495609 Sigma-AldrichInSolution™ Okadaic Acid, Prorocentrum sp. - Calbiochem
InSolution™ Okadaic Acid, Prorocentrum sp. CAS 78111-17-8, is a 250 µM solution of Okadaic Acid in DMSO. Potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 (IC50 = 10-15 nM) and 2A (IC50 = 0.1 nM).
More>> InSolution™ Okadaic Acid, Prorocentrum sp. CAS 78111-17-8, is a 250 µM solution of Okadaic Acid in DMSO. Potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 (IC50 = 10-15 nM) and 2A (IC50 = 0.1 nM). Less<<Recommended Products
Overview
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Key Spec Table
| Empirical Formula |
|---|
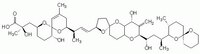
| C₄₄H₆₈O₁₃ |
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | 495609 |
| Brand Family | Calbiochem® |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| ATP Competitive | N |
| Form | Liquid |
| Formulation | A 250 µM (25 µg/124 µl) solution of Okadaic Acid, (Cat. No. 495604) in DMSO. |
| Hill Formula | C₄₄H₆₈O₁₃ |
| Chemical formula | C₄₄H₆₈O₁₃ |
| Hygroscopic | Hygroscopic |
| Reversible | N |
| Structure formula Image | |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Primary Target | protein phosphatase |
| Primary Target IC<sub>50</sub> | 10-15 nM against protein phosphatase 1; 0.1 nM against protein phosphatase 2A |
| Purity | ≥95% by HPLC |
| Physicochemical Information | |
|---|---|
| Cell permeable | N |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Product Usage Statements |
|---|
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Packaged under inert gas | Packaged under inert gas |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | GTIN |
| 495609 | 0 |
Documentation
InSolution™ Okadaic Acid, Prorocentrum sp. - Calbiochem SDS
| Title |
|---|
InSolution™ Okadaic Acid, Prorocentrum sp. - Calbiochem Certificates of Analysis
| Title | Lot Number |
|---|---|
| 495609 |
References
| Reference overview |
|---|
| Gjertsen, B.T., et al. 1994. J. Cell Sci. 107, 3363. Kiguchi, K., et al. 1994. Cell Growth Differentiation 5, 995. Ohaka, Y., et al. 1993. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 197, 916. Gopalakrishna, R., et al. 1992. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 189, 950. Kreienbuhl, P., et al. 1992. Blood 80, 2911. Nomura, M., et al. 1992. Biochemistry 31, 11915. Song, Q., et al. 1992. J. Cell Physiol. 153, 550. Tada, Y., et al. 1992. Immunopharmacol. 24, 17. Cohen, P., et al. 1990. Trends Biochem. Sci. 15, 98. Cohen, P. 1989. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 58, 453. Cohen, P., and Cohen, P.T. 1989. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 21435. Haystead, T.A., et al. 1989. Nature 337, 78. |
Citations
| Title | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Data Sheet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Note that this data sheet is not lot-specific and is representative of the current specifications for this product. Please consult the vial label and the certificate of analysis for information on specific lots. Also note that shipping conditions may differ from storage conditions.
|