205546 Sigma-AldrichCaffeic Acid - CAS 331-39-5 - Calbiochem
A natural dietary compound reported to have anti-carcinogenic and anti-inflammatory properties.
More>> A natural dietary compound reported to have anti-carcinogenic and anti-inflammatory properties. Less<<Synonyms: 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic Acid
Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| CAS # | Empirical Formula |
|---|---|
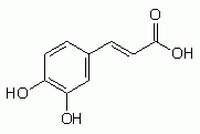
| 331-39-5 | C₉H₈O₄ |
Products
| Catalogue Number | Packaging | Qty/Pack | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 205546-500MG | Plastic ampoule | 500 mg |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| CAS number | 331-39-5 |
| ATP Competitive | N |
| Form | Tan crystalline solid |
| Hill Formula | C₉H₈O₄ |
| Chemical formula | C₉H₈O₄ |
| Reversible | N |
| Structure formula Image | |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Applications |
|---|
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Primary Target | 5-lipoxygenase |
| Primary Target IC<sub>50</sub> | 3.7 µM against 5-lipoxygenase |
| Purity | ≥95% by HPLC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
|---|---|
| Cell permeable | Y |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS | |
|---|---|
| RTECS | GD8950000 |
| Safety Information | |
|---|---|
| R Phrase | R: 40 Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect. |
| S Phrase | S: 36/37 Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves. |
| Product Usage Statements |
|---|
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Packaged under inert gas | Packaged under inert gas |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | GTIN |
| 205546-500MG | 04055977203134 |
Documentation
Caffeic Acid - CAS 331-39-5 - Calbiochem SDS
| Title |
|---|
Caffeic Acid - CAS 331-39-5 - Calbiochem Certificates of Analysis
| Title | Lot Number |
|---|---|
| 205546 |
References
| Reference overview |
|---|
| Yamanaka, N., et al. 1997. FEBS Lett. 405, 186. Chan, W.S., et al. 1995. Anticancer Res. 15, 703. Ploemen, J.H., et al. 1993. Food Chem. Toxicol. 31, 475. Koshihara, Y., et al. 1984. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 792, 92. |