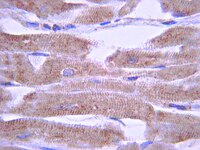
Lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation attenuates taste progenitor cell proliferation and shortens the life span of taste bud cells.
Cohn, ZJ; Kim, A; Huang, L; Brand, J; Wang, H
BMC neuroscience
11
72
2009
Afficher le résumé
The mammalian taste bud, a complex collection of taste sensory cells, supporting cells, and immature basal cells, is the structural unit for detecting taste stimuli in the oral cavity. Even though the cells of the taste bud undergo constant turnover, the structural homeostasis of the bud is maintained by balancing cell proliferation and cell death. Compared with nongustatory lingual epithelial cells, taste cells express higher levels of several inflammatory receptors and signalling proteins. Whether inflammation, an underlying condition in some diseases associated with taste disorders, interferes with taste cell renewal and turnover is unknown. Here we report the effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation on taste progenitor cell proliferation and taste bud cell turnover in mouse taste tissues.Intraperitoneal injection of LPS rapidly induced expression of several inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interferon (IFN)-gamma, and interleukin (IL)-6, in mouse circumvallate and foliate papillae. TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma immunoreactivities were preferentially localized to subsets of cells in taste buds. LPS-induced inflammation significantly reduced the number of 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU)-labeled newborn taste bud cells 1-3 days after LPS injection, suggesting an inhibition of taste bud cell renewal. BrdU pulse-chase experiments showed that BrdU-labeled taste cells had a shorter average life span in LPS-treated mice than in controls. To investigate whether LPS inhibits taste cell renewal by suppressing taste progenitor cell proliferation, we studied the expression of Ki67, a cell proliferation marker. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR revealed that LPS markedly reduced Ki67 mRNA levels in circumvallate and foliate epithelia. Immunofluorescent staining using anti-Ki67 antibodies showed that LPS decreased the number of Ki67-positive cells in the basal regions surrounding circumvallate taste buds, the niche for taste progenitor cells. PCR array experiments showed that the expression of cyclin B2 and E2F1, two key cell cycle regulators, was markedly downregulated by LPS in the circumvallate and foliate epithelia.Our results show that LPS-induced inflammation inhibits taste progenitor cell proliferation and interferes with taste cell renewal. LPS accelerates cell turnover and modestly shortens the average life span of taste cells. These effects of inflammation may contribute to the development of taste disorders associated with infections. | 20537148
 |
Kcnq1 contributes to an adrenergic-sensitive steady-state K+ current in mouse heart.
Bjorn C Knollmann, Syevda Sirenko, Qi Rong, Alexander N Katchman, Mathew Casimiro, Karl Pfeifer, Steven N Ebert
Biochemical and biophysical research communications
360
212-8
2007
Afficher le résumé
It has been suggested that Kcne1 subunits are required for adrenergic regulation of Kcnq1 potassium channels. However, in adult mouse hearts, which do not express Kcne1, loss of Kcnq1 causes a Long QT phenotype during adrenergic challenge, raising the possibility that native Kcnq1 currents exist and are adrenergically regulated even in absence of Kcne1. Here, we used immunoblotting and immunohistochemical staining to show that Kcnq1 protein is present in adult mouse hearts. Voltage-clamp experiments demonstrated that Kcnq1 contributes to a steady-state outward current (I(SS)) in wild-type (Kcnq1(+/+)) ventricular myocytes during isoproterenol stimulation, resulting in a significant 7.1% increase in I(SS) density (0.43+/-0.16 pA/pF, p 0.05, n =15), an effect that was absent in Kcnq1-deficient (Kcnq1(-/-)) myocytes (-0.14+/-0.13 pA/pF, n =17). These results demonstrate for the first time that Kcnq1 protein is expressed in adult mouse hearts where it contributes to a beta-adrenergic-induced component of I(SS) that does not require co-assembly with Kcne1. Article en texte intégral | 17597584
 |
The KCNE2 potassium channel ancillary subunit is essential for gastric acid secretion.
Roepke, TK; Anantharam, A; Kirchhoff, P; Busque, SM; Young, JB; Geibel, JP; Lerner, DJ; Abbott, GW
The Journal of biological chemistry
281
23740-7
2005
Afficher le résumé
Genes in the KCNE family encode single transmembrane domain ancillary subunits that co-assemble with voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel alpha subunits to alter their function. KCNE2 (also known as MiRP1) is expressed in the heart, is associated with human cardiac arrhythmia, and modulates cardiac Kv alpha subunits hERG and KCNQ1 in vitro. KCNE2 and KCNQ1 are also expressed in parietal cells, leading to speculation they form a native channel complex there. Here, we disrupted the murine kcne2 gene and found that kcne2 (-/-) mice have a severe gastric phenotype with profoundly reduced parietal cell proton secretion, abnormal parietal cell morphology, achlorhydria, hypergastrinemia, and striking gastric glandular hyperplasia arising from an increase in the number of non-acid secretory cells. KCNQ1 exhibited abnormal distribution in gastric glands from kcne2 (-/-) mice, with increased expression in non-acid secretory cells. Parietal cells from kcne2 (+/-) mice exhibited normal architecture but reduced proton secretion, and kcne2 (+/-) mice were hypochlorhydric, indicating a gene-dose effect and a primary defect in gastric acid secretion. These data demonstrate that KCNE2 is essential for gastric acid secretion, the first genetic evidence that a member of the KCNE gene family is required for normal gastrointestinal function. | 16754665
 |