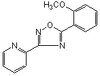
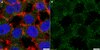
Expression of 1N3R-Tau isoform inhibits cell proliferation by inducing S phase arrest in N2a cells.
Li, L; Xu, ZP; Liu, GP; Xu, C; Wang, ZH; Li, XG; Liu, EJ; Zeng, J; Chai, DM; Yao, WL; Wang, JZ
PloS one
10
e0119865
2015
Show Abstract
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein implicated in neurodegenerative tauopathies. Six tau isoforms are generated from a single gene through alternative splicing of exons 2, 3 and 10 in human brain. Differential expression of tau isoforms has been detected in different brain areas, during neurodevelopment and in neurodegenerative disorders. However, the biological significance of different tau isoforms is not clear. Here, we investigated the individual effect of six different isoforms of tau on cell proliferation and the possible mechanisms by transient expression of eGFP-labeled tau isoform plasmid in N2a cells. Our study showed the transfection efficiency was comparable between different isoforms of tau by examining GFP expression. Compared with other isoforms, we found expression of 1N3R-tau significantly inhibited cell proliferation by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay and BrdU incorporation. Flow cytometry analysis further showed expression of 1N3R-tau induced S phase arrest. Compared with the longest isoform of tau, expression of 1N3R-tau induced cyclin E translocation from the nuclei to cytoplasm, while it did not change the level of cell cycle checkpoint proteins. These data indicate that 1N3R-tau inhibits cell proliferation through inducing S phase arrest. | Immunocytochemistry | 25822823
 |
Peptide-mediated disruption of calmodulin-cyclin E interactions inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and neointima formation.
Hui, S; Choi, J; Zaidi, S; Momen, A; Steinbach, SK; Sadi, AM; Ban, K; Husain, M
Circulation research
108
1053-62
2011
Show Abstract
Cell cycle progression in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) is a therapeutic target for restenosis.Having discovered that calmodulin (CaM)-dependent cyclin E/CDK2 activity underlies Ca(2+)-sensitive G(1)-to-S phase transitions in VSMCs, we sought to explore the physiological importance of the CaM-cyclin E interaction.A peptide based on the CaM binding sequence (CBS) of cyclin E was designed to interfere with CaM-cyclin E binding. Compared with control peptides, CBS blocked activating Thr160 phosphorylation of CDK2, decreased basal cyclin E/CDK2 activity, and eliminated Ca(2+)-sensitive cyclin E/CDK2 activity in nuclear extracts from mouse VSMCs. Nucleofection with CBS, or treatment with CBS conjugated to the HIV-1 TAT protein transduction domain to improve bioavailability, inhibited G(1)-to-S cell cycle progression in a dose-dependent manner. These effects were not observed with control peptides. TAT-CBS inhibited (3)H-thymidine incorporation in primary human aortic SMCs (HA-SMCs) in vitro, manifested greater transduction into HA-SMCs compared with endothelial cells in vitro, and limited decreased SM22α expression, neointima formation, and medial thickening without affecting collagen deposition or reendothelialization in a mouse model of carotid artery injury in vivo. The antiproliferative effects of CBS remained evident in mouse embryonic fibroblasts derived from wild-type mice but not cyclin E1/E2 double knockout mice.A synthetic peptide designed to disrupt CaM-cyclin E binding inhibits Ca(2+)/CaM-dependent CDK2 activity, cell cycle progression, and proliferation in VSMCs and limits arterial remodeling following injury. Importantly, this effect appears to be cyclin E-dependent and may form the basis of a potentially novel therapeutic approach for restenosis. | | 21372285
 |
Dissecting the role of p53 phosphorylation in homologous recombination provides new clues for gain-of-function mutants.
Restle, A; Färber, M; Baumann, C; Böhringer, M; Scheidtmann, KH; Müller-Tidow, C; Wiesmüller, L
Nucleic acids research
36
5362-75
2008
Show Abstract
Regulation of homologous recombination (HR) represents the best-characterized DNA repair function of p53. The role of p53 phosphorylation in DNA repair is largely unknown. Here, we show that wild-type p53 repressed repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) by HR in a manner partially requiring the ATM/ATR phosphorylation site, serine 15. Cdk-mediated phosphorylation of serine 315 was dispensable for this anti-recombinogenic effect. However, without targeted cleavage of the HR substrate, serine 315 phosphorylation was necessary for the activation of topoisomerase I-dependent HR by p53. Moreover, overexpression of cyclin A1, which mimics the situation in tumors, inappropriately stimulated DSB-induced HR in the presence of oncogenic p53 mutants (not Wtp53). This effect required cyclin A1/cdk-mediated phosphorylation for stable complex formation with topoisomerase I. We conclude that p53 mutants have lost the balance between activation and repression of HR, which results in a net increase of potentially mutagenic DNA rearrangements. Our data provide new insight into the mechanism underlying gain-of-function of mutant p53 in genomic instability. Full Text Article | | 18697815
 |
Inhibition of integrin-linked kinase/protein kinase B/Akt signaling: mechanism for ganglioside-induced apoptosis
Wang, X. Q., et al
J Biol Chem, 276:44504-11 (2001)
2001
| Immunoprecipitation, Immunoblotting (Western) | 11577096
 |
Divergence in signal transduction pathways of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors. Involvement of sphingosine 1-phosphate in PDGF but not EGF signaling.
Rani, C S, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 272: 10777-83 (1997)
1997
Show Abstract
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and serum, but not epidermal growth factor (EGF), stimulated sphingosine kinase activity in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts and increased intracellular concentrations of sphingosine 1-phosphate (SPP), a sphingolipid second messenger (Olivera, A., and Spiegel, S. (1993) Nature 365, 557-560). We report herein that DL-threo-dihydrosphingosine (DHS), a competitive inhibitor of sphingosine kinase that prevents PDGF-induced SPP formation, specifically inhibited the activation of two cyclin-dependent kinases (p34(cdc2) kinase and Cdk2 kinase) induced by PDGF, but not by EGF. SPP reversed the inhibitory effects of DHS on PDGF-stimulated cyclin-dependent kinases and DNA synthesis, demonstrating that the DHS effects were mediated via inhibition of sphingosine kinase. DHS also markedly reduced PDGF-stimulated but not EGF-stimulated mitogen-activated protein kinase activity and DNA binding activity of activator protein-1. Examination of the early signaling events of PDGF action revealed that DHS did not affect PDGF-induced autophosphorylation of the growth factor receptor or phosphorylation of the SH2/SH3 adaptor protein Shc and its association with Grb2. This sphingosine kinase inhibitor did not abrogate activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by PDGF. In agreement, treatment with SPP had no effect on these responses but did, however, potently stimulate phosphorylation of Crk, another SH2/SH3 adaptor protein. Moreover, DHS inhibited PDGF-stimulated, but not EGF-stimulated, Crk phosphorylation. Thus, regulation of sphingosine kinase activity defines divergence in signal transduction pathways of PDGF and EGF receptors leading to mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. | | 9099730
 |
Sublytic complement attack induces cell cycle in oligodendrocytes.
Rus, H G, et al.
J. Immunol., 156: 4892-900 (1996)
1996
Show Abstract
Sublytic complement attack on oligodendrocytes (OLG) by activation of terminal complement complexes (TCC) selectively enhances the decay of myelin protein mRNAs. We have investigated whether TCC also stimulate differentiated OLG to enter the cell cycle and whether the cell cycle induction is related to the oncogene expression. Complement activation and TCC assembly induced expression of c-jun, JunD, and c-fos mRNAs, increased AP-1 DNA-binding activity within 1 h, and increased [3H]thymidine uptake. The c-jun NH2-terminal kinase activity was increased to the maximum level 20 min after TCC assembly. The increase in thymidine uptake was inhibited by pretreatment of OLG with antisense c-jun oligonucleotides. Studies on cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) activation revealed that complement increased cyclin-dependent cell cycle associated kinase-2 activity in G1, while cdk2 and cdk4 showed low activity during G1 progression. However, the activity of cdk4 complexed with cyclin D2 showed a marked increase in G1/S transition. Our data provide evidence that sublytic TCC stimulate OLG to enter the cell cycle by induction of c-jun through activation of the c-jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway. In addition, sublytic TCC assembly significantly reduced the number of OLG undergoing apoptotic cell death, which occurs spontaneously in defined medium. These changes together with enhanced degradation of myelin protein mRNA may represent a mechanism for differentiated primary OLG to respond to limited complement activation in inflammation. | | 8648139
 |
CDK2 encodes a 33-kDa cyclin A-associated protein kinase and is expressed before CDC2 in the cell cycle.
Elledge, S J, et al.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 89: 2907-11 (1992)
1992
Show Abstract
Critical cell cycle transitions are controlled by the coordinate actions of the p34cdc2 protein kinase and its regulatory subunits, cyclins. Recently we identified another human p34 homolog, cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) by complementation of a cdc28-4 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a lambda YES human cDNA expression library. CDK2 is 66% identical to CDC2Hs and 89% identical to the Xenopus Eg1 gene, forming a distinct subfamily of CDC2-related protein kinases. We have found that CDK2 encodes a 33-kDa cyclin A-associated protein kinase that contains phosphotyrosine, two characteristics it shares with CDC2Hs. However, we show that the subunit composition of these two protein kinase complexes can vary in different cell types, that they have different in vitro substrate preferences, and that CDK2 mRNA is observed much earlier than CDC2Hs mRNA when lymphocytes are stimulated to enter the cell cycle. We suggest that cells in different developmental or transformed states may have different mechanisms of cell cycle regulation. | | 1372993
 |
A new human p34 protein kinase, CDK2, identified by complementation of a cdc28 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a homolog of Xenopus Eg1.
Elledge, S J and Spottswood, M R
EMBO J., 10: 2653-9 (1991)
1991
Show Abstract
The onset of S-phase and M-phase in both Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires the function of the cdc2/CDC28 gene product, p34, a serine-threonine protein kinase. A human homolog, p34cdc2, was identified by functional complementation of the S.pombe cdc2 mutation (Lee and Nurse, 1987). Using a human cDNA expression library to search for suppressors of cdc28 mutations in S. cerevisiae, we have identified a second functional p34 homolog, CDK2 cell division kinase). This gene is expressed as a 2.1 kb transcript encoding a polypeptide of 298 amino acids. This protein retains nearly all of the amino acids highly conserved among previously identified p34 homologs from other species, but is considerably divergent from all previous p34cdc2 homologs, approximately 65% identity. This gene encodes the human homolog of the Xenopus Eg1 gene, sharing 89% amino acid identity, and defines a second sub-family of CDC2 homologs. A second chromosomal mutation which arose spontaneously was required to allow complementation of the cdc28-4 mutation by CDK2. This mutation blocked the ability of this strain to mate. These results suggest that the machinery controlling the human cell cycle is more complex than that for fission and budding yeast. | | 1714386
 |