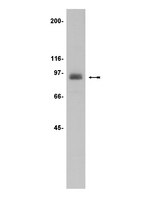
Proplatelet generation in the mouse requires PKCε-dependent RhoA inhibition.
Gobbi, G; Mirandola, P; Carubbi, C; Masselli, E; Sykes, SM; Ferraro, F; Nouvenne, A; Thon, JN; Italiano, JE; Vitale, M
Blood
122
1305-11
2013
요약 표시
During thrombopoiesis, megakaroycytes undergo extensive cytoskeletal remodeling to form proplatelet extensions that eventually produce mature platelets. Proplatelet formation is a tightly orchestrated process that depends on dynamic regulation of both tubulin reorganization and Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase/RhoA activity. A disruption in tubulin dynamics or RhoA activity impairs proplatelet formation and alters platelet morphology. We previously observed that protein kinase Cepsilon (PKCε), a member of the protein kinase C family of serine/threonine-kinases, expression varies during human megakaryocyte differentiation and modulates megakaryocyte maturation and platelet release. Here we used an in vitro model of murine platelet production to investigate a potential role for PKCε in proplatelet formation. By immunofluorescence we observed that PKCε colocalizes with α/β-tubulin in specific areas of the marginal tubular-coil in proplatelets. Moreover, we found that PKCε expression escalates during megakarocyte differentiation and remains elevated in proplatelets, whereas the active form of RhoA is substantially downregulated in proplatelets. PKCε inhibition resulted in lower proplatelet numbers and larger diameter platelets in culture as well as persistent RhoA activation. Finally, we demonstrate that pharmacological inhibition of RhoA is capable of reversing the proplatelet defects mediated by PKCε inhibition. Collectively, these data indicate that by regulating RhoA activity, PKCε is a critical mediator of mouse proplatelet formation in vitro. | Western Blotting | 23838351
 |
Leucine supplementation augments insulin secretion in pancreatic islets of malnourished mice.
Amaral AG, Rafacho A, Machado de Oliveira CA, Batista TM, Ribeiro RA, Latorraca MQ, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM
Pancreas
39
847-55.
2010
요약 표시
OBJECTIVES: We investigated the influence of leucine supplementation on insulin secretion and on some proteins related to insulin secretion in malnourished mice. | | 20697208
 |
Keratin 8/18 modulation of protein kinase C-mediated integrin-dependent adhesion and migration of liver epithelial cells.
Bordeleau, F; Galarneau, L; Gilbert, S; Loranger, A; Marceau, N
Molecular biology of the cell
21
1698-713
2010
요약 표시
Keratins are intermediate filament (IF) proteins of epithelial cells, expressed as pairs in a lineage/differentiation manner. Hepatocyte and hepatoma cell IFs are made solely of keratins 8/18 (K8/K18), the hallmark of all simple epithelia. Cell attachment/spreading (adhesion) and migration involve the formation of focal adhesions at sites of integrin interactions with extracellular matrix, actin adaptors such as talin and vinculin, and signaling molecules such as focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and member(s) of the protein kinase C (PKC) family. Here, we identify the novel PKCdelta as mediator of the K8/K18 modulation of hepatoma cell adhesion and migration. We also demonstrate a K8/K18-dependent relationship between PKCdelta and FAK activation through an integrin/FAK-positive feedback loop, in correlation with a reduced FAK time residency at focal adhesions. Notably, a K8/K18 loss results to a time course modulation of the receptor of activated C-kinase-1, beta1-integrin, plectin, PKC, and c-Src complex formation. Although the K8/K18 modulation of hepatocyte adhesion also occurs through a PKC mediation, these differentiated epithelial cells exhibit minimal migrating ability, in link with marked differences in protein partner content and distribution. Together, these results uncover a key regulatory function for K8/K18 IFs in the PKC-mediated integrin/FAK-dependent adhesion and migration of simple epithelial cells. 기사 전문 | | 20357007
 |
VEGF stimulates RCAN1.4 expression in endothelial cells via a pathway requiring Ca2+/calcineurin and protein kinase C-delta.
Holmes, K; Chapman, E; See, V; Cross, MJ
PloS one
5
e11435
2010
요약 표시
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has previously been shown to upregulate the expression of the endogenous calcineurin inhibitor, regulator of calcineurin 1, variant 4 (RCAN1.4). The aim of this study was to determine the role and regulation of VEGF-mediated RCAN1.4 expression, using human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMECs) as a model system.We show that VEGF is able to induce RCAN1.4 expression during cellular proliferation and differentiation, and that VEGF-mediated expression of RCAN1.4 was inhibited by the use of inhibitors to protein kinase C (PKC) and calcineurin. Further analysis revealed that siRNA silencing of PKC-delta expression partially inhibited VEGF-stimulated RCAN1.4 expression. Knockdown of RCAN1.4 with siRNA resulted in a decrease in cellular migration and disrupted tubular morphogenesis when HDMECs were either stimulated with VEGF in a collagen gel or in an endothelial/fibroblast co-culture model of angiogenesis. Analysis of intracellular signalling revealed that siRNA mediated silencing of RCAN1.4 resulted in increased expression of specific nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) regulated genes.Our data suggests that RCAN1.4 expression is induced by VEGFR-2 activation in a Ca(2+) and PKC-delta dependent manner and that RCAN1.4 acts to regulate calcineurin activity and gene expression facilitating endothelial cell migration and tubular morphogenesis. | Western Blotting | 20625401
 |
Neuroprotective preconditioning of rat brain cultures with ethanol: potential transduction by PKC isoforms and focal adhesion kinase upstream of increases in effector heat shock proteins.
Sreevidya Sivaswamy,Edward J Neafsey,Michael A Collins
The European journal of neuroscience
32
2010
요약 표시
Preconditioning rat hippocampal-entorhinocortical (HEC) slice or cerebellar cell cultures with moderate concentrations of ethanol (20-30 mm) neuroprotects against pro-inflammatory proteins such as HIV-1 glycoprotein 120 (gp120) or amyloid-β. The neuroprotective mechanism of ethanol is unclear, but it conceivably involves sensors→transducers→effectors, analogous to other preconditioning modalities. We initially found that the preconditioning augmented two likely heat shock protein (HSP) 'effectors', HSP70 and HSP27, and that precluding HSP upregulation abolished neuroprotection. Here we examined whether pro-survival kinases are transducers potentially leading to HSP effectors. In cerebellar cultures, protein kinase C (PKC) activity increased modestly after 2 days of 30 mm ethanol and was significantly induced after 6 days, when neuroprotection against gp120 becomes manifest. After 4 and particularly after 6 days of preconditioning, immunoblots showed highly elevated PKCε levels and moderately increased PKCα and PKCδ, accompanied by increased membrane translocation (activation) of these isoforms. Also, at the latter preconditioning duration, focal adhesion kinase (FAK), an important actin-associated kinase, and its Y397-phosphorylated form (p-FAK) were elevated, along with parallel increases in HSP27, S85p-HSP27 and HSP70. Furthermore, while confirming increased HSP27 and HSP70 in HEC slices ethanol-preconditioned for 6 days, we detected elevations in PKC isoforms, FAK, p-FAK and p-HSP27 in these organotypic cultures. Importantly, PKC inhibition with GF109203X suppressed FAK, HSP70 and HSP27 amplification/activation in ethanol-preconditioned cerebellar cultures, indicating that PKC is an upstream transducer of FAK and the HSP effectors. Neuroprotection associated with increases in HSP27/HSP70 from ethanol preconditioning entails upregulation/activation of PKC isoforms and FAK, the latter kinase implicating actin cytoskeletal prosurvival pathways in brain preconditioning. | | 21050276
 |
Hypoxia-regulated activity of PKCepsilon in the lens.
Akoyev, V; Das, S; Jena, S; Grauer, L; Takemoto, DJ
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science
50
1271-82
2009
요약 표시
To show that hypoxia is necessary to prevent opacification of the lens. Protein kinase C (PKC)-epsilon serves a role that is distinct from PKC-gamma when both PKC isoforms are expressed in the lens. PKCepsilon serves a very important role in hypoxic conditions, helping to prevent opacification of the lens.Digital image analysis, confocal microscopy, dye transfer assay, coimmunoprecipitation, Western blot analysis, and enzyme activity assays were used, respectively, to study opacification of the lens, intercellular communications, cellular localization of connexin-43 (Cx43), and the interactions between PKCepsilon, PKCgamma, and Cx43 in the lens epithelial cells.Hypoxic conditions (1%-5% of oxygen) were very important in maintaining clarity of the lenses of wild-type (WT) mice. Normoxic conditions induced opacification of the WT lens. Lenses from the PKCepsilon-knockout mice underwent rapid opacification, even in hypoxic conditions. Hypoxia did not induce apoptosis in the lens epithelial cells, judging by the absence of active caspase-3, and it did not change intercellular communication and did not affect the number and localization of junctional Cx43 plaques in the lens epithelial cell culture. Hypoxia activated PKCepsilon, whereas phorbol ester (TPA), oxidation (H(2)O(2)), and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) activated PKCgamma and decreased the activity of PKCepsilon. Hypoxia did not induce the phosphorylation of the Cx43.Hypoxia-induced activation of PKCepsilon is very important in surviving hypoxia and maintaining the clarity of the lens. However, PKCgamma is utilized in the control of Cx43 gap junctions. | | 18997087
 |
Post-ischaemic activation of kinases in the pre-conditioning-like cardioprotective effect of the platelet-activating factor.
Penna C, Mognetti B, Tullio F, Gattullo D, Mancardi D, Moro F, Pagliaro P, Alloatti G
Acta Physiol (Oxf)
197
175-85. Epub 2009 May 7.
2009
요약 표시
AIM: Platelet-activating factor (PAF) triggers cardiac pre-conditioning against ischemia/reperfusion injury. The actual protection of ischaemic pre-conditioning occurs in the reperfusion phase. Therefore, we studied in this phase the kinases involved in PAF-induced pre-conditioning. | | 19432589
 |
Two conventional protein kinase C isoforms, alpha and beta I, are involved in the ATP-induced activation of volume-regulated anion channel and glutamate release in cultured astrocytes.
Alena Rudkouskaya,Artur Chernoguz,Renée E Haskew-Layton,Alexander A Mongin
Journal of neurochemistry
105
2008
요약 표시
Volume-regulated anion channels (VRACs) are activated by cell swelling and are permeable to inorganic and small organic anions, including the excitatory amino acids glutamate and aspartate. In astrocytes, ATP potently enhances VRAC activity and glutamate release via a P2Y receptor-dependent mechanism. Our previous pharmacological study identified protein kinase C (PKC) as a major signaling enzyme in VRAC regulation by ATP. However, conflicting results obtained with potent PKC blockers prompted us to re-evaluate the involvement of PKC in regulation of astrocytic VRACs by using small interfering RNA (siRNA) and pharmacological inhibitors that selectively target individual PKC isoforms. In primary rat astrocyte cultures, application of hypoosmotic medium (30% reduction in osmolarity) and 20 microM ATP synergistically increased the release of excitatory amino acids, measured with a non-metabolized analog of L-glutamate, D-[(3)H]aspartate. Both Go6976, the selective inhibitor of Ca(2+)-sensitive PKCalpha, betaI/II, and gamma, and MP-20-28, a cell permeable pseudosubstrate inhibitory peptide of PKCalpha and betaI/II, reduced the effects of ATP on D-[(3)H]aspartate release by approximately 45-55%. Similar results were obtained with a mixture of siRNAs targeting rat PKCalpha and betaI. Surprisingly, down-regulation of individual alpha and betaI PKC isozymes by siRNA was completely ineffective. These data suggest that ATP regulates VRAC activity and volume-sensitive excitatory amino acid release via cooperative activation of PKCalpha and betaI. | | 18315563
 |
Protein kinase C epsilon activates lens mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV during hypoxia.
Michael Barnett, Dingbo Lin, Vladimir Akoyev, Lloyd Willard, Dolores Takemoto, Michael Barnett, Dingbo Lin, Vladimir Akoyev, Lloyd Willard, Dolores Takemoto
Experimental eye research
86
226-34
2008
요약 표시
Protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms have been identified as major cellular signaling proteins that act directly in response to oxidation conditions. In retina and lens two isoforms of PKC respond to changes in oxidative stress, PKCgamma and PKCepsilon, while only PKCepsilon is found in heart. In heart the PKCepsilon acts on connexin 43 to protect from hypoxia. The presence of both isoforms in the lens led to this study to determine if lens PKCepsilon had unique targets. Both lens epithelial cells in culture and whole mouse lens were examined using PKC isoform-specific enzyme activity assays, co-immunoprecipitation, confocal microscopy, immunoblots, and light and electron microscopy. PKCepsilon was found in lens epithelium and cortex but not in the nucleus of mouse lens. The PKCepsilon isoform was activated in both epithelium and whole lens by 5% oxygen when compared to activity at 21% oxygen. In hypoxic conditions (5% oxygen) the PKCepsilon co-immunoprecipitated with the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase IV subunit (CytCOx). Concomitant with this the CytCOx enzyme activity was elevated and increased co-localization of CytCOx with PCKvarepsilon was observed using immunolabeling and confocal microscopy. In contrast, no hypoxia-induced activation of CytCOx was observed in lenses from the PKCepsilon knockout mice. Lens from 6-week-old PKCepsilon knockout mice had a disorganized bow region which was filled with vacuoles indicating a possible loss of mitochondria but the size of the lens was not altered. Electron microscopy demonstrated that the nuclei of the PCKepsilon knockout mice were abnormal in shape. Thus, PKCepsilon is found to be activated by hypoxia and this results in the activation of the mitochondrial protein CytCOx. This could protect the lens from mitochondrial damage under the naturally hypoxic conditions observed in this tissue. Lens oxygen levels must remain low. Elevation of oxygen which occurs during vitreal detachment or liquification is associated with cataracts. We hypothesize that elevated oxygen could cause inhibition of PKCepsilon resulting in a loss of mitochondrial protection. 기사 전문 | | 18070622
 |
Platelet-activating factor induces cardioprotection in isolated rat heart akin to ischemic preconditioning: role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and protein kinase C activation.
Penna, C; Alloatti, G; Cappello, S; Gattullo, D; Berta, G; Mognetti, B; Losano, G; Pagliaro, P
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology
288
H2512-20
2005
요약 표시
Ischemic preconditioning (IP) is a cardioprotective mechanism against myocellular death and cardiac dysfunction resulting from reperfusion of the ischemic heart. At present, the precise list of mediators involved in IP and the pathways of their mechanisms of action are not completely known. The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of platelet-activating factor (PAF), a phospholipid mediator that is known to be released by the ischemic-reperfused heart, as a possible endogenous agent involved in IP. Experiments were performed on Langendorff-perfused rat hearts undergoing 30 min of ischemia followed by 2 h of reperfusion. Treatment with a low concentration of PAF (2 x 10(-11) M) before ischemia reduced the extension of infarct size and improved the recovery of left ventricular developed pressure during reperfusion. The cardioprotective effect of PAF was comparable to that observed in hearts in which IP was induced by three brief (3 min) periods of ischemia separated by 5-min reperfusion intervals. The PAF receptor antagonist WEB-2170 (1 x 10(-9) M) abrogated the cardioprotective effect induced by both PAF and IP. The protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor chelerythrine (5 x 10(-6) M) or the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY-294002 (5 x 10(-5) M) also reduced the cardioprotective effect of PAF. Western blot analysis revealed that following IP treatment or PAF infusion, the phosphorylation of PKC-epsilon and Akt (the downstream target of PI3K) was higher than that in control hearts. The present data indicate that exogenous applications of low quantities of PAF induce a cardioprotective effect through PI3K and PKC activation, similar to that afforded by IP. Moreover, the study suggests that endogenous release of PAF, induced by brief periods of ischemia and reperfusion, may participate to the triggering of the IP of the heart. | Western Blotting | 15637120
 |