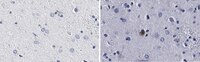
Identification of distinct conformations associated with monomers and fibril assemblies of mutant huntingtin.
Ko, J; Isas, JM; Sabbaugh, A; Yoo, JH; Pandey, NK; Chongtham, A; Ladinsky, M; Wu, WL; Rohweder, H; Weiss, A; Macdonald, D; Munoz-Sanjuan, I; Langen, R; Patterson, PH; Khoshnan, A
Hum Mol Genet
27
2330-2343
2018
Mostrar resumen
The N-terminal fragments of mutant huntingtin (mHTT) misfold and assemble into oligomers, which ultimately bundle into insoluble fibrils. Conformations unique to various assemblies of mHTT remain unknown. Knowledge on the half-life of various multimeric structures of mHTT is also scarce. Using a panel of four new antibodies named PHP1-4, we have identified new conformations in monomers and assembled structures of mHTT. PHP1 and PHP2 bind to epitopes within the proline-rich domain (PRD), whereas PHP3 and PHP4 interact with motifs formed at the junction of polyglutamine (polyQ) and polyproline (polyP) repeats of HTT. The PHP1- and PHP2-reactive epitopes are exposed in fibrils of mHTT exon1 (mHTTx1) generated from recombinant proteins and mHTT assemblies, which progressively accumulate in the nuclei, cell bodies and neuropils in the brains of HD mouse models. Notably, electron microscopic examination of brain sections of HD mice revealed that PHP1- and PHP2-reactive mHTT assemblies are present in myelin sheath and in vesicle-like structures. Moreover, PHP1 and PHP2 antibodies block seeding and subsequent fibril assembly of mHTTx1 in vitro and in a cell culture model of HD. PHP3 and PHP4 bind to epitopes in full-length and N-terminal fragments of monomeric mHTT and binding diminishes as the mHTTx1 assembles into fibrils. Interestingly, PHP3 and PHP4 also prevent the aggregation of mHTTx1 in vitro highlighting a regulatory function for the polyQ-polyP motifs. These newly detected conformations may affect fibril assembly, stability and intercellular transport of mHTT. | 29912367
 |