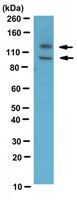
ADAM17 is regulated by a rapid and reversible mechanism that controls access to its catalytic site.
Le Gall, Sylvain M, et al.
J. Cell. Sci., 123: 3913-22 (2010)
2010
요약 표시
Protein ectodomain shedding is crucial for cell-cell interactions because it controls the bioavailability of soluble tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) and ligands of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor, and the release of many other membrane proteins. Various stimuli can rapidly trigger ectodomain shedding, yet much remains to be learned about the identity of the enzymes that respond to these stimuli and the mechanisms underlying their activation. Here, we demonstrate that the membrane-anchored metalloproteinase ADAM17, but not ADAM10, is the sheddase that rapidly responds to the physiological signaling pathways stimulated by thrombin, EGF, lysophosphatidic acid and TNFα. Stimulation of ADAM17 is swift and quickly reversible, and does not depend on removal of its inhibitory pro-domain by pro-protein convertases, or on dissociation of an endogenous inhibitor, TIMP3. Moreover, activation of ADAM17 by physiological stimuli requires its transmembrane domain, but not its cytoplasmic domain, arguing against inside-out signaling via cytoplasmic phosphorylation as the underlying mechanism. Finally, experiments with the tight binding hydroxamate inhibitor DPC333, used here to probe the accessibility of the active site of ADAM17, demonstrate that this inhibitor can quickly bind to ADAM17 in stimulated, but not quiescent cells. These findings support the concept that activation of ADAM17 involves a rapid and reversible exposure of its catalytic site. | 20980382
 |
Evidence for regulation of the tumor necrosis factor alpha-convertase (TACE) by protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPH1.
Zheng, Yufang, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 277: 42463-70 (2002)
2002
요약 표시
Tumor necrosis factor alpha-convertase (TACE) is a metalloprotease-disintegrin involved in the ectodomain shedding of several proteins and is critical for proper murine development. TACE-mediated ectodomain shedding is regulated, and the cytoplasmic domain of TACE contains several potential signaling motifs, suggesting that this domain may play a role in regulating the metalloprotease activity. Here we report that the protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPH1, which contains both a band 4.1 domain and a single PDZ domain, can interact with the cytoplasmic domain of TACE. The interaction was initially observed in a yeast two-hybrid screen and was confirmed using an in vitro binding assay and co-immunoprecipitations from eukaryotic cell extracts. The interaction is mediated via binding of the PDZ domain of PTPH1 to the COOH terminus of TACE. The latter represents a novel group I PDZ binding sequence characterized by a terminal cysteine residue. In co-expression experiments, significantly lower levels of TACE were observed in the presence of catalytically active forms of PTPH1 compared with catalytically inactive forms of PTPH1. Furthermore, phorbol ester-stimulated shedding of the TACE substrate tumor necrosis factor-alpha was decreased in cells expressing catalytically active PTPH1 compared with inactive PTPH1. Taken together, these results suggest that PTPH1 may be a negative regulator of TACE levels and function, and thus provide the first evidence for the regulation of TACE through a cytoplasmic protein. | 12207026
 |
Intracellular maturation and localization of the tumour necrosis factor alpha convertase (TACE).
Schlöndorff, J, et al.
Biochem. J., 347 Pt 1: 131-8 (2000)
2000
요약 표시
Tumour necrosis factor alpha convertase (TACE) is a metalloprotease/disintegrin involved in the ectodomain shedding of several proteins, a process thought to be important in inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis and murine development. The characterization of the intracellular maturation and subcellular localization of endogenous TACE is decribed in the present study. Similarly to other proteolytically active metalloprotease/disintegrins, two forms of TACE are found in cells; a full-length precursor and a mature form lacking the prodomain. Prodomain removal occurs in a late Golgi compartment, consistent with the proposed role of a furin type proprotein convertase in this process. An additional form of TACE, lacking the pro and cytoplasmic domains, is detected when cell lysates are prepared in the presence of EDTA instead of a hydroxamate-based metalloprotease inhibitor or 1,10-phenanthroline. This form appears to be generated by mature TACE cleaving its own cytoplasmic tail and may explain why little mature TACE has been detected in previous studies. In cell-surface labelling experiments, mature TACE was detected on the cell surface but immunofluorescence data indicate that TACE is predominantly localized to a perinuclear compartment similar to that described for tumour necrosis factor (TNF)alpha. This raises the possibility that TACE-mediated ectodomain shedding may occur in an intracellular compartment in addition to the cell surface. | 10727411
 |