Selection and characterization of llama single domain antibodies against N-terminal huntingtin.
Schut, MH; Pepers, BA; Klooster, R; van der Maarel, SM; El Khatabi, M; Verrips, T; den Dunnen, JT; van Ommen, GJ; van Roon-Mom, WM
Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology
36
429-34
2015
Show Abstract
Huntington disease is caused by expansion of a CAG repeat in the huntingtin gene that is translated into an elongated polyglutamine stretch within the N-terminal domain of the huntingtin protein. The mutation is thought to introduce a gain-of-toxic function in the mutant huntingtin protein, and blocking this toxicity by antibody binding could alleviate Huntington disease pathology. Llama single domain antibodies (VHH) directed against mutant huntingtin are interesting candidates as therapeutic agents or research tools in Huntington disease because of their small size, high thermostability, low cost of production, possibility of intracellular expression, and potency of blood-brain barrier passage. We have selected VHH from llama phage display libraries that specifically target the N-terminal domain of the huntingtin protein. Our VHH are capable of binding wild-type and mutant human huntingtin under native and denatured conditions and can be used in Huntington disease studies as a novel antibody that is easy to produce and manipulate. | | 25294428
 |
Inhibition of mitochondrial protein import by mutant huntingtin.
Yano, H; Baranov, SV; Baranova, OV; Kim, J; Pan, Y; Yablonska, S; Carlisle, DL; Ferrante, RJ; Kim, AH; Friedlander, RM
Nature neuroscience
17
822-31
2014
Show Abstract
Mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with neuronal loss in Huntington's disease (HD), a neurodegenerative disease caused by an abnormal polyglutamine expansion in huntingtin (Htt). However, the mechanisms linking mutant Htt and mitochondrial dysfunction in HD remain unknown. We identify an interaction between mutant Htt and the TIM23 mitochondrial protein import complex. Remarkably, recombinant mutant Htt directly inhibited mitochondrial protein import in vitro. Furthermore, mitochondria from brain synaptosomes of presymptomatic HD model mice and from mutant Htt-expressing primary neurons exhibited a protein import defect, suggesting that deficient protein import is an early event in HD. The mutant Htt-induced mitochondrial import defect and subsequent neuronal death were attenuated by overexpression of TIM23 complex subunits, demonstrating that deficient mitochondrial protein import causes mutant Htt-induced neuronal death. Collectively, these findings provide evidence for a direct link between mutant Htt, mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal pathology, with implications for mitochondrial protein import-based therapies in HD. | | 24836077
 |
Phosphorylation of mutant huntingtin at serine 116 modulates neuronal toxicity.
Watkin, EE; Arbez, N; Waldron-Roby, E; O'Meally, R; Ratovitski, T; Cole, RN; Ross, CA
PloS one
9
e88284
2014
Show Abstract
Phosphorylation has been shown to have a significant impact on expanded huntingtin-mediated cellular toxicity. Several phosphorylation sites have been identified on the huntingtin (Htt) protein. To find new potential therapeutic targets for Huntington's Disease (HD), we used mass spectrometry to identify novel phosphorylation sites on N-terminal Htt, expressed in HEK293 cells. Using site-directed mutagenesis we introduced alterations of phosphorylation sites in a N586 Htt construct containing 82 polyglutamine repeats. The effects of these alterations on expanded Htt toxicity were evaluated in primary neurons using a nuclear condensation assay and a direct time-lapse imaging of neuronal death. As a result of these studies, we identified several novel phosphorylation sites, validated several known sites, and discovered one phospho-null alteration, S116A, that had a protective effect against expanded polyglutamine-mediated cellular toxicity. The results suggest that S116 is a potential therapeutic target, and indicate that our screening method is useful for identifying candidate phosphorylation sites. | | 24505464
 |
MAP kinase phosphatase 1 (MKP-1/DUSP1) is neuroprotective in Huntington's disease via additive effects of JNK and p38 inhibition.
Taylor, DM; Moser, R; Régulier, E; Breuillaud, L; Dixon, M; Beesen, AA; Elliston, L; Silva Santos, Mde F; Kim, J; Jones, L; Goldstein, DR; Ferrante, RJ; Luthi-Carter, R
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
33
2313-25
2013
Show Abstract
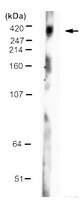
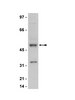
We previously demonstrated that sodium butyrate is neuroprotective in Huntington's disease (HD) mice and that this therapeutic effect is associated with increased expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase/dual-specificity phosphatase 1 (MKP-1/DUSP1). Here we show that enhancing MKP-1 expression is sufficient to achieve neuroprotection in lentiviral models of HD. Wild-type MKP-1 overexpression inhibited apoptosis in primary striatal neurons exposed to an N-terminal fragment of polyglutamine-expanded huntingtin (Htt171-82Q), blocking caspase-3 activation and significantly reducing neuronal cell death. This neuroprotective effect of MKP-1 was demonstrated to be dependent on its enzymatic activity, being ablated by mutation of its phosphatase domain and being attributed to inhibition of specific MAP kinases (MAPKs). Overexpression of MKP-1 prevented the polyglutamine-expanded huntingtin-induced activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) and p38 MAPKs, whereas extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 activation was not altered by either polyglutamine-expanded Htt or MKP-1. Moreover, mutants of MKP-1 that selectively prevented p38 or JNK binding confirmed the important dual contributions of p38 and JNK regulation to MKP-1-mediated neuroprotection. These results demonstrate additive effects of p38 and JNK MAPK inhibition by MKP-1 without consequence to ERK activation in this striatal neuron-based paradigm. MKP-1 also provided neuroprotection in vivo in a lentiviral model of HD neuropathology in rat striatum. Together, these data extend previous evidence that JNK- and p38-mediated pathways contribute to HD pathogenesis and, importantly, show that therapies simultaneously inhibiting both JNK and p38 signaling pathways may lead to improved neuroprotective outcomes. | Western Blotting, Immunohistochemistry, Immunocytochemistry | 23392662
 |
MicroRNA-22 (miR-22) overexpression is neuroprotective via general anti-apoptotic effects and may also target specific Huntington's disease-related mechanisms.
Jovicic, A; Zaldivar Jolissaint, JF; Moser, R; Silva Santos, Mde F; Luthi-Carter, R
PloS one
8
e54222
2013
Show Abstract
Whereas many causes and mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases have been identified, very few therapeutic strategies have emerged in parallel. One possible explanation is that successful treatment strategy may require simultaneous targeting of more than one molecule of pathway. A new therapeutic approach to have emerged recently is the engagement of microRNAs (miRNAs), which affords the opportunity to target multiple cellular pathways simultaneously using a single sequence.We identified miR-22 as a potentially neuroprotective miRNA based on its predicted regulation of several targets implicated in Huntington's disease (histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4), REST corepresor 1 (Rcor1) and regulator of G-protein signaling 2 (Rgs2)) and its diminished expression in Huntington's and Alzheimer's disease brains. We then tested the hypothesis that increasing cellular levels of miRNA-22 would achieve neuroprotection in in vitro models of neurodegeneration. As predicted, overexpression of miR-22 inhibited neurodegeneration in primary striatal and cortical cultures exposed to a mutated human huntingtin fragment (Htt171-82Q). Overexpression of miR-22 also decreased neurodegeneration in primary neuronal cultures exposed to 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP), a mitochondrial complex II/III inhibitor. In addition, miR-22 improved neuronal viability in an in vitro model of brain aging. The mechanisms underlying the effects of miR-22 included a reduction in caspase activation, consistent with miR-22's targeting the pro-apoptotic activities of mitogen-activated protein kinase 14/p38 (MAPK14/p38) and tumor protein p53-inducible nuclear protein 1 (Tp53inp1). Moreover, HD-specific effects comprised not only targeting HDAC4, Rcor1 and Rgs2 mRNAs, but also decreasing focal accumulation of mutant Htt-positive foci, which occurred via an unknown mechanism.These data show that miR-22 has multipartite anti-neurodegenerative activities including the inhibition of apoptosis and the targeting of mRNAs implicated in the etiology of HD. These results motivate additional studies to evaluate the feasibility and therapeutic efficacy of manipulating miR-22 in vivo. | | 23349832
 |
S-nitrosylation of dynamin-related protein 1 mediates mutant huntingtin-induced mitochondrial fragmentation and neuronal injury in Huntington's disease.
Haun, F; Nakamura, T; Shiu, AD; Cho, DH; Tsunemi, T; Holland, EA; La Spada, AR; Lipton, SA
Antioxidants & redox signaling
19
1173-84
2013
Show Abstract
Dynamin-related protein1 (Drp1) is a large GTPase that mediates mitochondrial fission. We recently reported in Alzheimer's disease (AD) that S-nitrosylation of Drp1 (forming S-nitroso [SNO]-Drp1) results in GTPase hyperactivity and mitochondrial fragmentation, thus impairing bioenergetics and inducing synaptic damage and neuronal loss. Here, since aberrant mitochondrial dynamics are also key features of Huntington's disease (HD), we investigated whether formation of SNO-Drp1 contributes to the pathogenesis of HD in cell-based and animal models.We found that expression of mutant huntingtin (mutHTT) protein in primary cultured neurons triggers significant production of nitric oxide (NO). Consistent with this result, increased levels of SNO-Drp1 were found in the striatum of a transgenic mouse model of HD as well as in human postmortem brains from HD patients. Using specific fluorescence markers, we found that formation of SNO-Drp1 induced excessive mitochondrial fragmentation followed by loss of dendritic spines, signifying synaptic damage. These neurotoxic events were significantly abrogated after transfection with non-nitrosylatable mutant Drp1(C644A), or by the blocking of NO production using an nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. These findings suggest that SNO-Drp1 is a key mediator of mutHTT toxicity, and, thus, may represent a novel drug target for HD.Our findings indicate that aberrant S-nitrosylation of Drp1 is a prominent pathological feature of neurodegenerative diseases such as AD and HD. Moreover, the SNO-Drp1 signaling pathway links mutHTT neurotoxicity to a malfunction in mitochondrial dynamics, resulting in neuronal synaptic damage in HD. | | 23641925
 |
Dose-dependent neuroprotection of VEGF₁₆₅ in Huntington's disease striatum.
Ellison, SM; Trabalza, A; Tisato, V; Pazarentzos, E; Lee, S; Papadaki, V; Goniotaki, D; Morgan, S; Mirzaei, N; Mazarakis, ND
Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy
21
1862-75
2013
Show Abstract
Huntington's disease (HD) is a devastating neurodegenerative disorder caused by abnormal polyglutamine expansion in the huntingtin protein (Exp-Htt). Currently, there are no effective treatments for HD. We used bidirectional lentiviral transfer vectors to generate in vitro and in vivo models of HD and to test the therapeutic potential of vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF₁₆₅). Lentiviral-mediated expression of Exp-Htt caused cell death and aggregate formation in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y and rat primary striatal cultures. Lentiviral-mediated VEGF₁₆₅ expression was found to be neuroprotective in both of these models. Unilateral stereotaxic vector delivery of Exp-Htt vector in adult rat striatum led to progressive inclusion formation and striatal neuron loss at 10 weeks post-transduction. Coinjection of a lower dose VEGF₁₆₅ significantly attenuated DARPP-32(+) neuronal loss, enhanced NeuN staining and reduced Exp-Htt aggregation. A tenfold higher dose VEGF₁₆₅ led to overt neuronal toxicity marked by tissue damage, neovascularization, extensive astrogliosis, vascular leakage, chronic inflammation and distal neuronal loss. No overt behavioral phenotype was observed in these animals. Expression of VEGF₁₆₅ at this higher dose in the brain of wild-type rats led to early mortality with global neuronal loss. This report raises important safety concerns about unregulated VEGF₁₆₅ CNS applications. | | 23799534
 |
Sirt1 mediates neuroprotection from mutant huntingtin by activation of the TORC1 and CREB transcriptional pathway.
Jeong, H; Cohen, DE; Cui, L; Supinski, A; Savas, JN; Mazzulli, JR; Yates, JR; Bordone, L; Guarente, L; Krainc, D
Nature medicine
18
159-65
2012
Show Abstract
Sirt1, a NAD-dependent protein deacetylase, has emerged as a key regulator of mammalian transcription in response to cellular metabolic status and stress. Here we show that Sirt1 has a neuroprotective role in models of Huntington's disease, an inherited neurodegenerative disorder caused by a glutamine repeat expansion in huntingtin protein (HTT). Brain-specific knockout of Sirt1 results in exacerbation of brain pathology in a mouse model of Huntington's disease, whereas overexpression of Sirt1 improves survival, neuropathology and the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in Huntington's disease mice. We show that Sirt1 deacetylase activity directly targets neurons to mediate neuroprotection from mutant HTT. The neuroprotective effect of Sirt1 requires the presence of CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 1 (TORC1), a brain-specific modulator of CREB activity. We show that under normal conditions, Sirt1 deacetylates and activates TORC1 by promoting its dephosphorylation and its interaction with CREB. We identified BDNF as a key target of Sirt1 and TORC1 transcriptional activity in both normal and Huntington's disease neurons. Mutant HTT interferes with the TORC1-CREB interaction to repress BDNF transcription, and Sirt1 rescues this defect in vitro and in vivo. These studies suggest a key role for Sirt1 in transcriptional networks in both the normal and Huntington's disease brain and offer an opportunity for therapeutic development. | | 22179316
 |
Examination of mesenchymal stem cell-mediated RNAi transfer to Huntington's disease affected neuronal cells for reduction of huntingtin.
Olson, SD; Kambal, A; Pollock, K; Mitchell, GM; Stewart, H; Kalomoiris, S; Cary, W; Nacey, C; Pepper, K; Nolta, JA
Molecular and cellular neurosciences
49
271-81
2012
Show Abstract
Huntington's disease (HD) is a fatal, autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder caused by an expanded trinucleotide (CAG) repeat in exon 1 of the huntingtin gene (Htt). This expansion creates a toxic polyglutamine tract in the huntingtin protein (HTT). Currently, there is no treatment for either the progression or prevention of the disease. RNA interference (RNAi) technology has shown promise in transgenic mouse models of HD by reducing expression of mutant HTT and slowing disease progression. The advancement of RNAi therapies to human clinical trials is hampered by problems delivering RNAi to affected neurons in a robust and sustainable manner. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have demonstrated a strong safety profile in both completed and numerous ongoing clinical trials. MSC exhibit a number of innate therapeutic effects, such as immune system modulation, homing to injury, and cytokine release into damaged microenvironments. The ability of MSC to transfer larger molecules and even organelles suggested their potential usefulness as delivery vehicles for therapeutic RNA inhibition. In a series of model systems we have found evidence that MSC can transfer RNAi targeting both reporter genes and mutant huntingtin in neural cell lines. MSC expressing shRNA antisense to GFP were found to decrease expression of GFP in SH-SY5Y cells after co-culture when assayed by flow cytometry. Additionally MSC expressing shRNA antisense to HTT were able to decrease levels of mutant HTT expressed in both U87 and SH-SY5Y target cells when assayed by Western blot and densitometry. These results are encouraging for expanding the therapeutic abilities of both RNAi and MSC for future treatments of Huntington's disease. | | 22198539
 |
Adenovirus vector-based in vitro neuronal cell model for Huntington's disease with human disease-like differential aggregation and degeneration.
Xiaomin Dong,Shan Zong,Anke Witting,Katrin S Lindenberg,Stefan Kochanek,Bin Huang
The journal of gene medicine
14
2012
Show Abstract
Neuronal degeneration, in particular in the striatum, and the formation of nuclear and cytoplasmic inclusions are characteristics of Huntington's disease (HD) as a result of the expansion of a polyglutamine tract located close to the N-terminus of huntingtin (htt). Because of the large (10-kb) size of the htt cDNA, expression of full-length htt in primary neurons has proved difficult in the past. | | 22700462
 |
























-(+)-1-Phenylethylamine[807031_(R)-(+)-1-Phenylethylamine-ALL].jpg)