Ablation of PRMT6 reveals a role as a negative transcriptional regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor.
Neault, M; Mallette, FA; Vogel, G; Michaud-Levesque, J; Richard, S
Nucleic acids research
40
9513-21
2012
Show Abstract
Arginine methylation of histones is a well-known regulator of gene expression. Protein arginine methyltransferase 6 (PRMT6) has been shown to function as a transcriptional repressor by methylating the histone H3 arginine 2 [H3R2(me2a)] repressive mark; however, few targets are known. To define the physiological role of PRMT6 and to identify its targets, we generated PRMT6(-/-) mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs). We observed that early passage PRMT6(-/-) MEFs had growth defects and exhibited the hallmarks of cellular senescence. PRMT6(-/-) MEFs displayed high transcriptional levels of p53 and its targets, p21 and PML. Generation of PRMT6(-/-); p53(-/-) MEFs prevented the premature senescence, suggesting that the induction of senescence is p53-dependent. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, we observed an enrichment of PRMT6 and H3R2(me2a) within the upstream region of Trp53. The PRMT6 association and the H3R2(me2a) mark were lost in PRMT6(-/-) MEFs and an increase in the H3K4(me3) activator mark was observed. Our findings define a new regulator of p53 transcriptional regulation and define a role for PRMT6 and arginine methylation in cellular senescence. | Western Blotting | | 22904064
 |
The HPV E6 oncoprotein targets histone methyltransferases for modulating specific gene transcription.
Hsu, CH; Peng, KL; Jhang, HC; Lin, CH; Wu, SY; Chiang, CM; Lee, SC; Yu, WC; Juan, LJ
Oncogene
31
2335-49
2012
Show Abstract
Expression of viral proteins causes important epigenetic changes leading to abnormal cell growth. Whether viral proteins directly target histone methyltransferases (HMTs), a key family enzyme for epigenetic regulation, and modulate their enzymatic activities remains elusive. Here we show that the E6 proteins of both low-risk and high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) interact with three coactivator HMTs, CARM1, PRMT1 and SET7, and downregulate their enzymatic activities in vitro and in HPV-transformed HeLa cells. Furthermore, these three HMTs are required for E6 to attenuate p53 transactivation function. Mechanistically, E6 hampers CARM1- and PRMT1-catalyzed histone methylation at p53-responsive promoters, and suppresses the binding of p53 to chromatinized DNA independently of E6-mediated p53 degradation. p53 pre-methylated at lysine-372 (p53K372 mono-methylation) by SET7 protects p53 from E6-induced degradation. Consistently, E6 downregulates p53K372 mono-methylation and thus reduces p53 protein stability. As a result of the E6-mediated inhibition of HMT activity, expression of p53 downstream genes is suppressed. Together, our results not only reveal a clever approach for the virus to interfere with p53 function, but also demonstrate the modulation of HMT activity as a novel mechanism of epigenetic regulation by a viral oncoprotein. | Western Blotting | | 21963854
 |
Protein arginine methyltransferase 7 regulates cellular response to DNA damage by methylating promoter histones H2A and H4 of the polymerase δ catalytic subunit gene, POLD1.
Karkhanis, V; Wang, L; Tae, S; Hu, YJ; Imbalzano, AN; Sif, S
The Journal of biological chemistry
287
29801-14
2012
Show Abstract
Covalent modification of histones by protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) impacts genome organization and gene expression. In this report, we show that PRMT7 interacts with the BRG1-based hSWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex and specifically methylates histone H2A Arg-3 (H2AR3) and histone H4 Arg-3 (H4R3). To elucidate the biological function of PRMT7, we knocked down its expression in NIH 3T3 cells and analyzed global gene expression. Our findings show that PRMT7 negatively regulates expression of genes involved in DNA repair, including ALKBH5, APEX2, POLD1, and POLD2. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) revealed that PRMT7 and dimethylated H2AR3 and H4R3 are enriched at target DNA repair genes in parental cells, whereas PRMT7 knockdown caused a significant decrease in PRMT7 recruitment and H2AR3/H4R3 methylation. Decreased PRMT7 expression also resulted in derepression of target DNA repair genes and enhanced cell resistance to DNA-damaging agents. Furthermore, we show that BRG1 co-localizes with PRMT7 on target promoters and that expression of a catalytically inactive form of BRG1 results in derepression of PRMT7 target DNA repair genes. Remarkably, reducing expression of individual PRMT7 target DNA repair genes showed that only the catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase, POLD1, was able to resensitize PRMT7 knock-down cells to DNA-damaging agents. These results provide evidence for the important role played by PRMT7 in epigenetic regulation of DNA repair genes and cellular response to DNA damage. | | | 22761421
 |
The expression of myogenic microRNAs indirectly requires protein arginine methyltransferase (Prmt)5 but directly requires Prmt4.
Mallappa, C; Hu, YJ; Shamulailatpam, P; Tae, S; Sif, S; Imbalzano, AN
Nucleic acids research
39
1243-55
2011
Show Abstract
Myogenic microRNAs are important regulators of muscle development and differentiation. To better understand the roles of chromatin-modifying and remodeling enzymes in the activation of myogenic microRNA expression, we have functionally analyzed two different protein arginine methyltransferases, Prmt5 and Prmt4, both of which have previously been implicated in the regulation of myogenic mRNA expression. Both Prmts are required for myogenic microRNA induction during differentiation. Prmt5 is indirectly required due to the necessity of Prmt5 for expression of the transcriptional regulator, myogenin, as ectopic expression of myogenin eliminates Prmt5 dependency. By contrast, Prmt4 binds to the upstream regulatory regions of myogenic microRNAs and is required for dimethylation of the Prmt4 substrate, H3R17, at microRNA regulatory sequences. Deletion of Prmt4 does not alter MyoD binding at myogenic microRNA regulatory sequences but prevents the binding of both myogenin and the Brg1 ATPase that catalyzes SWI/SNF-dependent chromatin remodeling, resulting in an inhibition of microRNA expression. | Western Blotting | | 20947566
 |
HuD interacts with survival motor neuron protein and can rescue spinal muscular atrophy-like neuronal defects.
Hubers, L; Valderrama-Carvajal, H; Laframboise, J; Timbers, J; Sanchez, G; Côté, J
Human molecular genetics
20
553-79
2011
Show Abstract
Spinal muscular atrophy is an autosomal-recessive neuromuscular disease caused by disruption of the survival of motor neuron (SMN) gene, which promotes cytoplasmic assembly of the splicing core machinery. It remains unclear how a deficiency in SMN results in a disorder leading to selective degeneration of lower motor neurons. We report here that SMN interacts with RNA-binding protein HuD in neurites of motorneuron-derived MN-1 cells. This interaction is mediated through the Tudor domain of SMN and, importantly, naturally occurring Tudor mutations found in patients with severe spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) completely abrogate the interaction, underscoring its relevance to the disease process. We also characterized a regulatory pathway involving coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 (CARM1) and HuD. Specifically, we show that CARM1 expression is rapidly downregulated, at the protein level, following induction of differentiation through retinoid and neurotrophic signaling. Using purified proteins, we demonstrate that methylation of HuD by CARM1 reduces its interaction with the p21(cip1/waf1) mRNA, showing that CARM1 can directly influence RNA-binding activity. We further demonstrate that this CARM1-dependent regulatory switch mainly controls the activity of HuD in promoting cell-cycle exit, whereas the interaction between HuD and SMN is required for proper recruitment of HuD and its mRNA targets in neuronal RNA granules. Finally, we were able to rescue SMA-like defects in a hypomorphic Smn knockdown MN-1 cell line through overexpression of HuD. Together, these findings extend our understanding of specific role(s) of SMN in motor neurons and provide crucial insights into potential new avenues for SMA therapeutic strategies. | | | 21088113
 |
Carbon monoxide stimulates global protein methylation via its inhibitory action on cystathionine β-synthase.
Yamamoto T, Takano N, Ishiwata K, Suematsu M
J Clin Biochem Nutr
48
96-100. Epub 2010 Dec 28.
2011
Show Abstract
Although carbon monoxide derived from heme oxygenase has been reported to exert diverse biological actions in mammals, macromolecules responsible for its direct reception and functional outcomes of the gas binding remain largely unknown. Based on our previous results in vivo suggesting carbon monoxide serves as an inhibitor of cystathionine β-synthase that rate-limits transsulfuration pathway for generation of hydrogen sulfide, we have herein hypothesized that the gas might serve as a regulator of protein methylation through accelerating turnover of remethylation cycle residing at the upstream of the enzyme. Metabolomic analysis in human monoblastic leukemia U937 cells in culture revealed that application of carbon monoxide-releasing molecules caused increases in methionine and S-adenosylmethionine and a decrease in cystathionine in the cells, suggesting the cystathionine β-synthase inhibition by carbon monoxide. Under these circumstances, the cells exhibited global protein arginine methylation: this event was also reproduced by the cell treatment with hemin, a heme oxygenase-1 inducer. The protein arginine methylation elicited by carbon monoxide was attenuated by knocking down cystathionine β-synthase with its small interfering RNA or by blocking S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase with adenosine dialdehyde, suggesting remethylation cycling is necessary to trigger the methylation processing. Furthermore, proteins undergoing the carbon monoxide-induced arginine methylation involved histone H3 proteins, suggesting chromatin modification by the gas. Collectively with our studies in vivo showing its inhibitory action on endogenous hydrogen sulfide production, the current results suggest that not only inhibition of transsulfuration pathway for H(2)S generation but also activation of protein methylation accounts for notable biological actions of carbon monoxide via the cystathionine β-synthase inhibition. Full Text Article | | | 21297920
 |
Ordered transcriptional factor recruitment and epigenetic regulation of tnf-alpha in necrotizing acute pancreatitis.
Sandoval J, Pereda J, Rodriguez JL, Escobar J, Hidalgo J, Joosten LA, Franco L, Sastre J, López-Rodas G
Cell Mol Life Sci
67
1687-97. Epub 2010 Feb 4.
2010
Show Abstract
Tauhe expression of the critical initiator cytokine TNF-alpha was strongly upregulated in vivo in acute necrotic pancreatitis (AP) in rodents and in vitro in TNF-alpha activated acinar AR42J cells. Upregulation of tnf-alpha, inos, icam-1 and il-6 occurred both in TNF-alpha receptor 1 and 2 knock-out mice, but not in TNF-alpha knock-out mice, in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis showed that transcriptional factors (ELK-1, SP1, NF-kappaB and EGR-1) and chromatin modification complexes (HDAC1, HDAC2, GCN5, PCAF and CBP) were recruited and/or released from the promoter in a strictly ordered mechanism. Activation of tnf-alpha gene was also accompanied by an ordered increased level of histone H3K9, H3K14 and H3K18-acetylation and H3K4 methylation, as well as H4K5 acetylation. A better knowledge of the molecular mechanisms that control tnf-alpha gene regulation will provide deeper understanding of the initiation and development of the inflammatory processes occurring in acute pancreatitis triggered by TNF-alpha cytokine. | | | 20130956
 |
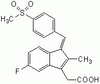
Effects of a novel arginine methyltransferase inhibitor on T-helper cell cytokine production.
Bonham, K; Hemmers, S; Lim, YH; Hill, DM; Finn, MG; Mowen, KA
The FEBS journal
277
2096-108
2010
Show Abstract
The protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) family of enzymes catalyzes the transfer of methyl groups from S-adenosylmethionine to the guanidino nitrogen atom of peptidylarginine to form monomethylarginine or dimethylarginine. We created several less polar analogs of the specific PRMT inhibitor arginine methylation inhibitor-1, and one such compound was found to have improved PRMT inhibitory activity over the parent molecule. The newly identified PRMT inhibitor modulated T-helper-cell function and thus may serve as a lead for further inhibitors useful for the treatment of immune-mediated disease. Full Text Article | | | 20345902
 |
Cell-type selective chromatin remodeling defines the active subset of FOXA1-bound enhancers.
Eeckhoute, J; Lupien, M; Meyer, CA; Verzi, MP; Shivdasani, RA; Liu, XS; Brown, M
Genome research
19
372-80
2009
Show Abstract
Selective activity of a specific set of enhancers defines tissue-specific gene transcription. The pioneer factor FOXA1 has been shown to induce functional enhancer competency through chromatin openings. We have previously found that FOXA1 is recruited to thousands of regions across the genome of a given cell type. Here, we monitored the chromatin structure at FOXA1 binding sites on a chromosome-wide scale using formaldehyde assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE). Surprisingly, we find that a significant fraction of FOXA1-bound sites have a relatively closed chromatin conformation linked to a shift of the epigenetic signature toward repressive histone marks. Importantly, these sites are not correlated with gene expression in a given cell type suggesting that FOXA1 is required, but not sufficient, for the functional activity of bound enhancers. Interestingly, we find that a significant proportion of the inactive FOXA1-bound regulatory sites in one cell type are actually functional in another cellular context. We found that at least half of the FOXA1 binding sites from a given cell type are shared with another cell lineage. Mechanisms that restrict the activity of shared FOXA1-bound enhancers likely play a significant role in defining the cell-type-specific functions of FOXA1. Full Text Article | | | 19129543
 |
Coactivator function defines the active estrogen receptor alpha cistrome.
Lupien, M; Eeckhoute, J; Meyer, CA; Krum, SA; Rhodes, DR; Liu, XS; Brown, M
Molecular and cellular biology
29
3413-23
2009
Show Abstract
Proper activation of transcriptional networks in complex organisms is central to the response to stimuli. We demonstrate that the selective activation of a subset of the estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) cistrome in MCF7 breast cancer cells provides specificity to the estradiol (E2) response. ERalpha-specific enhancers that are subject to E2-induced coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 (CARM1) action are critical to E2-stimulated gene expression. This is true for both FoxA1-dependent and independent enhancers. In contrast, a subset of E2-suppressed genes are controlled by FoxA1-independent ERalpha binding sites. Nonetheless, these are sites of E2-induced CARM1 activity. In addition, the MCF7 RNA polymerase II cistrome reveals preferential occupancy of E2-regulated promoters prior to stimulation. Interestingly, E2-suppressed genes tend to lie in otherwise silent genomic regions. Together, our results suggest that the transcriptional response to E2 in breast cancer cells is dependent on the interplay between polymerase II pre-occupied promoters and the subset of the ERalpha cistrome associated with coactivation. Full Text Article | | | 19364822
 |