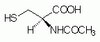
MAB3786-25UG Sigma-AldrichAnti-APC CT, clone C-APC 28.9
Anti-APC Antibody, C-terminus, clone C-APC 28.9 is a Mouse Monoclonal Antibody for detection of APC also known as Adenomatous Polyposis Coli Protein & has been validated in IF, IP, WB & IHC.
More>> Anti-APC Antibody, C-terminus, clone C-APC 28.9 is a Mouse Monoclonal Antibody for detection of APC also known as Adenomatous Polyposis Coli Protein & has been validated in IF, IP, WB & IHC. Less<<Produits recommandés
Aperçu
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Tableau de caractéristiques principal
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H, M | IF, IP, WB, IHC | M | Purified | Monoclonal Antibody |
| References |
|---|
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Purified |
| Control |
|
| Presentation | Purified immunoglobulin. Liquid in 0.02M phosphate buffer, 0.25M NaCl, pH 7.6, with 0.1% sodium azide. |
| Quality Level | MQ100 |
| Physicochemical Information |
|---|
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information |
|---|
| Storage and Shipping Information | |
|---|---|
| Storage Conditions | Maintain at 2-8°C in undiluted aliquots for up to 12 months from date of receipt. |
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 25 μg |
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Référence | GTIN |
| MAB3786-25UG | 04054839350399 |
Documentation
Anti-APC CT, clone C-APC 28.9 Certificats d'analyse
| Titre | Numéro de lot |
|---|---|
| Anti-APC CT, clone C-APC 28.9 - 3894993 | 3894993 |
| Anti-APC CT, clone C-APC 28.9 - 4185970 | 4185970 |
| Anti-APC CT, clone C-APC 28.9 - 4219959 | 4219959 |