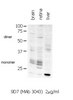
Dopamine receptors in human embryonic stem cell neurodifferentiation.
Belinsky, GS; Sirois, CL; Rich, MT; Short, SM; Moore, AR; Gilbert, SE; Antic, SD
Stem cells and development
22
1522-40
2013
概要を表示する
We tested whether dopaminergic drugs can improve the protocol for in vitro differentiation of H9 human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) into dopaminergic neurons. The expression of 5 dopamine (DA) receptor subtypes (mRNA and protein) was analyzed at each protocol stage (1, undifferentiated hESCs; 2, embryoid bodies [EBs]; 3, neuroepithelial rosettes; 4, expanding neuroepithelium; and 5, differentiating neurons) and compared to human fetal brain (gestational week 17-19). D2-like DA receptors (D2, D3, and D4) predominate over the D1-like receptors (D1 and D5) during derivation of neurons from hESCs. D1 was the receptor subtype with the lowest representation in each protocol stage (Stages 1-5). D1/D5-agonist SKF38393 and D2/D3/D4-agonist quinpirole (either alone or combined) evoked Ca(2+) responses, indicating functional receptors in hESCs. To identify when receptor activation causes a striking effect on hESC neurodifferentiation, and what ligands and endpoints are most interesting, we varied the timing, duration, and drug in the culture media. Dopaminergic agonists or antagonists were administered either early (Stages 1-3) or late (Stages 4-5). Early DA exposure resulted in more neuroepithelial colonies, more neuronal clusters, and more TH(+) clusters. The D1/D5 antagonist SKF83566 had a strong effect on EB morphology and the expression of midbrain markers. Late exposure to DA resulted in a modest increase in TH(+) neuron clusters (∼75%). The increase caused by DA did not occur in the presence of dibutyryl cAMP (dbcAMP), suggesting that DA acts through the cAMP pathway. However, a D2-antagonist (L741) decreased TH(+) cluster counts. Electrophysiological parameters of the postmitotic neurons were not significantly affected by late DA treatment (Stages 4-5). The mRNA of mature neurons (VGLUT1 and GAD1) and the midbrain markers (GIRK2, LMX1A, and MSX1) were lower in hESCs treated by DA or a D2-antagonist. When hESCs were neurodifferentiated on PA6 stromal cells, DA also increased expression of tyrosine hydroxylase. Although these results are consistent with DA's role in potentiating DA neurodifferentiation, dopaminergic treatments are generally less efficient than dbcAMP alone. | Western Blotting | | 23286225
 |
Modification of dopaminergic markers expression in the striatum by neonatal exposure to glutamate during development.
S J López-Pérez, P Vergara, J P Ventura-Valenzuela, M E Ureña-Guerrero, J Segovia, C Beas-Zárate
International journal of developmental neuroscience : the official journal of the International Society for Developmental Neuroscience
23
335-42
2005
概要を表示する
Monosodium l-glutamate (MSG) was administered subcutaneously to male neonatal rats, and the effect on developmental profile of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), D1, D2 receptors, and dopamine (DA) transporter expression in the striatum was examined using Western blot. In addition, TH-immunopositive neurons at substantia nigra (SN) were also examined. MSG treatment (4mg/g of body weight, administered on postnatal days 1, 3, 5, and 7) resulted in a reduction of D1 and D2 receptor expression from 30 days of age and persisted to adulthood (120 days of age), while DA transporter expression was significantly reduced from 14 days of age to adulthood. TH immunopositive neurons at SN showed a significant reduction, as well as TH expression on postnatal days 10, 30, 60, and 120 at striatum was reduced. No changes of TH were observed at 14 days of age. Results indicate that an over-stimulation of the glutamatergic system by neonatal exposure to a high glutamate concentration induces a partial loss in TH-positive neurons in the SN and an important reduction in dopaminergic markers expression in the striatum, suggesting that early excitotoxicity could contribute to developmental alterations in the nigrostriatal pathway, which may be associated with various disorders of the basal ganglia. | | | 15927757
 |
Estrogen protects against the synergistic toxicity by HIV proteins, methamphetamine and cocaine.
Turchan, J; Anderson, C; Hauser, KF; Sun, Q; Zhang, J; Liu, Y; Wise, PM; Kruman, I; Maragos, W; Mattson, MP; Booze, R; Nath, A
BMC neuroscience
2
3
2001
概要を表示する
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection continues to increase at alarming rates in drug abusers, especially in women. Drugs of abuse can cause long-lasting damage to the brain and HIV infection frequently leads to a dementing illness. To determine how these drugs interact with HIV to cause CNS damage, we used an in vitro human neuronal culture characterized for the presence of dopaminergic receptors, transporters and estrogen receptors. We determined the combined effects of dopaminergic drugs, methamphetamine, or cocaine with neurotoxic HIV proteins, gp120 and Tat.Acute exposure to these substances resulted in synergistic neurotoxic responses as measured by changes in mitochondrial membrane potential and neuronal cell death. Neurotoxicity occurred in a sub-population of neurons. Importantly, the presence of 17beta-estradiol prevented these synergistic neurotoxicities and the neuroprotective effects were partly mediated by estrogen receptors.Our observations suggest that methamphetamine and cocaine may affect the course of HIV dementia, and additionally suggest that estrogens modify the HIV-drug interactions. | Immunofluorescence | Human | 11252157
 |
Schizophrenia: dopamine D1 receptor sequence is normal, but has DNA polymorphisms.
Ohara, K, et al.
Neuropsychopharmacology, 8: 131-5 (1993)
1993
概要を表示する
Genes that regulate dopamine (DA) receptors may underlie the overactive DA system in schizophrenia. Since it is known that there is an abnormally reduced or absent regulation of the DA D2 receptor by the DA D1 receptor in the postmortem schizophrenia brain, the human DA D1 receptor gene was sequenced from genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of seven schizophrenic individuals. The tissues from two schizophrenics had previously been found to have a reduced link between DA D1 and D2 receptors. The D1 receptor genes were amplified by the polymerase chain reaction, subcloned, and sequenced. Although three DNA polymorphisms were found, the deduced amino acid sequence of the DA D1 receptor was normal in these tissues. | | | 8471124
 |