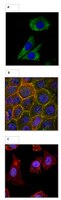
Expression and localization of axin 2 in colorectal carcinoma and its clinical implication.
Schaal, U; Grenz, S; Merkel, S; Rau, TT; Hadjihannas, MV; Kremmer, E; Chudasama, P; Croner, RS; Behrens, J; Stürzl, M; Naschberger, E
International journal of colorectal disease
28
1469-78
2013
Afficher le résumé
Aberrant activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway plays a major role in the development of colorectal carcinoma (CRC). Axin 2 is a key protein of this pathway and is upregulated in CRC. Here, we investigated RNA- and protein expression of axin 2 in CRC tissues at the single cell level. Moreover, the association of axin 2 with prognosis and survival was investigated in a large cohort of CRC patients (n = 280).Localization and expression of axin 2 and β-catenin was investigated using in situ hybridization and immunohistochemical staining. The quantitative expression levels of axin 2 were determined using RT-qPCR. The association of axin 2 expression with prognosis and survival of the patients was determined by statistical analysis (logrank test, Kaplan-Meier).Our results confirmed the upregulation of axin 2 in CRC and showed that it is broadly expressed in the cytoplasm of the tumor epithelial cells both, in the tumor center and at the invasion front. Axin 2 was rarely expressed by tumor stromal cells and only weakly by normal colonic epithelial cells. Staining of β-catenin and axin 2 in consecutive CRC tissue sections revealed that nuclear translocation of β-catenin in the tumor front was not associated with changes in the cytoplasmic localization of axin 2. Axin 2 did not show any association with proven prognostic factors or survival of the CRC patients.The generally increased expression of axin 2 in all tumor stages as compared to normal tissue suggests an initiating pathogenic function in the development of CRC. | 23702820
 |