Transcriptome-wide regulation of pre-mRNA splicing and mRNA localization by muscleblind proteins.
Wang, Eric T, et al.
Cell, 150: 710-24 (2012)
2012
概要を表示する
The muscleblind-like (Mbnl) family of RNA-binding proteins plays important roles in muscle and eye development and in myotonic dystrophy (DM), in which expanded CUG or CCUG repeats functionally deplete Mbnl proteins. We identified transcriptome-wide functional and biophysical targets of Mbnl proteins in brain, heart, muscle, and myoblasts by using RNA-seq and CLIP-seq approaches. This analysis identified several hundred splicing events whose regulation depended on Mbnl function in a pattern indicating functional interchangeability between Mbnl1 and Mbnl2. A nucleotide resolution RNA map associated repression or activation of exon splicing with Mbnl binding near either 3' splice site or near the downstream 5' splice site, respectively. Transcriptomic analysis of subcellular compartments uncovered a global role for Mbnls in regulating localization of mRNAs in both mouse and Drosophila cells, and Mbnl-dependent translation and protein secretion were observed for a subset of mRNAs with Mbnl-dependent localization. These findings hold several new implications for DM pathogenesis. | Western Blotting | Mouse | 22901804
 |
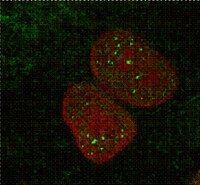
Defective mRNA in myotonic dystrophy accumulates at the periphery of nuclear splicing speckles.
Holt, I; Mittal, S; Furling, D; Butler-Browne, GS; Brook, JD; Morris, GE
Genes to cells : devoted to molecular & cellular mechanisms
12
1035-48
2007
概要を表示する
Nuclear speckles are storage sites for small nuclear RNPs (snRNPs) and other splicing factors. Current ideas about the role of speckles suggest that some pre-mRNAs are processed at the speckle periphery before being exported as mRNA. In myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1), the export of mutant DMPK mRNA is prevented by the presence of expanded CUG repeats that accumulate in nuclear foci. We now show that these foci accumulate at the periphery of nuclear speckles. In myotonic dystrophy type 2 (DM2), mRNA from the mutant ZNF9 gene is exported normally because the expanded CCUG repeats are removed during splicing. We now show that the nuclear foci formed by DM2 intronic repeats are widely dispersed in the nucleoplasm and not associated with either nuclear speckles or exosomes. We hypothesize that the expanded CUG repeats in DMPK mRNA are blocking a stage in its export pathway that would normally occur at the speckle periphery. Localization of the expanded repeats at the speckle periphery is not essential for their pathogenic effects because DM1 and DM2 are quite similar clinically. | | | 17825047
 |