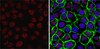
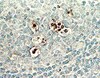
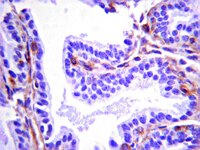
Increased Infiltration of Extra-Cardiac Cells in Myxomatous Valve Disease.
Sauls, K; Toomer, K; Williams, K; Johnson, AJ; Markwald, RR; Hajdu, Z; Norris, RA
Journal of cardiovascular development and disease
2
200-213
2015
Abstract anzeigen
Mutations in the actin-binding gene Filamin-A have been linked to non-syndromic myxomatous valvular dystrophy and associated mitral valve prolapse. Previous studies by our group traced the adult valve defects back to developmental errors in valve interstitial cell-mediated extracellular matrix remodeling during fetal valve gestation. Mice deficient in Filamin-A exhibit enlarged mitral leaflets at E17.5, and subsequent progression to a myxomatous phenotype is observed by two months. For this study, we sought to define mechanisms that contribute to myxomatous degeneration in the adult Filamin-A-deficient mouse. In vivo experiments demonstrate increased infiltration of hematopoietic-derived cells and macrophages in adolescent Filamin-A conditional knockout mice. Concurrent with this infiltration of hematopoietic cells, we show an increase in Erk activity, which localizes to regions of MMP2 expression. Additionally, increases in cell proliferation are observed at two months, when hematopoietic cell engraftment and signaling are pronounced. Similar changes are observed in human myxomatous mitral valve tissue, suggesting that infiltration of hematopoietic-derived cells and/or increased Erk signaling may contribute to myxomatous valvular dystrophy. Consequently, immune cell targeting and/or suppression of pErk activities may represent an effective therapeutic option for mitral valve prolapse patients. | | 26473162
 |
The effect of stromal cell-derived factor-1α/heparin coating of biodegradable vascular grafts on the recruitment of both endothelial and smooth muscle progenitor cells for accelerated regeneration.
Jian Yu,Aijun Wang,Zhenyu Tang,Jeffrey Henry,Benjamin Li-Ping Lee,Yiqian Zhu,Failei Yuan,Fengping Huang,Song Li
Biomaterials
33
2011
Abstract anzeigen
Small-diameter synthetic vascular grafts have high failure rate and tissue-engineered blood vessels are limited by the scalability. Here we engineered bioactive materials for in situ vascular tissue engineering, which recruits two types of endogenous progenitor cells for the regeneration of blood vessels. Heparin was conjugated to microfibrous vascular grafts to suppress thrombogenic responses, and stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α) was immobilized onto heparin to recruit endogenous progenitor cells. Heparin-bound SDF-1α was more stable than adsorbed SDF-1α under both static and flow conditions. Microfibrous grafts were implanted in rats by anastomosis to test the functional performance. Heparin coating improved the short-term patency, and immobilized SDF-1α further improved the long-term patency. SDF-1α effectively recruited endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) to the luminal surface of the grafts, which differentiated into endothelial cells (ECs) and accelerated endothelialization. More interestingly, SDF-1α increased the recruitment of smooth muscle progenitor cells (SMPCs) to the grafts, and SMPCs differentiated into smooth muscle cells (SMCs) in vivo and in vitro. Consistently, SDF-1α-immobilized grafts had significantly higher elastic modulus. This work demonstrates the feasibility of simultaneously recruiting progenitor cells of ECs and SMCs for in situ blood vessel regeneration. This in situ tissue engineering approach will have broad applications in regenerative medicine. | | 22884813
 |
Regional heterogeneity in murine lung fibroblasts from normal mice or mice exposed once to cigarette smoke.
Preobrazhenska, O; Wright, JL; Churg, A
PloS one
7
e39761
2011
Abstract anzeigen
Chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD) is characterized by matrix deposition in the small airways but matrix loss from the parenchyma, phenomena which must depend on the ability of local fibroblasts to produce matrix after smoke exposure. To investigate this idea, we exposed C57Bl/6 mice once to cigarette smoke or to air (control) and prepared primary cultures of lung fibroblasts by microdissecting large airways (trachea, LAF), medium size airways (major bronchi, MAF) and parenchyma (PF). Control PF showed the lowest rate of wound closure and wound closure was depressed in all lines by a single in vivo smoke exposure. Gene expression of matrix proteins differed considerably among the sites; decorin, which may sequester TGFβ, was markedly higher in PF. PF showed higher intrinsic ratios of pSmad2/Smad2. Smoke caused much greater increases in secreted and matrix deposited collagens 1 and 3 in PF than in LAF or MAF. Expression of Thy-1, a gene that suppresses myofibroblast differentiation, was increased by smoke in PF. We conclude that there is considerable regional heterogeneity in murine lung fibroblasts in terms of matrix production, either basally or after in vivo smoke exposure; that PF have lower ability to repair wounds and higher intrinsic TGFβ signaling; and that a single exposure to smoke produces lasting changes in the pattern of matrix production and wound repair, changes that may be mediated in part by smoke-induced release of TGFβ. However, PF still retain the ability to repair by producing new matrix after a single in vivo smoke exposure. | Western Blotting | 22761892
 |