Anthracycline-containing chemotherapy causes long-term impairment of mitochondrial respiration and increased reactive oxygen species release in skeletal muscle.
Gouspillou, G; Scheede-Bergdahl, C; Spendiff, S; Vuda, M; Meehan, B; Mlynarski, H; Archer-Lahlou, E; Sgarioto, N; Purves-Smith, FM; Konokhova, Y; Rak, J; Chevalier, S; Taivassalo, T; Hepple, RT; Jagoe, RT
Scientific reports
5
8717
2015
Show Abstract
Anticancer treatments for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) are highly effective but are now implicated in causing impaired muscle function in long-term survivors. However, no comprehensive assessment of skeletal muscle mitochondrial functions in long-term survivors has been performed and the presence of persistent chemotherapy-induced skeletal muscle mitochondrial dysfunction remains a strong possibility. Non-tumour-bearing mice were treated with two drugs that have been used frequently in ALL treatment (doxorubicin and dexamethasone) for up to 4 cycles at 3-week intervals and euthanized 3 months after the 4th cycle. Treated animals had impaired growth and lower muscle mass as well as reduced mitochondrial respiration and increased reactive oxygen species production per unit oxygen consumption. Mitochondrial DNA content and protein levels of key mitochondrial membrane proteins and markers of mitochondrial biogenesis were unchanged, but protein levels of Parkin were reduced. This suggests a novel pattern of chemotherapy-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle that persists because of an acquired defect in mitophagy signaling. The results could explain the observed functional impairments in adult survivors of childhood ALL and may also be relevant to long-term survivors of other cancers treated with similar regimes. | 25732599
 |
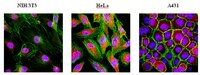
A genome-wide screen identifies conserved protein hubs required for cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion.
Toret, CP; D'Ambrosio, MV; Vale, RD; Simon, MA; Nelson, WJ
The Journal of cell biology
204
265-79
2014
Show Abstract
Cadherins and associated catenins provide an important structural interface between neighboring cells, the actin cytoskeleton, and intracellular signaling pathways in a variety of cell types throughout the Metazoa. However, the full inventory of the proteins and pathways required for cadherin-mediated adhesion has not been established. To this end, we completed a genome-wide (~14,000 genes) ribonucleic acid interference (RNAi) screen that targeted Ca(2+)-dependent adhesion in DE-cadherin-expressing Drosophila melanogaster S2 cells in suspension culture. This novel screen eliminated Ca(2+)-independent cell-cell adhesion, integrin-based adhesion, cell spreading, and cell migration. We identified 17 interconnected regulatory hubs, based on protein functions and protein-protein interactions that regulate the levels of the core cadherin-catenin complex and coordinate cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. Representative proteins from these hubs were analyzed further in Drosophila oogenesis, using targeted germline RNAi, and adhesion was analyzed in Madin-Darby canine kidney mammalian epithelial cell-cell adhesion. These experiments reveal roles for a diversity of cellular pathways that are required for cadherin function in Metazoa, including cytoskeleton organization, cell-substrate interactions, and nuclear and cytoplasmic signaling. | 24446484
 |
Systematic survey of deubiquitinase localization identifies USP21 as a regulator of centrosome- and microtubule-associated functions.
Urbé, S; Liu, H; Hayes, SD; Heride, C; Rigden, DJ; Clague, MJ
Mol Biol Cell
23
1095-103
2012
Show Abstract
Ubiquitination is a reversible modification that influences a broad range of physiological processes. There are approximately 90 deubiquitinases (DUBs) encoded in the human genome, of which 79 are predicted to have catalytic activity. We tagged 66 DUBs with green fluorescent protein and systematically surveyed their subcellular distribution, identifying enzymes specific to the nucleus, plasma membrane, and secretory and endocytic pathways. USP21 is unique in showing clear association with both centrosomes and microtubules. Using an in vitro assay, we show that microtubule binding is direct and identify a novel microtubule-binding motif encompassed within amino acids 59-75 of the N-terminus of USP21. Our functional studies indicate a key role for USP21 in the governance of microtubule- and centrosome-associated physiological processes: Depletion of USP21 in A549 cells compromises the reestablishment of a radial array of microtubules during recovery from cold-induced depolymerization and also reduces the probability of primary cilium formation, whereas USP21 knockdown in PC12 cells inhibits nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth. | 22298430
 |
Regulation of cell death in human fetal and adult ovaries--role of Bok and Bcl-X(L).
Minna Jääskeläinen,Anni Nieminen,Reeta-Maria Pökkylä,Marjut Kauppinen,Annikki Liakka,Markku Heikinheimo,Tommi E Vaskivuo,Juha Klefström,Juha S Tapanainen
Molecular and cellular endocrinology
330
2010
Show Abstract
Of eight million oocytes formed in fetal ovaries, only 400 are ovulated and the rest are degraded via apoptosis. Studies in rodents suggest an important role for Bok and Bcl-X(L) in ovarian apoptosis, but their expression patterns and roles in human ovaries are not well known. Protein expression of Bok and Bcl-X(L) as well as the death pathway effectors TNF and caspase-3 were determined in an important collection of samples consisting of human fetal and adult ovaries. A penetrant expression of Bok, Bcl-X(L), TNF and full length and cleaved caspase-3 were characterized in fetal ovaries, with specific patterns in oocytes and pre-granulosa/granulosa cells. Bok and Bcl-X(L) were detected also in adult ovaries. Lentiviral shRNA delivery demonstrated that loss of Bok markedly reduces vulnerability to apoptosis and, conversely, loss of Bcl-X(L) increases apoptosis in human granulosa tumour cell line. The results suggest important roles for Bok and Bcl-X(L) in human ovarian development, follicle maturation and apoptosis. | 20673843
 |
Elevated levels of NR2A and PSD-95 in the lateral amygdala in depression.
Beata Karolewicz,Katalin Szebeni,Tempestt Gilmore,Dorota Maciag,Craig A Stockmeier,Gregory A Ordway
The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology / official scientific journal of the Collegium Internationale Neuropsychopharmacologicum (CINP)
12
2009
Show Abstract
Compelling evidence suggests that major depression is associated with dysfunction of the brain glutamatergic transmission, and that the glutamatergic N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor plays a role in antidepressant activity. Recent post-mortem studies demonstrate that depression is associated with altered concentrations of proteins associated with NMDA receptor signalling in the brain. The present study investigated glutamate signalling proteins in the amygdala from depressed subjects, given strong evidence for amygdala pathology in depression. Lateral amygdala samples were obtained from 13-14 pairs of age- sex-, and post-mortem-interval-matched depressed and psychiatrically healthy control subjects. Concentrations of NR1 and NR2A subunits of the NMDA receptor, as well as NMDA receptor-associated proteins such as post-synaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95) and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) were measured by Western immunoblotting. Additionally, levels of enzymes involved in glutamate metabolism, including glutamine synthetase and glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD-67), were measured in the same amygdala samples. NR2A protein levels were markedly and significantly elevated (+115%, p=0.03) in depressed subjects compared to controls. Interestingly, PSD-95 levels were also highly elevated (+128%, p=0.01) in the same depressed subjects relative to controls. Amounts of NR1, nNOS, glutamine synthetase, and GAD-67 were unchanged. Increased levels of NR2A and PSD-95 suggest that glutamate signalling at the NMDA receptor in the amygdala is disrupted in depression. Full Text Article | 18570704
 |