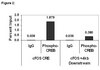
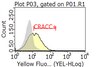
Activation of endothelial TLR2 by bacterial lipoprotein upregulates proteins specific for the neutrophil response.
Wilhelmsen, K; Mesa, KR; Prakash, A; Xu, F; Hellman, J
Innate immunity
18
602-16
2012
Show Abstract
The vascular endothelium is integrally involved in the host response to infection and in organ failure during acute inflammatory disorders such as sepsis. Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial lipoproteins circulate in sepsis and can directly activate the endothelium by binding to endothelial cell (EC) TLR2. In this report, we perform the most comprehensive analysis to date of the immune-related genes regulated after activation of endothelial TLR2 by bacterial di- and triacylated lipopeptides. We found that TLR2 activation specifically induces the expression of the genes IL-6, IL-8, CSF2, CSF3, ICAM1 and SELE by human umbilical vein ECs and human lung microvascular ECs. These proteins participate in neutrophil recruitment, adherence and activation at sites of inflammation. Significantly, our studies demonstrate that TLR2-mediated EC responses are specifically geared towards recruitment, activation, and survival of neutrophils and not mononuclear leukocytes, that ECs do not require priming by other inflammatory stimuli to respond to bacterial lipopeptides and, unlike mononuclear leukocytes, TLR2 agonists do not induce ECs to secrete TNF-α. This study suggests that endothelial TLR2 may be an important regulator of neutrophil trafficking to sites of infection in general, and that direct activation of lung endothelial TLR2 may contribute to acute lung injury during sepsis. | 22186927
 |
ERK5 protein promotes, whereas MEK1 protein differentially regulates, the Toll-like receptor 2 protein-dependent activation of human endothelial cells and monocytes.
Wilhelmsen, K; Mesa, KR; Lucero, J; Xu, F; Hellman, J
The Journal of biological chemistry
287
26478-94
2012
Show Abstract
Endothelial cell (EC) Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) activation up-regulates the expression of inflammatory mediators and of TLR2 itself and modulates important endothelial functions, including coagulation and permeability. We defined TLR2 signaling pathways in EC and tested the hypothesis that TLR2 signaling differs in EC and monocytes. We found that ERK5, heretofore unrecognized as mediating TLR2 activation in any cell type, is a central mediator of TLR2-dependent inflammatory signaling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, primary human lung microvascular EC, and human monocytes. Additionally, we observed that, although MEK1 negatively regulates TLR2 signaling in EC, MEK1 promotes TLR2 signaling in monocytes. We also noted that activation of TLR2 led to the up-regulation of intracellularly expressed TLR2 and inflammatory mediators via NF-κB, JNK, and p38-MAPK. Finally, we found that p38-MAPK, JNK, ERK5, and NF-κB promote the attachment of human neutrophils to lung microvascular EC that were pretreated with TLR2 agonists. This study newly identifies ERK5 as a key regulator of TLR2 signaling in EC and monocytes and indicates that there are fundamental differences in TLR signaling pathways between EC and monocytes. | 22707717
 |
Activity of cholinergic neurons in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus during emission of 22kHz vocalization in rats.
Stefan M Brudzynski,Amaka Iku,Alison Harness Neé Savoy
Behavioural brain research
225
2011
Show Abstract
It has been postulated that the ascending cholinergic tegmental system is responsible for the initiation of the aversive emotional state with a concomitant alarm vocalization in the rat. It is assumed that the activity of cholinergic neurons of the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LDT) will cause release of acetylcholine in the target areas and will initiate the emission of 22kHz vocalizations. The goal of the present study was to test the hypothesis that the cholinergic neurons of the LDT increase their activity during emission of 22kHz alarm calls. Vocalizations were induced by an air puff or by intrahypothalamic-preoptic injection of carbachol. The activity of the LDT cholinergic neurons was studied by a double histochemical labelling for choline acetyltransferase, as a marker of cholinergic somata, and for c-Fos protein, as a marker of cells with heighten metabolic activity. Both air puff stimulation and intracerebral carbachol induced comparable 22kHz alarm vocalizations. The activity of neurons in the LDT was significantly higher during prolonged emission of 22kHz alarm calls induced by air puff or injection of carbachol than in the non-vocalizing or low-vocalizing controls. There were approximately two times more of all c-Fos-labelled cells in the LDT of vocalizing animals and 2.5 times more active cholinergic neurons during prolonged 22kHz vocalization than in the control conditions without vocalization. However, the active cholinergic neurons constituted only a small proportion of all active LDT cells (2.3%). At the same time, there were no significant increases in the number of c-Fos-labelled cells in the neighbouring pedunculopontine nucleus (PPT). These findings lead to the conclusion that the neurons of the LDT, including cholinergic neurons, but not those of the PPT, significantly increased their activity during prolonged emission of alarm vocalizations, as evidenced by the c-Fos immunoreactivity. | 21827793
 |
Orexin-B-like immunoreactivity localized in both luteinizing hormone- and thyroid-stimulating hormone-containing cells in the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) pituitary.
H Suzuki, A Matsumoto, T Yamamoto
Tissue cell
41
75-8
2009
Show Abstract
Immunohistochemical techniques were employed to examine orexin-like immunoreactivities in the pituitary of the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Rabbit anti-orexin-A serum and mouse anti-orexin-B monoclonal antibodies were used as primary antibodies. Orexin-B immunoreactive cells corresponded to luteinizing hormone (LH)- or thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)-containing cells, and all LH- and TSH-containing cells were immunoreactive for orexin-B. However, we found no orexin-A immunoreactive cells in the pituitary. In the Nile tilapia, an orexin-B-like substance may be secreted from LH- or TSH-containing cells and may regulate pituitary function, rather than the orexin-A-like substance in the pituitaries of Japanese seaperch and medaka. | 18656218
 |
PR_b-targeted PEGylated liposomes for prostate cancer therapy.
Döne Demirgöz, Ashish Garg, Efrosini Kokkoli
Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids
24
13518-24
2008
Show Abstract
In recent years, there has been considerable effort in designing improved delivery systems by including site-directed surface ligands to further enhance their selective targeting. The goal of this study is to engineer alpha5beta1-targeted stealth liposomes (nanoparticles covered with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)) that will bind to alpha5beta1-expressing LNCaP human prostate cancer cells and efficiently release the encapsulated load intracellularly. For this purpose, liposomes (with and without PEG2000) were functionalized with a fibronectin-mimetic peptide (PR_b) and delivered to LNCaPs. The amount of PEG2000 and other liposomal components were characterized by 1H NMR, and the amount of peptide by the bicinchoninic acid protein assay. Fibronectin is the natural ligand for alpha5beta1, and a promising design for a fibronectinmimetic peptide includes both the primary binding site (RGD) and the synergy site (PHSRN) connected by a linker and extended off a surface by a spacer. We have previously designed a peptide-amphiphile, PRb, that employed a hydrophobic tail, connected to the N-terminus of a peptide headgroup composed of a spacer, the synergy site sequence, a linker mimicking both the distance and hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity present in the native protein fibronectin (thus presenting an overall "neutral" linker), and finally the primary binding sequence. We have examined different liposomal formulations, functionalized only with PR_b or with PR_b and PEG2000. For PR_b-targeted PEGylated liposomes, efficient cell binding was observed for peptide concentrations of 2 mol % and higher. When compared to GRGDSP-targeted stealth liposomes, PR_b functionalization was superior to that of GRGDSP as shown by increased LNCaP binding, internalization efficiency, as well as cytotoxicity after incubation of LNCaPs with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha)-encapsulated liposomes. More importantly, PR_b is alpha5beta1-specific, whereas many integrins bind to small RGD peptides. Thus, the proposed PR_b-targeted delivery system has the potential to deliver a therapeutic payload to prostate cancer cells in an efficient and specific manner. | 18954096
 |
Differential distribution of orexin-A-like and orexin receptor 1 (OX1R)-like immunoreactivities in the Xenopus pituitary.
H Suzuki, Y Takemoto, T Yamamoto
Tissue cell
39
423-30
2007
Show Abstract
Immunohistochemical techniques were employed to investigate orexin-A-like and orexin receptor 1 (OX1R)-like immunoreactivities in the Xenopus pituitary gland. Orexin-A-immunoreactive cells were mainly scattered in the posterior half of the pars distalis. They corresponded to thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)-containing cells and so far have not corresponded to other types of pituitary adenocytes. On the other hand, OX1R-immunoreactive cells were mainly distributed in the anterior half of the pars distalis and corresponded to prolactin (PRL)-containing cells; however, we found that OX1R-immunoreactive cells did not correspond to other types of adenocytes in the Xenopus pituitary. These results suggest that an orexin-A-like substance secretes with and/or without TSH from TSH-containing cells and that the peptide modulates the functions of PRL-containing cells via OX1R in a paracrine fashion. | 17897692
 |
Spontaneous regeneration of the corticospinal tract after transection in young rats: a key role of reactive astrocytes in making favorable and unfavorable conditions for regeneration.
T Iseda, T Nishio, S Kawaguchi, M Yamanoto, T Kawasaki, S Wakisaka
Neuroscience
126
365-74
2004
Show Abstract
We demonstrated the occurrence of marked regeneration of the corticospinal tract (CST) after a single transection and failure of regeneration after a repeated transection in young rats. To provide convincing evidence for the complete transection and regeneration we used retrograde neuronal double labeling. Double-labeled neurons that took up the first tracer from the transection site and the second tracer from the injection site caudal to the transection site were observed in the sensorimotor cortex. The anterograde tracing method revealed various patterns of regeneration. In the most successful cases the vast majority of regenerated fibers descended in the normal tract and terminated normally whereas a trace amount of fibers coursed aberrantly. In the less successful cases fibers descended partly normally and partly aberrantly or totally aberrantly. To clarify the role of astrocytes in determining the success or failure of regeneration we compared expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), vimentin and neurofilament (NF) immunoreactivity (IR) in the lesion between single and repeated transections. In either transection, astrocytes disappeared from the CST near the lesion site as early as 3 h after lesioning. However, by 24 h after a single transection, immature astrocytes coexpressing GFAP- and vimentin-IR appeared in the former astrocyte-free area and NF-positive axons crossed the lesion. By contrast, after a repeated transection the astrocyte-free area spread and NF-positive axons never crossed the lesion. It appears likely that the major sign, and possibly cause of failure of regeneration is the prolonged disappearance of astrocytes in the lesioned tract area. | 15207354
 |
Interactions of proteases, protease inhibitors, and the beta1 integrin/laminin gamma3 protein complex in the regulation of ectoplasmic specialization dynamics in the rat testis.
Siu, MK; Cheng, CY
Biology of reproduction
70
945-64
2004
Show Abstract
During spermatogenesis, developing germ cells migrate progressively across the seminiferous epithelium. This event requires extensive restructuring of cell-cell actin-based adherens junctions (AJs), such as the ectoplasmic specialization (ES, a testis-specific AJ type), between Sertoli cells and elongating/elongate spermatids. It was postulated that proteases and protease inhibitors worked in a yin-yang relationship to regulate these events. If this is true, then it is anticipated that both proteases and protease inhibitors are found at the ES. Indeed, matrix metalloprotease (MMP)-2, membrane-type 1 (MT1)-MMP and their inhibitor, tissue-inhibitor of metalloproteases (TIMP)-2, were shown to localize at the apical ES. In order to identify the putative MMP substrate as well as the unknown binding ligand for alpha6beta1 integrin in the ES, immunofluorescent microscopy coupled with immunoprecipitation techniques were used to demonstrate that laminin gamma3, largely a germ cell product, was present at the apical ES and could form a bona fide complex with beta1-integrin. Furthermore, the structural interactions of MMP-2 and MT1-MMP with laminin gamma3 and beta1-integrin, but not with N-cadherin or nectin-3, have implicated the crucial role of MMP-2/MT1-MMP in the regulation of integrin/laminin-based ES dynamics. Using an in vivo model to study AJ dynamics where adult rats were treated with 1-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)-indazole-3-carbohydrazide (AF-2364) to disrupt Sertoli-germ cell adhesive function, an induction of active MMP-2, active MT1-MMP and TIMP-2 but not active MMP-9 was detected between 0.5 and 8 h after AF-2364 treatment. This time frame coincided with the depletion of elongating/elongate spermatids from the epithelium, illustrating the synergistic relationships between MMP-2, MT1-MMP, and TIMP-2 in AJ disassembly. Perhaps the most important of all, the use of a specific MMP-2 and MMP-9 inhibitor, (2R)-2-[(4-biphenylylsulfonyl)amino]-3-phenylpropionic acid, could effectively delay the AF-2364-induced elongating/elongate spermatid loss from the epithelium, demonstrating the pivotal role of MMP-2 activation in ES disassembly. Collectively, these studies illustrate that the beta1-integrin/laminin gamma3 complex is a putative ES-structural protein complex, which is regulated, at least in part, by the activation of MMP-2 involving MT1-MMP and TIMP-2 at the apical ES. The net result of this interaction likely regulates germ cell movement in the seminiferous epithelium. | 14645107
 |