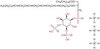
PF121 Sigma-Aldrichα-Sarcin, Aspergillus giganteus
Productos recomendados
Descripción
| Replacement Information |
|---|
Tabla espec. clave
| CAS # |
|---|
| 86243-64-3 |
| References | |
|---|---|
| References | Olma, N., et al. 2001. Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 2113. |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| CAS number | 86243-64-3 |
| Form | Lyophilized |
| Applications |
|---|
| Biological Information | |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Physicochemical Information | |
|---|---|
| Contaminants | A trace amount of the dimeric form. |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Materials Information |
|---|
| Toxicological Information |
|---|
| Safety Information according to GHS |
|---|
| Safety Information | |
|---|---|
| R Phrase | R: 42 May cause sensitization by inhalation. |
| S Phrase | S: 36 Wear suitable protective clothing. |
| Product Usage Statements |
|---|
| Packaging Information |
|---|
| Transport Information |
|---|
| Supplemental Information |
|---|
| Specifications |
|---|
| Global Trade Item Number | |
|---|---|
| Número de referencia | GTIN |
| PF121 | 0 |
Documentation
α-Sarcin, Aspergillus giganteus Ficha datos de seguridad (MSDS)
| Título |
|---|
α-Sarcin, Aspergillus giganteus Certificados de análisis
| Cargo | Número de lote |
|---|---|
| PF121 |
Referencias bibliográficas
| Visión general referencias |
|---|
| Olma, N., et al. 2001. Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 2113. |
Folleto
| Cargo |
|---|
| Caspases and other Apoptosis Related Tools Brochure |