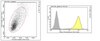
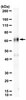Analysis of the interactions of viral and cellular factors with human cytomegalovirus lytic origin of replication, oriLyt.
Kagele, D; Rossetto, CC; Tarrant, MT; Pari, GS
Virology
424
106-14
2012
Show Abstract
Human cytomegalovirus transient lytic DNA replication relies on the cis-acting element oriLyt, six viral-encoded core proteins, the proposed DNA replication initiator protein UL84, IE2, IRS1 and the gene products from the UL112/113 loci. In an effort to elucidate cellular and viral-encoded factors that may play a role in oriLyt-dependent replication we used DNA-affinity purification and mass spectrometry to isolate and identify several previously unknown cellular and viral factors that interact with HCMV oriLyt DNA. These proteins include the multifunctional hnRNP-K, BUB3, HMGB1, PTB-1, UL83, UL112/113, and IRS1. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays confirmed an interaction of several of these factors with oriLyt. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments detected an interaction between UL84 and hnRNP-K in infected and transfected cells. Knockdown of hnRNP K expression by siRNA inhibited the amplification of oriLyt in the transient assay. Together, these data suggest a possible regulatory role in DNA replication for several previously unidentified viral and cellular factors. | 22236369
 |
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates cardiac dysfunction in a rat model of heart failure: a mechanism through cardiac mitochondrial protection.
Wang X, Wang Q, Guo W, Zhu YZ
Biosci Rep
31
87-98.
2011
Show Abstract
HF (heart failure) after MI (myocardial infarction) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Recent studies have shown that hydrogen sulfide (H2S) has cardioprotective effects. Hence, we aimed to elucidate the potential effects of H2S on HF after MI in rats. The HF model after MI was made by ligating the left anterior descending coronary artery. HF groups and sham-operated groups of rats were treated with vehicle, sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) or PAG (propagylglycine). Equal volumes of saline, 3.136 mg · kg-1 · day-1 NaHS or 37.5 mg · kg-1 · day-1 PAG, were intraperitoneally injected into rats for 6 weeks after operation. Survival, lung-to-body weight ratio and left ventricular haemodynamic parameters were measured. The protein and gene expression of Bcl-2, Bax, caspase 3 and cytochrome c were analysed by Western blotting and RT-PCR (reverse transcription-PCR). TUNEL (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labelling) and EM (electron microscopy) were used to examine apoptosis of heart tissues. NaHS was found to improve the survival and lower the lung-to-body weight ratio. It increased the LVSP (left ventricular systolic pressure) and the maximum rate of pressure and decreased LVEDP (left ventricular end-diastolic pressure). Furthermore, NaHS promoted Bcl-2 protein and mRNA expression and demoted Bax, caspase 3 protein and mRNA expression in HF rats. We also showed that NaHS decreased the leakage of cytochrome c protein from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm. Histological observation by TUNEL and EM proved that NaHS inhibited cardiac apoptosis in HF hearts and improved mitochondrial derangements, but that PAG aggravated those indices. Hence, H2S has protective effects in HF rats. Full Text Article | 20450490
 |
Enhancement of neutrophil function by interleukin-18 therapy protects burn-injured mice from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Kinoshita, M; Miyazaki, H; Ono, S; Inatsu, A; Nakashima, H; Tsujimoto, H; Shinomiya, N; Saitoh, D; Seki, S
Infection and immunity
79
2670-80
2011
Show Abstract
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection is a grave concern in burn-injured patients. We investigated the efficacy of interleukin-18 (IL-18) treatment in postburn MRSA infection. Alternate-day injections of IL-18 into burn-injured C57BL/6 mice significantly increased their survival after MRSA infection and after methicillin-sensitive S. aureus infection. Although IL-18 treatment of burn-injured mice augmented natural IgM production before MRSA infection and gamma interferon (IFN-γ) production after MRSA infection, neither IgM nor IFN-γ significantly contributed to the improvement in mouse survival. IL-18 treatment increased/restored the serum tumor necrosis factor (TNF), IL-17, IL-23, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP-2) levels, as well as the neutrophil count, after MRSA infection of burn-injured mice; it also improved impaired neutrophil functions, phagocytic activity, production of reactive oxygen species, and MRSA-killing activity. However, IL-18 treatment was ineffective against MRSA infection in both burn- and sham-injured neutropenic mice. Enhancement of neutrophil functions by IL-18 was also observed in vitro. Furthermore, when neutrophils from IL-18-treated burn-injured mice were adoptively transferred into nontreated burn-injured mice 2 days after MRSA challenge, survival of the recipient mice increased. NOD-SCID mice that have functionally intact neutrophils and macrophages (but not T, B, or NK cells) were substantially resistant to MRSA infection. IL-18 treatment increased the survival of NOD-SCID mice after burn injury and MRSA infection. An adoptive transfer of neutrophils using NOD-SCID mice also showed a beneficial effect of IL-18-activated neutrophils, similar to that seen in C57BL/6 mice. Thus, although neutrophil functions were impaired in burn-injured mice, IL-18 therapy markedly activated neutrophil functions, thereby increasing survival from postburn MRSA infection. Full Text Article | 21536791
 |
Cardiac dysfunction induced by experimental myocardial infarction impairs the host defense response to bacterial infection in mice because of reduced phagocytosis of Kupffer cells.
Nogami Y, Kinoshita M, Takase B, Inatsu A, Ishihara M, Seki S, Maehara T
J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg
2010
Show Abstract
OBJECTIVE: This study was undertaken to investigate the effects of cardiac dysfunction induced by experimental myocardial infarction on the host defense response to bacterial infection and the role of Kupffer cells in mediating this response. METHODS: Myocardial infarction was induced in C57BL/6 mice by ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery. Mice were challenged with Escherichia coli intravenously 1, 5, and 14 days after myocardial infarction or sham operation. Thereafter, the cytokine production and the function of their Kupffer cells were assessed. RESULTS: Mice with myocardial infarction showed remarkable cardiac dysfunction and had a significantly lower survival than sham mice after bacterial challenge at 5 days after surgery; bacterial challenge at 1 or 14 days after surgery resulted in no difference in survival between myocardial infarction and sham mice. The phagocytic activity of Kupffer cells, assessed by fluorescein isothiocyanate microspheres, remarkably decreased in mice with myocardial infarction 5 days after surgery. Serum peaks of tumor necrosis factor and interferon-gamma after bacterial challenge were also suppressed in mice with myocardial infarction at 5 days. Production of these cytokines and immunoglobulin-M from liver mononuclear cells was also impaired in mice with myocardial infarction. Enhancement of the phagocytic activity of Kupffer cells by C-reactive protein significantly improved survival after infection in mice with myocardial infarction, although neither interleukin-18 nor immunoglobulin-M treatment improved survival. CONCLUSION: Cardiac dysfunction induced by myocardial infarction renders mice susceptible to bacterial infection and increases mortality because of a reduced ability of Kupffer cells to clear infectious bacteria. C-reactive protein-enhanced phagocytic activity of Kupffer cells may improve the poor prognosis after bacterial infection in mice with myocardial infarction. Copyright © 2010 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved. | 20138636
 |
An immunohistochemical method for identifying fibroblasts in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue.
Goodpaster, T; Legesse-Miller, A; Hameed, MR; Aisner, SC; Randolph-Habecker, J; Coller, HA
The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry : official journal of the Histochemistry Society
56
347-58
2008
Show Abstract
Fibroblasts are critical for tissue homeostasis, and their inappropriate proliferation and activation can result in common and debilitating conditions including fibrosis and cancer. We currently have a poor understanding of the mechanisms that control the growth and activation of fibroblasts in vivo, in part because of a lack of suitable fibroblast markers. We have taken advantage of an antibody previously shown to stain stromal cells in frozen tissues (TE-7) and identified conditions in which it can be used to stain fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in the paraffin-embedded tissue samples routinely collected for pathological analysis. We show that this antibody recognizes growing and quiescent fibroblasts and myofibroblasts by immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and ELISA assays. We also present its staining patterns in normal tissue samples and in breast tumors. | 18071065
 |
Restoration of natural IgM production from liver B cells by exogenous IL-18 improves the survival of burn-injured mice infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Manabu Kinoshita, Nariyoshi Shinomiya, Satoshi Ono, Hironori Tsujimoto, Toshinobu Kawabata, Atsushi Matsumoto, Hoshio Hiraide, Shuhji Seki
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950)
177
4627-35
2006
Show Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common bacterium of postburn infection. In the present study we investigated the immune mechanism of susceptibility to this type of postburn infection and also examined the efficacy of IL-18 treatment. C57BL/6 mice were challenged with P. aeruginosa on day 7 after burn injury. Although the burn-injured mice showed a poor survival rate after bacterial challenge, they retained their IFN-gamma production. The burned mice showed lower serum IgM levels and a poor IgM response following P. aeruginosa challenge in comparison with the sham mice, whereas IL-18 treatment after burn injury (alternate day injections for 1 wk) greatly improved the serum IgM levels, which are P. aeruginosa-independent natural IgM before bacterial challenge, thereby increasing the survival rate after the challenge. IL-18 treatment also induced specific IgM to P. aeruginosa in the sera 5 days after bacterial challenge in the burned mice. Interestingly, CD43(+)CD5(-)CD23(-)B220(dim) cells, namely B-1b cells, increased in the liver after the IL-18 treatment and were found to actively produce IgM in vitro without any additional stimulation. Furthermore, the IL-18 treatment up-regulated the neutrophil count and the C3a levels in the blood as a result of the increased IgM level, which may thus play a critical role in the opsonization and elimination of any invading bacteria. IL-18 treatment for the burned mice and their resultant natural IgM production were thus found to strengthen the host defense against P. aeruginosa infection. | 16982901
 |