The Forkhead Transcription Factor FOXP2 Is Required for Regulation of p21WAF1/CIP1 in 143B Osteosarcoma Cell Growth Arrest.
Gascoyne, DM; Spearman, H; Lyne, L; Puliyadi, R; Perez-Alcantara, M; Coulton, L; Fisher, SE; Croucher, PI; Banham, AH
PloS one
10
e0128513
2015
Pokaż streszczenie
Mutations of the forkhead transcription factor FOXP2 gene have been implicated in inherited speech-and-language disorders, and specific Foxp2 expression patterns in neuronal populations and neuronal phenotypes arising from Foxp2 disruption have been described. However, molecular functions of FOXP2 are not completely understood. Here we report a requirement for FOXP2 in growth arrest of the osteosarcoma cell line 143B. We observed endogenous expression of this transcription factor both transiently in normally developing murine osteoblasts and constitutively in human SAOS-2 osteosarcoma cells blocked in early osteoblast development. Critically, we demonstrate that in 143B osteosarcoma cells with minimal endogenous expression, FOXP2 induced by growth arrest is required for up-regulation of p21WAF1/CIP1. Upon growth factor withdrawal, FOXP2 induction occurs rapidly and precedes p21WAF1/CIP1 activation. Additionally, FOXP2 expression could be induced by MAPK pathway inhibition in growth-arrested 143B cells, but not in traditional cell line models of osteoblast differentiation (MG-63, C2C12, MC3T3-E1). Our data are consistent with a model in which transient upregulation of Foxp2 in pre-osteoblast mesenchymal cells regulates a p21-dependent growth arrest checkpoint, which may have implications for normal mesenchymal and osteosarcoma biology. | 26034982
 |
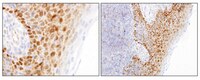
Aberrant expression of the neuronal transcription factor FOXP2 in neoplastic plasma cells.
Campbell, Andrew J, et al.
Br. J. Haematol., 149: 221-30 (2010)
2009
Pokaż streszczenie
FOXP2 mutation causes a severe inherited speech and language defect, while the related transcription factors FOXP1, FOXP3 and FOXP4 are implicated in cancer. FOXP2 mRNA and protein expression were characterised in normal human tissues, haematological cell lines and multiple myeloma (MM) patients' samples. FOXP2 mRNA and protein were absent in mononuclear cells from different anatomical sites, lineages and stages of differentiation. However, FOXP2 mRNA and protein was detected in several lymphoma (8/20) and all MM-derived cell lines (n = 4). FOXP2 mRNA was expressed in bone marrow samples from 96% of MM patients (24/25), 66.7% of patients with the pre-neoplastic plasma cell proliferation monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) (6/9), but not in reactive plasma cells. The frequency of FOXP2 protein expression in CD138(+) plasma cells was significantly higher in MGUS (P = 0.0005; mean 46.4%) and MM patients (P < or = 0.0001; mean 57.3%) than in reactive marrows (mean 2.5%). FOXP2 (>10% nuclear positivity) was detectable in 90.2% of MM (55/61) and 90.9% of MGUS (10/11) patients, showing more frequent expression than CD56 and labelling 75% of CD56-negative MM (9/12). FOXP2 represents the first transcription factor whose expression consistently differentiates normal and abnormal plasma cells and FOXP2 target genes are implicated in MM pathogenesis. | 20096010
 |