Decitabine alters the expression of Mecp2 isoforms via dynamic DNA methylation at the Mecp2 regulatory elements in neural stem cells.
Liyanage, VR; Zachariah, RM; Rastegar, M
Molecular autism
4
46
2013
Show Abstract
Aberrant MeCP2 expression in brain is associated with neurodevelopmental disorders including autism. In the brain of stressed mouse and autistic human patients, reduced MeCP2 expression is correlated with Mecp2/MECP2 promoter hypermethylation. Altered expression of MeCP2 isoforms (MeCP2E1 and MeCP2E2) is associated with neurological disorders, highlighting the importance of proper regulation of both isoforms. While known regulatory elements (REs) within the MECP2/Mecp2 promoter and intron 1 are involved in MECP2/Mecp2 regulation, Mecp2 isoform-specific regulatory mechanisms are unknown. We hypothesized that DNA methylation at these REs may impact the expression of Mecp2 isoforms.We used a previously characterized in vitro differentiating neural stem cell (NSC) system to investigate the interplay between Mecp2 isoform-specific expression and DNA methylation at the Mecp2 REs. We studied altered expression of Mecp2 isoforms, affected by global DNA demethylation and remethylation, induced by exposure and withdrawal of decitabine (5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine). Further, we performed correlation analysis between DNA methylation at the Mecp2 REs and the expression of Mecp2 isoforms after decitabine exposure and withdrawal.At different stages of NSC differentiation, Mecp2 isoforms showed reciprocal expression patterns associated with minor, but significant changes in DNA methylation at the Mecp2 REs. Decitabine treatment induced Mecp2e1/MeCP2E1 (but not Mecp2e2) expression at day (D) 2, associated with DNA demethylation at the Mecp2 REs. In contrast, decitabine withdrawal downregulated both Mecp2 isoforms to different extents at D8, without affecting DNA methylation at the Mecp2 REs. NSC cell fate commitment was minimally affected by decitabine under tested conditions. Expression of both isoforms negatively correlated with methylation at specific regions of the Mecp2 promoter, both at D2 and D8. The correlation between intron 1 methylation and Mecp2e1 (but not Mecp2e2) varied depending on the stage of NSC differentiation (D2: negative; D8: positive).Our results show the correlation between the expression of Mecp2 isoforms and DNA methylation in differentiating NSC, providing insights on the potential role of DNA methylation at the Mecp2 REs in Mecp2 isoform-specific expression. The ability of decitabine to induce Mecp2e1/MeCP2E1, but not Mecp2e2 suggests differential sensitivity of Mecp2 isoforms to decitabine and is important for future drug therapies for autism. | | | 24238559
 |
Disease Modeling Using Embryonic Stem Cells: MeCP2 Regulates Nuclear Size and RNA Synthesis in Neurons.
Morteza Yazdani,Rub Deogracias,Jacky Guy,Raymond A Poot,Adrian Bird,Yves-Alain Barde
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio)
30
2012
Show Abstract
Mutations in the gene encoding the methyl-CpG-binding protein MECP2 are the major cause of Rett syndrome, an autism spectrum disorder mainly affecting young females. MeCP2 is an abundant chromatin-associated protein, but how and when its absence begins to alter brain function is still far from clear. Using a stem cell-based system allowing the synchronous differentiation of neuronal progenitors, we found that in the absence of MeCP2, the size of neuronal nuclei fails to increase at normal rates during differentiation. This is accompanied by a marked decrease in the rate of ribonucleotide incorporation, indicating an early role of MeCP2 in regulating total gene transcription, not restricted to selected mRNAs. We also found that the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) were decreased in mutant neurons, while those of the presynaptic protein synaptophysin increased at similar rates in wild-type and mutant neurons. By contrast, nuclear size, transcription rates, and BDNF levels remained unchanged in astrocytes lacking MeCP2. Re-expressing MeCP2 in mutant neurons rescued the nuclear size phenotype as well as BDNF levels. These results reveal a new role of MeCP2 in regulating overall RNA synthesis in neurons during the course of their maturation, in line with recent findings indicating a reduced nucleolar size in neurons of the developing brain of mice lacking Mecp2. STEM Cells2012;30:2128-2139. | | | 22865604
 |
Association of time-dependent changes in mu opioid receptor mRNA, but not BDNF, TrkB, or MeCP2 mRNA and protein expression in the rat nucleus accumbens with incubation of heroin craving.
Theberge, FR; Pickens, CL; Goldart, E; Fanous, S; Hope, BT; Liu, QR; Shaham, Y
Psychopharmacology
224
559-71
2012
Show Abstract
Responding to heroin cues progressively increases after cessation of heroin self-administration (incubation of heroin craving). We investigated whether this incubation is associated with time-dependent changes in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) signaling and mu opioid receptor (MOR) expression in nucleus accumbens (NAc), dorsal striatum (DS), and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). We also investigated the effect of the preferential MOR antagonist naloxone on cue-induced heroin seeking during abstinence.We trained rats to self-administer heroin or saline for 9-10 days and then dissected the NAc, DS, and mPFC at different abstinence days and measured mRNA and protein levels of BDNF, TrkB, and MeCP2, as well as MOR mRNA (Oprm1). In other groups, we assessed cue-induced heroin seeking in extinction tests after 1, 11, and 30 abstinence days, and naloxone's (0-1.0 mg/kg) effect on extinction responding after 1 and 15 days.Cue-induced heroin seeking progressively increased or incubated during abstinence. This incubation was not associated with changes in BDNF, TrkB, or MeCP2 mRNA or protein levels in NAc, DS, or mPFC; additionally, no molecular changes were observed after extinction tests on day 11. In NAc, but not DS or mPFC, MOR mRNA decreased on abstinence day 1 and returned to basal levels over time. Naloxone significantly decreased cue-induced heroin seeking after 15 abstinence days but not 1 day.Results suggest a role of MOR in incubation of heroin craving. As previous studies implicated NAc BDNF in incubation of cocaine craving, our data suggest that different mechanisms contribute to incubation of heroin versus cocaine craving. | | | 22790874
 |
A critical and cell-autonomous role for MeCP2 in synaptic scaling up.
Blackman, MP; Djukic, B; Nelson, SB; Turrigiano, GG
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
32
13529-36
2012
Show Abstract
Rett syndrome (Rett) is the leading genetic cause of mental retardation in females. Most cases of Rett are caused by loss-of-function mutations in the gene coding for the transcriptional regulator methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2), but despite much effort, it remains unclear how a loss of MeCP2 function generates the neurological deficits of Rett. Here we show that MeCP2 plays an essential and cell-autonomous role in homeostatic synaptic scaling up in response to reduced firing or reduced sensory drive in rat visual cortical pyramidal neurons. We found that acute RNAi knockdown of MeCP2 blocked synaptic scaling within targeted neocortical pyramidal neurons. Furthermore, MeCP2 knockdown decreased excitatory synapse number without affecting basal mEPSC amplitude or AMPAR accumulation at spared synapses, demonstrating that MeCP2 acts cell-autonomously to maintain both excitatory synapse number and synaptic scaling in individual neocortical neurons. Finally, we used a mouse model of Rett to show that MeCP2 loss prevents homeostatic synaptic scaling up in response to visual deprivation in vivo, demonstrating for the first time that MeCP2 loss disrupts homeostatic plasticity within the intact developing neocortex. Our results establish MeCP2 as a critical mediator of synaptic scaling and raise the possibility that some of the neurological defects of Rett arise from a disruption of homeostatic plasticity. | | | 23015442
 |
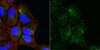
Novel MeCP2 isoform-specific antibody reveals the endogenous MeCP2E1 expression in murine brain, primary neurons and astrocytes.
Zachariah, RM; Olson, CO; Ezeonwuka, C; Rastegar, M
PloS one
7
e49763
2012
Show Abstract
Rett Syndrome (RTT) is a severe neurological disorder in young females, and is caused by mutations in the X-linked MECP2 gene. MECP2/Mecp2 gene encodes for two protein isoforms; MeCP2E1 and MeCP2E2 that are identical except for the N-terminus region of the protein. In brain, MECP2E1 transcripts are 10X higher, and MeCP2E1 is suggested to be the relevant isoform for RTT. However, due to the unavailability of MeCP2 isoform-specific antibodies, the endogenous expression pattern of MeCP2E1 is unknown. To gain insight into the expression of MeCP2E1 in brain, we have developed an anti-MeCP2E1 antibody and validated its specificity in cells exogenously expressing individual MeCP2 isoforms. This antibody does not show any cross-reactivity with MeCP2E2 and detects endogenous MeCP2E1 in mice brain, with no signal in Mecp2(tm1.1Bird) y/- null mice. Additionally, we show the endogenous MeCP2E1 expression throughout different brain regions in adult mice, and demonstrate its highest expression in the brain cortex. Our results also indicate that MeCP2E1 is highly expressed in primary neurons, as compared to primary astrocytes. This is the first report of the endogenous MeCP2E1 expression at the protein levels, providing novel avenues for understanding different aspects of MeCP2 function. | | | 23185431
 |
Nuclear calcium signaling controls methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) phosphorylation on serine 421 following synaptic activity.
Buchthal, Bettina, et al.
J. Biol. Chem., 287: 30967-74 (2012)
2012
Show Abstract
The function of MeCP2, a methylated DNA-interacting protein that may act as a global chromatin modifier, is controlled by its phosphorylation on serine 421. Here we show that in hippocampal neurons, nuclear calcium signaling controls synaptic activity-induced phosphorylation of MeCP2 on serine 421. Pharmacological inhibition of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein (CaM)kinases blocked activity-induced MeCP2 serine 421 phosphorylation. CaM kinase II (CaMKII) but not CaMKIV, the major nuclear CaM kinase in hippocampal neurons, appeared to mediate this phosphorylation event. Biochemical subcellular fractionations and immunolocalization studies revealed that several isoforms of CaMKII (i.e. CaMKIIα, -β, -γ, and -δ) are expressed in the cytosol but are also detectable in the cell nucleus of hippocampal neurons, suggesting that nuclear CaMKII catalyzes MeCP2 serine 421 phosphorylation. Thus, in addition to the classical nuclear calcium-CaMKIV-CREB/CBP (cAMP-response element-binding protein/CREB-binding protein) pathway that regulates transcription of specific target genes, nuclear calcium may also modulate genome-wide the chromatin state in response to synaptic activity via nuclear CaMKII-MeCP2 signaling. | | | 22822052
 |
Isoform-specific toxicity of Mecp2 in postmitotic neurons: suppression of neurotoxicity by FoxG1.
Dastidar, SG; Bardai, FH; Ma, C; Price, V; Rawat, V; Verma, P; Narayanan, V; D'Mello, SR
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
32
2846-55
2012
Show Abstract
The methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) is a widely expressed protein, the mutations of which cause Rett syndrome. The level of MeCP2 is highest in the brain where it is expressed selectively in mature neurons. Its functions in postmitotic neurons are not known. The MeCP2 gene is alternatively spliced to generate two proteins with different N termini, designated as MeCP2-e1 and MeCP2-e2. The physiological significance of these two isoforms has not been elucidated, and it is generally assumed they are functionally equivalent. We report that in cultured cerebellar granule neurons induced to die by low potassium treatment and in Aβ-treated cortical neurons, Mecp2-e2 expression is upregulated whereas expression of the Mecp2-e1 isoform is downregulated. Knockdown of Mecp2-e2 protects neurons from death, whereas knockdown of the e1 isoform has no effect. Forced expression of MeCP2-e2, but not MeCP2-e1, promotes apoptosis in otherwise healthy neurons. We find that MeCP2-e2 interacts with the forkhead protein FoxG1, mutations of which also cause Rett syndrome. FoxG1 has been shown to promote neuronal survival and its downregulation leads to neuronal death. We find that elevated FoxG1 expression inhibits MeCP2-e2 neurotoxicity. MeCP2-e2 neurotoxicity is also inhibited by IGF-1, which prevents the neuronal death-associated downregulation of FoxG1 expression, and by Akt, the activation of which is necessary for FoxG1-mediated neuroprotection. Finally, MeCP2-e2 neurotoxicity is enhanced if FoxG1 expression is suppressed or in neurons cultured from FoxG1-haplodeficient mice. Our results indicate that Mecp2-e2 promotes neuronal death and that this activity is normally inhibited by FoxG1. Reduced FoxG1 expression frees MecP2-e2 to promote neuronal death. | | | 22357867
 |
The expression of spinal methyl-CpG-binding protein 2, DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylases is modulated in persistent pain states.
Tochiki, KK; Cunningham, J; Hunt, SP; Géranton, SM
Molecular pain
8
14
2012
Show Abstract
DNA CpG methylation is carried out by DNA methyltransferases and induces chromatin remodeling and gene silencing through a transcription repressor complex comprising the methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) and a subset of histone deacetylases. Recently, we have found that MeCP2 activity had a crucial role in the pattern of gene expression seen in the superficial dorsal horn rapidly after injection of Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA) in the rat ankle joint. The aim of the present study was to analyse the changes in expression of MeCP2, DNA methyltransferases and a subset of histone deacetylases in the superficial dorsal horn during the maintenance phase of persistent pain states. In this process, the cell specific expression of MeCP2 was also investigated.Using immunohistochemistry, we found that neurones, oligodendrocytes and astrocytes expressed MeCP2. Microglia, oligodendrocyte precursor cells and Schwann cells never showed any positive stain for MeCP2. Quantitative analyses showed that MeCP2 expression was increased in the superficial dorsal horn 7 days following CFA injection in the ankle joint but decreased 7 days following spared nerve injury. Overall, the expression of DNA methyltransferases and a subset of histone deacetylases followed the same pattern of expression. However, there were no significant changes in the expression of the MeCP2 targets that we had previously shown are regulated in the early time points following CFA injection in the ankle joint. Finally, the expression of MeCP2 was also down regulated in damaged dorsal root ganglion neurones following spared nerve injury.Our results strongly suggest that changes in chromatin compaction, regulated by the binding of MeCP2 complexes to methylated DNA, are involved in the modulation of gene expression in the superficial dorsal horn and dorsal root ganglia during the maintenance of persistent pain states. | | | 22369085
 |
The role of EZH2 in the regulation of the activity of matrix metalloproteinases in prostate cancer cells.
Shin, YJ; Kim, JH
PloS one
7
e30393
2012
Show Abstract
Degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM), a critical step in cancer metastasis, is determined by the balance between MMPs (matrix metalloproteinases) and their inhibitors TIMPs (tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases). In cancer cells, this balance is shifted towards MMPs, promoting ECM degradation. Here, we show that EZH2 plays an active role in this process by repressing the expression of TIMP2 and TIMP3 in prostate cancer cells. The TIMP genes are derepressed by knockdown of EZH2 expression in human prostate cancer cells but repressed by overexpression of EZH2 in benign human prostate epithelial cells. EZH2 catalyzes H3K27 trimethylation and subsequent DNA methylation of the TIMP gene promoters. Overexpression of EZH2 confers an invasive phenotype on benign prostate epithelial cells; however, this phenotype is suppressed by cooverexpression of TIMP3. EZH2 knockdown markedly reduces the proteolytic activity of MMP-9, thereby decreasing the invasive activity of prostate cancer cells. These results suggest that the transcriptional repression of the TIMP genes by EZH2 may be a major mechanism to shift the MMPs/TIMPs balance in favor of MMP activity and thus to promote ECM degradation and subsequent invasion of prostate cancer cells. | | | 22272343
 |
The stress oncoprotein LEDGF/p75 interacts with the methyl CpG binding protein MeCP2 and influences its transcriptional activity.
Leoh, LS; van Heertum, B; De Rijck, J; Filippova, M; Rios-Colon, L; Basu, A; Martinez, SR; Tungteakkhun, SS; Filippov, V; Christ, F; De Leon, M; Debyser, Z; Casiano, CA
Molecular cancer research : MCR
10
378-91
2012
Show Abstract
The lens epithelium-derived growth factor p75 (LEDGF/p75) is a transcription coactivator that promotes resistance to oxidative stress- and chemotherapy-induced cell death. LEDGF/p75 is also known as the dense fine speckles autoantigen of 70 kDa (DFS70) and has been implicated in cancer, HIV-AIDS, autoimmunity, and inflammation. To gain insights into mechanisms by which LEDGF/p75 protects cancer cells against stress, we initiated an analysis of its interactions with other transcription factors and the influence of these interactions on stress gene activation. We report here that both LEDGF/p75 and its short splice variant LEDGF/p52 interact with MeCP2, a methylation-associated transcriptional modulator, in vitro and in various human cancer cells. These interactions were established by several complementary approaches: transcription factor protein arrays, pull-down and AlphaScreen assays, coimmunoprecipitation, and nuclear colocalization by confocal microscopy. MeCP2 was found to interact with the N-terminal region shared by LEDGF/p75 and p52, particularly with the PWWP-CR1 domain. Like LEDGF/p75, MeCP2 bound to and transactivated the Hsp27 promoter (Hsp27pr). LEDGF/p75 modestly enhanced MeCP2-induced Hsp27pr transactivation in U2OS osteosarcoma cells, whereas this effect was more pronounced in PC3 prostate cancer cells. LEDGF/p52 repressed Hsp27pr activity in U2OS cells. Interestingly, siRNA-induced silencing of LEDGF/p75 in U2OS cells dramatically elevated MeCP2-mediated Hsp27pr transactivation, whereas this effect was less pronounced in PC3 cells depleted of LEDGF/p75. These results suggest that the LEDGF/p75-MeCP2 interaction differentially influences Hsp27pr activation depending on the cellular and molecular context. These findings are of significance in understanding the contribution of this interaction to the activation of stress survival genes. | | | 22275515
 |