QIA97 Sigma-AldrichCu/Zn Superoxide Dismutase ELISA Kit
Recommended Products
개요
| Replacement Information |
|---|
가격 및 재고여부
| 카탈로그 번호 | 재고 정보 | 패킹 | 포장 단위 | 가격(VAT 별도) | 수량 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QIA97-1KITCN |
|
Glass bottle | 1 kit |
|
— |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Detection method | Colorimetric |
| Form | 96 Tests |
| Format | 96-well plate |
| Kit contains | Pre-Coated 96-Well Plate, Anti-Cu/Zn SOD/HRP-Conjugate, Cu/Zn SOD Standard, Wash Buffer Concentrate, Assay Buffer Concentrate, Phosphate Buffered Saline, Substrate Solution, Stop Solution, Plate Covers, and a user protocol. |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Applications | |
|---|---|
| Key Applications | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Assay time | 1.5 h |
| Sample Type | Cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma, urine, amniotic fluid, and other biological fluids |
| Species Reactivity |
|
| Physicochemical Information | |
|---|---|
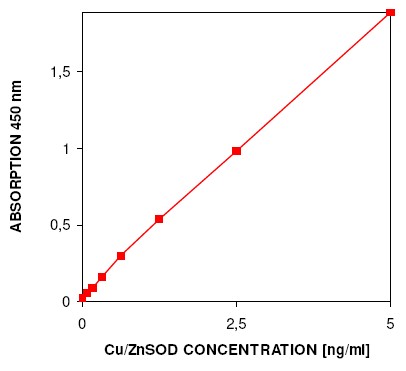
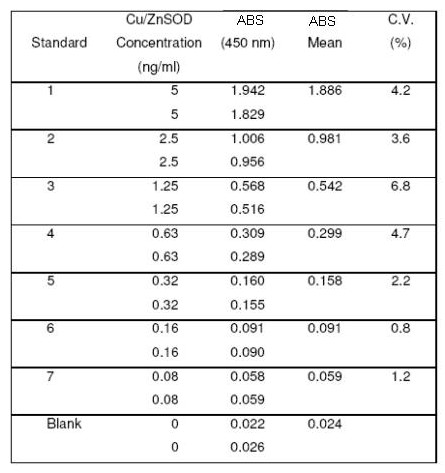
| Sensitivity | 40 pg/ml |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Packaging Information |
|---|
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| 카탈로그 번호 | GTIN |
| QIA97-1KITCN | 04055977209259 |
Documentation
Cu/Zn Superoxide Dismutase ELISA Kit MSDS
| 타이틀 |
|---|
Cu/Zn Superoxide Dismutase ELISA Kit Certificates of Analysis
| Title | Lot Number |
|---|---|
| QIA97 |
References
| 참고문헌 보기 |
|---|
| Herouart, D., et al. 1993. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 3108. Niwa, Y., et al. 1993. Am. J. Pathol. 143, 312. Suzuki, H., et al. 1993. J. Clin. Invest. 91, 2727. Holzgreve, W., et al. 1991. Diagnose Labor. 41, 162. Porstmann, T., et al. 1991. Prenat. Diagn. 11, 195. Shull, S., et al. 1991. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 24398. Porstmann, T., et al. 1990. Hum. Genet. 85, 362. Porstmann, T., et al. 1988. Clin. Chim. Acta 171, 1. Jolly, S.R., et al. 1984. Circ. Res. 54, 277. Goebel, K.M. and Storck, U. 1983. Am. J. Med. 74, 124. Barra, D., et al. 1980. FEBS Lett. 120, 53. Sinet, P.M., et al. 1976. Exp. Cell Res. 97, 47. Harta, J.W. and Deutsch, H.F. 1972. Biol. Chem. 247, 7043. |