480030 Sigma-AldrichNEMO-Binding Domain Binding Peptide, Cell-Permeable, Negative Control - Calbiochem
A cell-permeable Antennapedia-NBD mutated fusion peptide analog of NEMO-Binding Domain Binding Peptide that serves as a negative control.
More>> A cell-permeable Antennapedia-NBD mutated fusion peptide analog of NEMO-Binding Domain Binding Peptide that serves as a negative control. Less<<Synonyms: DRQIKIWFQNRRMKWKK-TALDASALQTE, NBD-Binding Peptide, Cell-Permeable, Negative Control
Recommended Products
-

407601 Sigma-Aldrich Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated-Kinase-1/4 Inhibitor - CAS 509093-47-4 - Calbiochem -
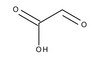
804107 Sigma-Aldrich Glyoxylic acid monohydrate -
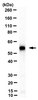
MABE1057 Sigma-Aldrich Anti-ADA3 Antibody, clone 5C9/C8 -

MFGL10SF3 Millipore Gamma sterilized Millipak® Final Fill 100 Filter Unit 0.22 µm 3/4 in. TC/TC -

454454-50MG Sigma-Aldrich Methoxysuccinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Val-p-nitroanilide - CAS 70967-90-7 - Calbiochem -

F1235-BC Sigma-Aldrich RPMI 1640 Liquid Medium with 20 mM HEPES -
 Antibody[209787-ALL].jpg)
MABS2160-25UG Sigma-Aldrich Anti-NARC-1 (PCSK9) Antibody, clone 13D3 -

5711-100GM Sigma-Aldrich Streptomycin Sulfate, Streptomyces sp. - CAS 3810-74-0 - Calbiochem -

391335-100GM Millipore BIS-Tris, ULTROL® Grade - CAS 6976-37-0 - Calbiochem
Overview
Key Spec Table
| Empirical Formula |
|---|
| C₁₅₄H₂₄₉N₄₇O₄₂S |
Products
| Catalogue Number | Packaging | Qty/Pack | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 480030-500UG | Plastic ampoule | 500 μg |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Overview | A cell-permeable Antennapedia-NBD mutated (Trp739 and Trp741 replaced with Ala) fusion peptide analog of NEMO-Binding Domain Binding Peptide (Cat. No. 480025) that serves as a negative control. Shown to be defective in binding to NEMO. Does not affect the TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of c-Jun and DNA binding of the transcription factor Oct-1. |
| Catalogue Number | 480030 |
| Brand Family | Calbiochem® |
| Synonyms | DRQIKIWFQNRRMKWKK-TALDASALQTE, NBD-Binding Peptide, Cell-Permeable, Negative Control |
| References | |
|---|---|
| References | Jimi, E., et al. 2004. Nat. Med., 10, 617. May, M.J., et al. 2000. Science 289, 1550. |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| ATP Competitive | N |
| Form | Lyophilized off-white solid |
| Formulation | Supplied as a trifluoroacetate salt. |
| Hill Formula | C₁₅₄H₂₄₉N₄₇O₄₂S |
| Chemical formula | C₁₅₄H₂₄₉N₄₇O₄₂S |
| Hygroscopic | Hygroscopic |
| Reversible | N |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Primary Target | Negative control defective in binding to NEMO |
| Purity | ≥95% by HPLC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
|---|---|
| Cell permeable | Y |
| Peptide Sequence | H₂N-Asp-Arg-Gln-Ile-Lys-Ile-Trp-Phe-Gln-Asn-Arg-Arg-Met-Lys-Trp-Lys-Lys-Thr-Ala-Leu-Asp-Ala-Ser-Ala-Leu-Gln-Thr-Glu-OH |
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Packaged under inert gas | Packaged under inert gas |
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | GTIN |
| 480030-500UG | 04055977201857 |







