PEGA resins
PEGA resins swell extensively in a wide range of solvents and are ideally suited for the preparation of peptide libraries, affinity purification, and on-resin enzyme assays.
Less<<
Recommended Products
-

126625 Sigma-Aldrich Albumin, Bovine Serum, 30% Aqueous Solution, Stabilizer-Free -

GM510/24-392 Millipore GMP500-1000 Male Bearing, EN1.4435/316L, MP Ra<0.25µm, SiC bearing, -

475843-50MG Sigma-Aldrich Minocycline, Hydrochloride - CAS 13614-98-7 - Calbiochem -

70767 Sigma-Aldrich pET Expression System 23 - Novagen -
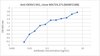
MABF2188-100UG Sigma-Aldrich Anti-Dengue Virus 1 Antibody, clone 271 -

P2B010A01 Millipore Pellicon® 2 Mini Cassette with Biomax® 10 kDa Membrane, A screen, 0.1 m² -

CWL671S03 Millipore Milligard® Low Protein Binding Cartridge Filter 10 in. Code 7 0.5 µm -
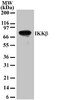
OP134 Sigma-Aldrich Anti-IKKβ Mouse mAb (10AG2) -

118603 Sigma-Aldrich Capping Reagent -

1133640009 Sigma-Aldrich Tetrahydrofuran-D8
Overview
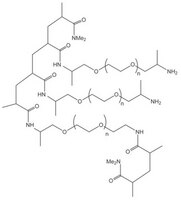
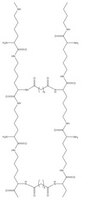
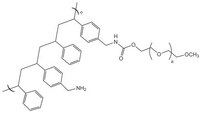
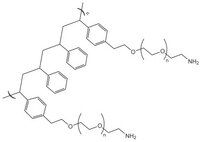
PEGA resins are hydrophilic polymers that consist of 2-acrylamidoprop-1-yl-(2-aminoprop-1-yl) polyethylene glycol800 and dimethylacylamide cross-linked with bis 2-acrylamidoprop-1-yl polyethylene glycol800 1. These supports swell extensively in a wide range of solvents, including water, DMF, DCM, THF and MeOH, and are freely permeable to macromolecules up to 35kD. These characteristics make them ideally suited for the preparation of peptide libraries, affinity purification, and on-resin enzyme assays. These properties have been exploited in the on-resin enzymatic synthesis of glycopeptides2; for determining the inhibitors of subtilisin Carlsberg3, Cruzipain4, cysteine proteases5, and matrix metalloproteinases6; and in studies on protein disulfide isomerases using fluorescence-quenched libraries7.
1. M. Meldal (1992) Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 3077.
2. M. Meldal et al. (1994) J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1849.
3. M. Meldal et al. (1994) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 3314.
4. M. Meldal, et al. (1998) J. Peptide Sci., 4, 83.
5. P. M. St. Hilaire, et al. (1999) J. Comb. Chem., 1, 509.
6. J. Buchardt, et al. (2000) J. Comb. Chem., 2, 624.
7. J. C. Spetzler, et al. (1998) J. Peptide Sci., 4, 128.