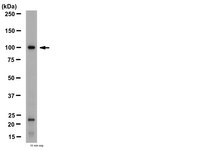
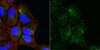
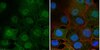
The mouse cyclophosphamide model of bladder pain syndrome: tissue characterization, immune profiling, and relationship to metabotropic glutamate receptors.
Golubeva, AV; Zhdanov, AV; Mallel, G; Dinan, TG; Cryan, JF
Physiological reports
2
e00260
2014
요약 표시
Abstract Painful bladder syndrome/Interstitial cystitis (PBS/IC) is a chronic disorder characterized clinically by recurring episodes of pelvic pain and increased urination frequency, significantly impairing patients' quality of life. Despite this, there is an unmet medical need in terms of effective diagnostics and treatment. Animal models are crucial in this endeavor. Systemic chronic administration of cyclophosphamide (CYP) in mice has been proposed as a relevant preclinical model of chronic bladder pain. However, molecular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of this model are lacking. Here, we show that mice, subjected to repetitive systemic injections of CYP, developed mild inflammatory response in bladder tissue characterized by submucosal edema, moderate increase in proinflammatory cytokine gene expression, and mastocytosis. No signs of massive inflammatory infiltrate, tissue hemorrhages, mucosal ulcerations and urothelium loss were observed. Instead, CYP treatment induced urothelium hyperplasia, accompanied by activation of proliferative signaling cascades, and a decrease in the expression of urothelium-specific markers. Metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors have been implicated in chronic pain disorders. CYP administration induced differential changes in mGlu receptors mRNA levels in bladder tissue, without affecting gene expression at spinal cord level, pointing to the potential link between peripheral mGlu receptors and inflammation-induced bladder malfunction and hyperalgesia. Taken together, these data indicate that chronic CYP treatment in mice is a model of PBS mostly relevant to the major, nonulcerative subtype of the syndrome, characterized by a relatively unaltered mucosa and a sparse inflammatory response. This model can help to elucidate the pathogenetic mechanisms of the disease. | Western Blotting | 24760514
 |
Native presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 (mGluR4) interacts with exocytosis proteins in rat cerebellum.
Ramos, C; Chardonnet, S; Marchand, CH; Decottignies, P; Ango, F; Daniel, H; Le Maréchal, P
The Journal of biological chemistry
287
20176-86
2012
요약 표시
The eight pre- or/and post-synaptic metabotropic glutamatergic receptors (mGluRs) modulate rapid excitatory transmission sustained by ionotropic receptors. They are classified in three families according to their percentage of sequence identity and their pharmacological properties. mGluR4 belongs to group III and is mainly localized presynaptically. Activation of group III mGluRs leads to depression of excitatory transmission, a process that is exclusively provided by mGluR4 at parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapse in rodent cerebellum. This function relies at least partly on an inhibition of presynaptic calcium influx, which controls glutamate release. To improve the understanding of molecular mechanisms of the mGluR4 depressant effect, we decided to identify the proteins interacting with this receptor. Immunoprecipitations using anti-mGluR4 antibodies were performed with cerebellar extracts. 183 putative partners that co-immunoprecipitated with anti-mGluR4 antibodies were identified and classified according to their cellular functions. It appears that native mGluR4 interacts with several exocytosis proteins such as Munc18-1, synapsins, and syntaxin. In addition, native mGluR4 was retained on a Sepharose column covalently grafted with recombinant Munc18-1, and immunohistochemistry experiments showed that Munc18-1 and mGluR4 colocalized at plasma membrane in HEK293 cells, observations in favor of an interaction between the two proteins. Finally, affinity chromatography experiments using peptides corresponding to the cytoplasmic domains of mGluR4 confirmed the interaction observed between mGluR4 and a selection of exocytosis proteins, including Munc18-1. These results could give indications to explain how mGluR4 can modulate glutamate release at parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapses in the cerebellum in addition to the inhibition of presynaptic calcium influx. | Western Blotting | 22528491
 |