present on mantle zone B cells but absent or weakly expressed in germinal center cells. Most lymphomas of germinal center origin (e.g. follicular lymphoma) and also many mantle cell lymphomas, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and most T-cell neoplasms expressed LCK. In contrast, BAFF-R was expressed in a variety of B-cell lymphomas, but often absent in grade 3 follicular lymphomas and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL). Both LCK-positive and BAFF-R-positive DLBCL tended to be of germinal-center phenotype. INTERPRETATION AND CONCLUSIONS: The reciprocal expression pattern of LCK and BAFF-R in germinal center and mantle zone B cells may reflect their opposing roles in apoptosis. Their detection in lymphoma tissue biopsies may therefore be of clinical relevance in predicting response to treatment. | | 16769579
 |
The Lck tyrosine kinase is expressed in brain neurons.
Omri, B, et al.
J. Neurochem., 67: 1360-4 (1996)
1996
Pokaż streszczenie
The lck gene product, p56lck, is a member of the src-related family of protein tyrosine kinases. It is known as lymphocyte specific and involved in thymocyte development and in the immune response mediated by the T cell receptor. We report that the lck gene is also expressed in adult mouse CNS and that brain p56lck is similar to the thymus protein. In situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry show that the lck gene is expressed in neurons throughout the brain in distinct regions, including hippocampus and cerebellum. In primary cultures from fetal mouse brain, neuronal cells are immunoreactive to Lck antiserum. This suggests that the lck gene product might be involved in a new signal transduction pathway in mouse brain. | | 8858916
 |