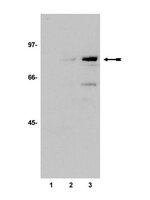
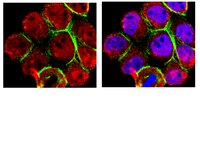
The RASSF6 tumor suppressor protein regulates apoptosis and the cell cycle via MDM2 protein and p53 protein.
Iwasa, H; Kudo, T; Maimaiti, S; Ikeda, M; Maruyama, J; Nakagawa, K; Hata, Y
The Journal of biological chemistry
288
30320-9
2013
Show Abstract
Ras association domain family (RASSF) 6 is a member of the C-terminal RASSF proteins such as RASSF1A and RASSF3. RASSF6 is involved in apoptosis in various cells under miscellaneous conditions, but it remains to be clarified how RASSF6 exerts tumor-suppressive roles. We reported previously that RASSF3 facilitates the degradation of MDM2, a major E3 ligase of p53, and stabilizes p53 to function as a tumor suppressor. In this study, we demonstrate that RASSF6 overexpression induces G1/S arrest in p53-positive cells. Its depletion prevents UV- and VP-16-induced apoptosis and G1/S arrest in HCT116 and U2OS cells. RASSF6-induced apoptosis partially depends on p53. RASSF6 binds MDM2 and facilitates its ubiquitination. RASSF6 depletion blocks the increase of p53 in response to UV exposure and up-regulation of p53 target genes. RASSF6 depletion delays DNA repair in UV- and VP-16-treated cells and increases polyploid cells after VP-16 treatment. These findings indicate that RASSF6 stabilizes p53, regulates apoptosis and the cell cycle, and functions as a tumor suppressor. Together with the previous reports regarding RASSF1A and RASSF3, the stabilization of p53 may be the common function of the C-terminal RASSF proteins. | | 24003224
 |
Specific acetylation of p53 by HDAC inhibition prevents DNA damage-induced apoptosis in neurons.
Brochier, C; Dennis, G; Rivieccio, MA; McLaughlin, K; Coppola, G; Ratan, RR; Langley, B
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
33
8621-32
2013
Show Abstract
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors have been used to promote neuronal survival and ameliorate neurological dysfunction in a host of neurodegenerative disease models. The precise molecular mechanisms whereby HDAC inhibitors prevent neuronal death are currently the focus of intensive research. Here we demonstrate that HDAC inhibition prevents DNA damage-induced neurodegeneration by modifying the acetylation pattern of the tumor suppressor p53, which decreases its DNA-binding and transcriptional activation of target genes. Specifically, we identify that acetylation at K382 and K381 prevents p53 from associating with the pro-apoptotic PUMA gene promoter, activating transcription, and inducing apoptosis in mouse primary cortical neurons. Paradoxically, acetylation of p53 at the same lysines in various cancer cell lines leads to the induction of PUMA expression and death. Together, our data provide a molecular understanding of the specific outcomes of HDAC inhibition and suggest that strategies aimed at enhancing p53 acetylation at K381 and K382 might be therapeutically viable for capturing the beneficial effects in the CNS, without compromising tumor suppression. | | 23678107
 |
Green tea polyphenols increase p53 transcriptional activity and acetylation by suppressing class I histone deacetylases.
Thakur, VS; Gupta, K; Gupta, S
International journal of oncology
41
353-61
2012
Show Abstract
Acetylation of the tumor suppressor gene p53 at the carboxy-terminal lysine (Lys) residues enhances its transcriptional activity associated with cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Histone deacetylases (HDACs), a family of evolutionarily conserved enzymes, counterbalance the acetylation of lysine residues on histone and non-histone proteins. In this study, we demonstrate that green tea polyphenols (GTPs) and their major constituent, (-) epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), activate p53 through acetylation at the Lys373 and Lys382 residues by inhibiting class I HDACs in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Treatment of cells with GTPs (2.5-10 µg/ml) and EGCG (5-20 µM) resulted in dose- and time-dependent inhibition of class I HDACs (HDAC1, 2, 3 and 8), albeit at varying levels. Discontinuation of treatment with GTP/EGCG resulted in the loss of p53 acetylation at both the sites in these cells. GTP/EGCG treatment also resulted in increased expression of p21/waf1 and Bax at the protein and message levels in these cells. The increased GTP/EGCG-mediated p53 acetylation enhanced its binding on the promoters of p21/waf1 and Bax, which was associated with increased accumulation of cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle and induction of apoptosis. Our findings indicate that GTP/EGCG causes acetylation of p53 by inhibiting class I HDACs, a function that is likely to be part of the mechanisms that control the physiological activity of p53. | Western Blotting | 22552582
 |
The new low-toxic histone deacetylase inhibitor S-(2) induces apoptosis in various acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Cellai, C, et al.
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, (2011)
2011
Show Abstract
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) induce tumor cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis, and some of them are currently used in cancer therapy. Recently, we described a series of powerful HDACi characterized by a 1,4-benzodiazepine (BDZ) ring hybridized with a linear alkyl chain bearing a hydroxamate function as Zn(++) -chelating group. Here, we explored the anti-leukemic properties of three novel hybrids, namely the chiral compounds (S)-2 and (R)-2, and their non-chiral analog 4, which were first comparatively tested in promyelocytic NB4 cells. (S)-2 and partially 4- but not (R)-2 - caused G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest by up-regulating cyclin G2 and p21 expression and down-regulating cyclin D2 expression, and also apoptosis as assessed by cell morphology and cytofluorimetric assay, histone H2AX phosphorylation and PARP cleavage. Notably, these events were partly prevented by an anti-oxidant. Moreover, novel HDACi prompted p53 and α-tubulin acetylation and, consistently, inhibited HDAC1 and 6 activity. The rank order of potency was (S)-2 > 4 > (R)-2, reflecting that of other biological assays and addressing (S)-2 as the most effective compound capable of triggering apoptosis in various acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell lines and blasts from patients with different AML subtypes. Importantly, (S)-2 was safe in mice (up to 150 mg/kg/week) as determined by liver, spleen, kidney and bone marrow histopathology; and displayed negligible affinity for peripheral/central BDZ-receptors. Overall, the BDZ-hydroxamate (S)-2 showed to be a low-toxic HDACi with powerful anti-proliferative and pro-apototic activities towards different cultured and primary AML cells, and therefore of clinical interest to support conventional anti-leukemic therapy. | | 22004558
 |
The histone acetyltransferase p300 promotes intrinsic axonal regeneration.
Gaub, P; Joshi, Y; Wuttke, A; Naumann, U; Schnichels, S; Heiduschka, P; Di Giovanni, S
Brain : a journal of neurology
134
2134-48
2011
Show Abstract
Axonal regeneration and related functional recovery following axonal injury in the adult central nervous system are extremely limited, due to a lack of neuronal intrinsic competence and the presence of extrinsic inhibitory signals. As opposed to what occurs during nervous system development, a weak proregenerative gene expression programme contributes to the limited intrinsic capacity of adult injured central nervous system axons to regenerate. Here we show, in an optic nerve crush model of axonal injury, that adenoviral (cytomegalovirus promoter) overexpression of the acetyltransferase p300, which is regulated during retinal ganglion cell maturation and repressed in the adult, can promote axonal regeneration of the optic nerve beyond 0.5 mm. p300 acetylates histone H3 and the proregenerative transcription factors p53 and CCAAT-enhancer binding proteins in retinal ganglia cells. In addition, it directly occupies and acetylates the promoters of the growth-associated protein-43, coronin 1 b and Sprr1a and drives the gene expression programme of several regeneration-associated genes. On the contrary, overall increase in cellular acetylation using the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A, enhances retinal ganglion cell survival but not axonal regeneration after optic nerve crush. Therefore, p300 targets both the epigenome and transcription to unlock a post-injury silent gene expression programme that would support axonal regeneration. | | 21705428
 |
Resveratrol improves hippocampal atrophy in chronic fatigue mice by enhancing neurogenesis and inhibiting apoptosis of granular cells.
Moriya J, Chen R, Yamakawa J, Sasaki K, Ishigaki Y, Takahashi T
Biol Pharm Bull
34
354-9.
2011
Show Abstract
Neuroimaging evidence showed structural and/or functional abnormalities existing in the central nervous system, especially the hippocampus, in chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) patients. However, its pathophysiologic mechanisms are unclear in part due to the lack of an applicable animal model. We established a chronic fatigue murine model by six repeated injections of Brucella abortus antigen to mice, which was manifested as reduced daily running activity and hippocampal atrophy. Thereafter, resveratrol, a polyphenolic activator of sirtuin 1, was used for treatment in this model. Daily running activity was increased by more than 20%, and the hippocampus was enlarged after 4-week resveratrol therapy. Furthermore, resveratrol inhibited neuronal apoptosis and expression of hippocampal acetylated p53 in the fatigue mice. Resveratrol also improved neurogenesis and expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in the hippocamous. We concluded that repeated injection of B. abortus antigen could induce hypoactivity and hippocampal atrophy in mice. Resveratrol may be effective for improving fatigue symptoms and enlarging the atrophic hippocampus by repressing apoptosis and promoting neurogenesis. | | 21372384
 |
A p53-CBP/p300 transcription module is required for GAP-43 expression, axon outgrowth, and regeneration.
Tedeschi, A; Nguyen, T; Puttagunta, R; Gaub, P; Di Giovanni, S
Cell death and differentiation
16
543-54
2009
Show Abstract
Transcription regulates axon outgrowth and regeneration. However, to date, no transcription complexes have been shown to control axon outgrowth and regeneration by regulating axon growth genes. Here, we report that the tumor suppressor p53 and its acetyltransferases CBP/p300 form a transcriptional complex that regulates the axonal growth-associated protein 43, a well-characterized pro-axon outgrowth and regeneration protein. Acetylated p53 at K372-3-82 drives axon outgrowth, GAP-43 expression, and binds specific elements on the neuronal GAP-43 promoter in a chromatin environment through CBP/p300 signaling. Importantly, in an axon regeneration model, both CBP and p53 K372-3-82 are induced following axotomy in facial motor neurons, where p53 K372-3-82 occupancy of GAP-43 promoter is enhanced as shown by in vivo chromatin immunoprecipitation. Finally, by comparing wild-type and p53 null mice, we demonstrate that the p53/GAP-43 transcriptional module is specifically switched on during axon regeneration in vivo. These data contribute to the understanding of gene regulation in axon outgrowth and may suggest new molecular targets for axon regeneration. | | 19057620
 |
Necdin regulates p53 acetylation via Sirtuin1 to modulate DNA damage response in cortical neurons.
Hasegawa, K; Yoshikawa, K
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience
28
8772-84
2008
Show Abstract
Sirtuin1 (Sirt1), a mammalian homolog of yeast Sir2, deacetylates the tumor suppressor protein p53 and attenuates p53-mediated cell death. Necdin, a p53-interacting protein expressed predominantly in postmitotic neurons, is a melanoma antigen family protein that promotes neuronal differentiation and survival. In mammals, the necdin gene (Ndn) is maternally imprinted, and mutant mice carrying mutated paternal Ndn show abnormalities of neuronal development. Here we report that necdin regulates the acetylation status of p53 via Sirt1 to suppress p53-dependent apoptosis in postmitotic neurons. Double-immunostaining analysis demonstrated that necdin colocalizes with Sirt1 in postmitotic neurons of mouse embryonic forebrain in vivo. Coimmunoprecipitation and in vitro binding analyses revealed that necdin interacts with both p53 and Sirt1 to potentiate Sirt1-mediated p53 deacetylation by facilitating their association. Primary cortical neurons prepared from paternal Ndn-deficient mice have high p53 acetylation levels and are sensitive to the DNA-damaging compounds camptothecin and hydrogen peroxide. Moreover, DNA transfection per se increases p53 acetylation and apoptosis in paternal Ndn-deficient neurons, whereas small interfering RNA-mediated p53 knockdown completely blocks these changes. However, Sirt1 knockdown increases both acetylated p53 level and apoptosis in wild-type neurons but fails to affect them in paternal Ndn-deficient neurons. In organotypic forebrain slice cultures treated with hydrogen peroxide, p53 is accumulated and colocalized with necdin and Sirt1 in cortical neurons. These results suggest that necdin downregulates p53 acetylation levels by forming a stable complex with p53 and Sirt1 to protect neurons from DNA damage-induced apoptosis. | Western Blotting | 18753379
 |
Site-specific acetylation of p53 directs selective transcription complex assembly.
Roy, S; Tenniswood, M
The Journal of biological chemistry
282
4765-71
2007
Show Abstract
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors are being investigated as possible adjuvant therapies for a number of diseases, including cancer. In addition to stabilization of acetylated histones, HDAC inhibitors stabilize the acetylation of a number of transcription factors, including p53. This study investigates the action of two HDAC inhibitors, CG-1521 and trichostatin A, which stabilize Ac-Lys-373 p53 and Ac-Lys-382 p53, respectively, in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Real-time PCR demonstrates that CG-1521 induces p21 transcription whereas trichostatin A does not alter the steady state level of p21 mRNA. Co-immunoprecipitation demonstrates that the selective acetylation of p53 directs the recruitment of mutually exclusive coactivator complexes on the p53 response elements in the p21 promoter. Furthermore, the co-activator complexes initiate the recruitment of the components of the basal transcription apparatus to the basal promoter with markedly different outcomes because only Ac-Lys-373 p53 promotes the assembly of the basal transcriptional apparatus on the p21 promoter. These data highlight the profound effects of post-translational modification, including acetylation, on the function of p53. The data also suggest a novel and critically important role for protein acetylation/deacetylation in the assembly of active transcription processes that may be as important as classical phosphorylation/dephosphorylation. | Immunoprecipitation | 17121856
 |
Histone deacetylase inhibitors differentially stabilize acetylated p53 and induce cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in prostate cancer cells.
Roy, S; Packman, K; Jeffrey, R; Tenniswood, M
Cell death and differentiation
12
482-91
2005
Show Abstract
In LNCaP prostate cancer cells CG-1521, a new inhibitor of histone deacetylases, alters the acetylation of p53 in a site-specific manner. While p53 is constitutively acetylated at Lys320 in LNCaP cells, treatment with CG-1521, stabilizes the acetylation of p53 at Lys373, elevating p21 (and inducing cell cycle arrest). Treatment with CG-1521 also promotes Bax translocation to the mitochondria and cleavage, and apoptosis. TSA stabilizes the acetylation of p53 at Lys382, elevating p21 levels and inducing cell cycle arrest, but does not induce Bax translocation or apoptosis. In LNCaP cells CG-1521, but not TSA, promotes the rapid degradation of HDAC2. These data suggest that the acetylation of p53 at Lys373 is required for the p53-mediated induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, while acetylation of p53 at Lys382 induces only cell cycle arrest. In p53(-/-) PC3 cells both compounds induce p21 and cell cycle arrest, but not Bax translocation or apoptosis, suggesting that both compounds can also induce p21 through a p53-independent mechanism. | | 15746940
 |