GSK-3 Antibodies, Proteins, Inhibitors
Produits recommandés
-

150442 Supelco SeQuant® ZIC®-HILIC 3.5µm,100Å 150 x 2.1 mm -
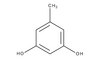
820933 Sigma-Aldrich Dihydroxy-3,5-toluène -

ABC926 Sigma-Aldrich Anti-TRIM11 Antibody -

KWSSA3THH1 Millipore Opticap XLT30 Milligard 0,5/0,2 µm, raccords cannelés 5/8" entrée/sortie -

CLM1510EMD- Sigma-Aldrich CLM1510EMD Glycerol (13C3, 99%) -
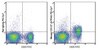
MABF382 Sigma-Aldrich Anti-CD127 (IL-7Ra) Antibody (mouse), PE-Cy7, clone A7R34 -

543840 Supelco Dihydrogénophosphate de sodium anhydre
Aperçu
Caractéristiques
Guide d'achat
Documentation
Produits & Applications associés
Catégories
| Life Science Research > Antibodies and Assays > Primary Antibodies |
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3), a multifunctional serine/threonine kinase, is a key regulator of numerous signaling pathways. Two isoforms of GSK-3 are reported in mammals: a 51 kDa GSK-3a and a 47 kDa GSK-3b. These two isoforms exhibit about 98% homology in their kinase domains, but share only about 36% identity in the last 76 C-terminal amino acid residues. GSK-3a contains a glycine-rich extension at its N-terminus. A minor (~15% of total) splice variant of GSK-3b, GSK-3b2, has also been identified, which contains a 13-residue insert within the kinase domain. It exhibits reduced kinase activity towards tau protein compared with ‘unspliced’ GSK-3b. GSK-3b2 is localized primarily to neuronal cell bodies, unlike unspliced GSK-3b that is also found in neuronal processes. GSK-3b plays a key inhibitory role in the Wnt signaling pathway. Wnt genes encode a large family of secreted, cysteine-rich proteins that are important in development and in maintenance of adult tissues.
GSK-3, a key component in glycogen metabolism, has been heavily implicated in the incidence and progression of a number of diseases including diabetes, cancer and AD. Its most well-known function is constitutive phosphorylation of glycogen synthase. Conversely, GSK-3 inhibition prevents Tau hyperphosphorylation and serves as a protectant against neuronal apoptosis, as well as blocking the accumulation and toxicity of Ab/tau. Unlike most other kinases, GSK-3 is constitutively active, and its effects are regulated primarily through inhibition of its activity. Increased expression and activity of GSK-3 have been implicated both in Type II diabetes and AD, whereas, decreases in its constitutive cellular function are closely linked to various forms of cancer. The therapeutic potential of GSK-3 inhibitors has become a major area of pharmaceutical interest, and the development of GSK-3 targeted therapeutics hold excellent opportunities for the treatment of GSK-3-associated disease states.






