Drosophila casein kinase I alpha regulates homolog pairing and genome organization by modulating condensin II subunit Cap-H2 levels.
Nguyen, HQ; Nye, J; Buster, DW; Klebba, JE; Rogers, GC; Bosco, G
PLoS genetics
11
e1005014
2015
Show Abstract
The spatial organization of chromosomes within interphase nuclei is important for gene expression and epigenetic inheritance. Although the extent of physical interaction between chromosomes and their degree of compaction varies during development and between different cell-types, it is unclear how regulation of chromosome interactions and compaction relate to spatial organization of genomes. Drosophila is an excellent model system for studying chromosomal interactions including homolog pairing. Recent work has shown that condensin II governs both interphase chromosome compaction and homolog pairing and condensin II activity is controlled by the turnover of its regulatory subunit Cap-H2. Specifically, Cap-H2 is a target of the SCFSlimb E3 ubiquitin-ligase which down-regulates Cap-H2 in order to maintain homologous chromosome pairing, chromosome length and proper nuclear organization. Here, we identify Casein Kinase I alpha (CK1α) as an additional negative-regulator of Cap-H2. CK1α-depletion stabilizes Cap-H2 protein and results in an accumulation of Cap-H2 on chromosomes. Similar to Slimb mutation, CK1α depletion in cultured cells, larval salivary gland, and nurse cells results in several condensin II-dependent phenotypes including dispersal of centromeres, interphase chromosome compaction, and chromosome unpairing. Moreover, CK1α loss-of-function mutations dominantly suppress condensin II mutant phenotypes in vivo. Thus, CK1α facilitates Cap-H2 destruction and modulates nuclear organization by attenuating chromatin localized Cap-H2 protein. | | | 25723539
 |
Multimer Formation Explains Allelic Suppression of PRDM9 Recombination Hotspots.
Baker, CL; Petkova, P; Walker, M; Flachs, P; Mihola, O; Trachtulec, Z; Petkov, PM; Paigen, K
PLoS genetics
11
e1005512
2015
Show Abstract
Genetic recombination during meiosis functions to increase genetic diversity, promotes elimination of deleterious alleles, and helps assure proper segregation of chromatids. Mammalian recombination events are concentrated at specialized sites, termed hotspots, whose locations are determined by PRDM9, a zinc finger DNA-binding histone methyltransferase. Prdm9 is highly polymorphic with most alleles activating their own set of hotspots. In populations exhibiting high frequencies of heterozygosity, questions remain about the influences different alleles have in heterozygous individuals where the two variant forms of PRDM9 typically do not activate equivalent populations of hotspots. We now find that, in addition to activating its own hotspots, the presence of one Prdm9 allele can modify the activity of hotspots activated by the other allele. PRDM9 function is also dosage sensitive; Prdm9+/- heterozygous null mice have reduced numbers and less active hotspots and increased numbers of aberrant germ cells. In mice carrying two Prdm9 alleles, there is allelic competition; the stronger Prdm9 allele can partially or entirely suppress chromatin modification and recombination at hotspots of the weaker allele. In cell cultures, PRDM9 protein variants form functional heteromeric complexes which can bind hotspots sequences. When a heteromeric complex binds at a hotspot of one PRDM9 variant, the other PRDM9 variant, which would otherwise not bind, can still methylate hotspot nucleosomes. We propose that in heterozygous individuals the underlying molecular mechanism of allelic suppression results from formation of PRDM9 heteromers, where the DNA binding activity of one protein variant dominantly directs recombination initiation towards its own hotspots, effectively titrating down recombination by the other protein variant. In natural populations with many heterozygous individuals, allelic competition will influence the recombination landscape. | | | 26368021
 |
Mutation of histone H3 serine 86 disrupts GATA factor Ams2 expression and precise chromosome segregation in fission yeast.
Lim, KK; Ong, TY; Tan, YR; Yang, EG; Ren, B; Seah, KS; Yang, Z; Tan, TS; Dymock, BW; Chen, ES
Scientific reports
5
14064
2015
Show Abstract
Eukaryotic genomes are packed into discrete units, referred to as nucleosomes, by organizing around scaffolding histone proteins. The interplay between these histones and the DNA can dynamically regulate the function of the chromosomal domain. Here, we interrogated the function of a pair of juxtaposing serine residues (S86 and S87) that reside within the histone fold of histone H3. We show that fission yeast cells expressing a mutant histone H3 disrupted at S86 and S87 (hht2-S86AS87A) exhibited unequal chromosome segregation, disrupted transcriptional silencing of centromeric chromatin, and reduced expression of Ams2, a GATA-factor that regulates localization of the centromere-specific histone H3 variant CENP-A. We found that overexpression of ams2(+) could suppress the chromosome missegregation phenotype that arose in the hht2-S86AS87A mutant. We further demonstrate that centromeric localization of SpCENP-A(cnp1-1) was significantly compromised in hht2-S86AS87A, suggesting synergism between histone H3 and the centromere-targeting domain of SpCENP-A. Taken together, our work presents evidence for an uncharacterized serine residue in fission yeast histone H3 that affects centromeric integrity via regulating the expression of the SpCENP-A-localizing Ams2 protein. [173/200 words]. | | | 26369364
 |
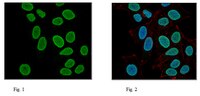
Histone acetylation associated up-regulation of the cell wall related genes is involved in salt stress induced maize root swelling.
Li, H; Yan, S; Zhao, L; Tan, J; Zhang, Q; Gao, F; Wang, P; Hou, H; Li, L
BMC plant biology
14
105
2014
Show Abstract
Salt stress usually causes crop growth inhibition and yield decrease. Epigenetic regulation is involved in plant responses to environmental stimuli. The epigenetic regulation of the cell wall related genes associated with the salt-induced cellular response is still little known. This study aimed to analyze cell morphological alterations in maize roots as a consequence of excess salinity in relation to the transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of the cell wall related protein genes.In this study, maize seedling roots got shorter and displayed swelling after exposure to 200 mM NaCl for 48 h and 96 h. Cytological observation showed that the growth inhibition of maize roots was due to the reduction in meristematic zone cell division activity and elongation zone cell production. The enlargement of the stele tissue and cortex cells contributed to root swelling in the elongation zone. The cell wall is thought to be the major control point for cell enlargement. Cell wall related proteins include xyloglucan endotransglucosylase (XET), expansins (EXP), and the plasma membrane proton pump (MHA). RT-PCR results displayed an up-regulation of cell wall related ZmEXPA1, ZmEXPA3, ZmEXPA5, ZmEXPB1, ZmEXPB2 and ZmXET1 genes and the down-regulation of cell wall related ZmEXPB4 and ZmMHA genes as the duration of exposure was increased. Histone acetylation is regulated by HATs, which are often correlated with gene activation. The expression of histone acetyltransferase genes ZmHATB and ZmGCN5 was increased after 200 mM NaCl treatment, accompanied by an increase in the global acetylation levels of histones H3K9 and H4K5. ChIP experiment showed that the up-regulation of the ZmEXPB2 and ZmXET1 genes was associated with the elevated H3K9 acetylation levels on the promoter regions and coding regions of these two genes.These data suggested that the up-regulation of some cell wall related genes mediated cell enlargement to possibly mitigate the salinity-induced ionic toxicity, and different genes had specific function in response to salt stress. Histone modification as a mediator may contribute to rapid regulation of cell wall related gene expression, which reduces the damage of excess salinity to plants. | Immunofluorescence | | 24758373
 |
Involvement of telomerase reverse transcriptase in heterochromatin maintenance.
Maida, Y; Yasukawa, M; Okamoto, N; Ohka, S; Kinoshita, K; Totoki, Y; Ito, TK; Minamino, T; Nakamura, H; Yamaguchi, S; Shibata, T; Masutomi, K
Molecular and cellular biology
34
1576-93
2014
Show Abstract
In the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, centromeric heterochromatin is maintained by an RNA-directed RNA polymerase complex (RDRC) and the RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS) complex in a manner that depends on the generation of short interfering RNA. In association with the telomerase RNA component (TERC), the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) forms telomerase and counteracts telomere attrition, and without TERC, TERT has been implicated in the regulation of heterochromatin at locations distinct from telomeres. Here, we describe a complex composed of human TERT (hTERT), Brahma-related gene 1 (BRG1), and nucleostemin (NS) that contributes to heterochromatin maintenance at centromeres and transposons. This complex produced double-stranded RNAs homologous to centromeric alpha-satellite (alphoid) repeat elements and transposons that were processed into small interfering RNAs targeted to these heterochromatic regions. These small interfering RNAs promoted heterochromatin assembly and mitotic progression in a manner dependent on the RNA interference machinery. These observations implicate the hTERT/BRG1/NS (TBN) complex in heterochromatin assembly at particular sites in the mammalian genome. | Western Blotting | | 24550003
 |
Targeted repression of AXIN2 and MYC gene expression using designer TALEs.
Rennoll, SA; Scott, SA; Yochum, GS
Biochemical and biophysical research communications
446
1120-5
2014
Show Abstract
Designer TALEs (dTALEs) are chimeric transcription factors that can be engineered to regulate gene expression in mammalian cells. Whether dTALEs can block gene transcription downstream of signal transduction cascades, however, has yet to be fully explored. Here we tested whether dTALEs can be used to target genes whose expression is controlled by Wnt/β-catenin signaling. TALE DNA binding domains were engineered to recognize sequences adjacent to Wnt responsive enhancer elements (WREs) that control expression of axis inhibition protein 2 (AXIN2) and c-MYC (MYC). These custom DNA binding domains were linked to the mSin3A interaction domain (SID) to generate TALE-SID chimeric repressors. The TALE-SIDs repressed luciferase reporter activity, bound their genomic target sites, and repressed AXIN2 and MYC expression in HEK293 cells. We generated a novel HEK293 cell line to determine whether the TALE-SIDs could function downstream of oncogenic Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Treating these cells with doxycycline and tamoxifen stimulates nuclear accumulation of a stabilized form of β-catenin found in a subset of colorectal cancers. The TALE-SIDs repressed AXIN2 and MYC expression in these cells, which suggests that dTALEs could offer an effective therapeutic strategy for the treatment of colorectal cancer. | | | 24667606
 |
An ARID domain-containing protein within nuclear bodies is required for sperm cell formation in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Zheng, B; He, H; Zheng, Y; Wu, W; McCormick, S
PLoS genetics
10
e1004421
2014
Show Abstract
In plants, each male meiotic product undergoes mitosis, and then one of the resulting cells divides again, yielding a three-celled pollen grain comprised of a vegetative cell and two sperm cells. Several genes have been found to act in this process, and DUO1 (DUO POLLEN 1), a transcription factor, plays a key role in sperm cell formation by activating expression of several germline genes. But how DUO1 itself is activated and how sperm cell formation is initiated remain unknown. To expand our understanding of sperm cell formation, we characterized an ARID (AT-Rich Interacting Domain)-containing protein, ARID1, that is specifically required for sperm cell formation in Arabidopsis. ARID1 localizes within nuclear bodies that are transiently present in the generative cell from which sperm cells arise, coincident with the timing of DUO1 activation. An arid1 mutant and antisense arid1 plants had an increased incidence of pollen with only a single sperm-like cell and exhibited reduced fertility as well as reduced expression of DUO1. In vitro and in vivo evidence showed that ARID1 binds to the DUO1 promoter. Lastly, we found that ARID1 physically associates with histone deacetylase 8 and that histone acetylation, which in wild type is evident only in sperm, expanded to the vegetative cell nucleus in the arid1 mutant. This study identifies a novel component required for sperm cell formation in plants and uncovers a direct positive regulatory role of ARID1 on DUO1 through association with histone acetylation. | | | 25057814
 |
Histones to the cytosol: exportin 7 is essential for normal terminal erythroid nuclear maturation.
Hattangadi, SM; Martinez-Morilla, S; Patterson, HC; Shi, J; Burke, K; Avila-Figueroa, A; Venkatesan, S; Wang, J; Paulsen, K; Görlich, D; Murata-Hori, M; Lodish, HF
Blood
124
1931-40
2014
Show Abstract
Global nuclear condensation, culminating in enucleation during terminal erythropoiesis, is poorly understood. Proteomic examination of extruded erythroid nuclei from fetal liver revealed a striking depletion of most nuclear proteins, suggesting that nuclear protein export had occurred. Expression of the nuclear export protein, Exportin 7 (Xpo7), is highly erythroid-specific, induced during erythropoiesis, and abundant in very late erythroblasts. Knockdown of Xpo7 in primary mouse fetal liver erythroblasts resulted in severe inhibition of chromatin condensation and enucleation but otherwise had little effect on erythroid differentiation, including hemoglobin accumulation. Nuclei in Xpo7-knockdown cells were larger and less dense than normal and accumulated most nuclear proteins as measured by mass spectrometry. Strikingly,many DNA binding proteins such as histones H2A and H3 were found to have migrated into the cytoplasm of normal late erythroblasts prior to and during enucleation, but not in Xpo7-knockdown cells. Thus, terminal erythroid maturation involves migration of histones into the cytoplasm via a process likely facilitated by Xpo7. | | | 25092175
 |
The deacetylase Sir2 from the yeast Clavispora lusitaniae lacks the evolutionarily conserved capacity to generate subtelomeric heterochromatin.
Froyd, CA; Kapoor, S; Dietrich, F; Rusche, LN
PLoS genetics
9
e1003935
2013
Show Abstract
Deacetylases of the Sir2 or sirtuin family are thought to regulate life cycle progression and life span in response to nutrient availability. This family has undergone successive rounds of duplication and diversification, enabling the enzymes to perform a wide variety of biological functions. Two evolutionarily conserved functions of yeast Sir2 proteins are the generation of repressive chromatin in subtelomeric domains and the suppression of unbalanced recombination within the tandem rDNA array. Here, we describe the function of the Sir2 ortholog ClHst1 in the yeast Clavispora lusitaniae, an occasional opportunistic pathogen. ClHst1 was localized to the non-transcribed spacer regions of the rDNA repeats and deacetylated histones at these loci, indicating that, like other Sir2 proteins, ClHst1 modulates chromatin structure at the rDNA repeats. However, we found no evidence that ClHst1 associates with subtelomeric regions or impacts gene expression directly. This surprising observation highlights the plasticity of sirtuin function. Related yeast species, including Candida albicans, possess an additional Sir2 family member. Thus, it is likely that the ancestral Candida SIR2/HST1 gene was duplicated and subfunctionalized, such that HST1 retained the capacity to regulate rDNA whereas SIR2 had other functions, perhaps including the generation of subtelomeric chromatin. After subsequent species diversification, the SIR2 paralog was apparently lost in the C. lusitaniae lineage. Thus, C. lusitaniae presents an opportunity to discover how subtelomeric chromatin can be reconfigured. | | | 24204326
 |
Crosstalk between NSL histone acetyltransferase and MLL/SET complexes: NSL complex functions in promoting histone H3K4 di-methylation activity by MLL/SET complexes.
Zhao, X; Su, J; Wang, F; Liu, D; Ding, J; Yang, Y; Conaway, JW; Conaway, RC; Cao, L; Wu, D; Wu, M; Cai, Y; Jin, J
PLoS genetics
9
e1003940
2013
Show Abstract
hMOF (MYST1), a histone acetyltransferase (HAT), forms at least two distinct multiprotein complexes in human cells. The male specific lethal (MSL) HAT complex plays a key role in dosage compensation in Drosophila and is responsible for histone H4K16ac in vivo. We and others previously described a second hMOF-containing HAT complex, the non-specific lethal (NSL) HAT complex. The NSL complex has a broader substrate specificity, can acetylate H4 on K16, K5, and K8. The WD (tryptophan-aspartate) repeat domain 5 (WDR5) and host cell factor 1 (HCF1) are shared among members of the MLL/SET (mixed-lineage leukemia/set-domain containing) family of histone H3K4 methyltransferase complexes. The presence of these shared subunits raises the possibility that there are functional links between these complexes and the histone modifications they catalyze; however, the degree to which NSL and MLL/SET influence one another's activities remains unclear. Here, we present evidence from biochemical assays and knockdown/overexpression approaches arguing that the NSL HAT promotes histone H3K4me2 by MLL/SET complexes by an acetylation-dependent mechanism. In genomic experiments, we identified a set of genes including ANKRD2, that are affected by knockdown of both NSL and MLL/SET subunits, suggested they are co-regulated by NSL and MLL/SET complexes. In ChIP assays, we observe that depletion of the NSL subunits hMOF or NSL1 resulted in a significant reduction of both H4K16ac and H3K4me2 in the vicinity of the ANKRD2 transcriptional start site proximal region. However, depletion of RbBP5 (a core component of MLL/SET complexes) only reduced H3K4me2 marks, but not H4K16ac in the same region of ANKRD2, consistent with the idea that NSL acts upstream of MLL/SET to regulate H3K4me2 at certain promoters, suggesting coordination between NSL and MLL/SET complexes is involved in transcriptional regulation of certain genes. Taken together, our results suggest a crosstalk between the NSL and MLL/SET complexes in cells. | | | 24244196
 |