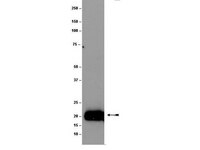
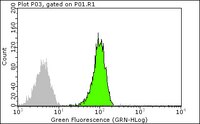
Innate inflammation induced by the 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1-KRAS-NF-κB pathway.
Aguilera-Aguirre, L; Bacsi, A; Radak, Z; Hazra, TK; Mitra, S; Sur, S; Brasier, AR; Ba, X; Boldogh, I
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950)
193
4643-53
2014
Show Abstract
8-Oxoguanine-DNA glycosylase-1 (OGG1) is the primary enzyme for repairing 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG) via the DNA base excision repair pathway (OGG1-BER). Accumulation of 8-oxoG in the genomic DNA leads to genetic instability and carcinogenesis and is thought to contribute to the worsening of various inflammatory and disease processes. However, the disease mechanism is unknown. In this study, we proposed that the mechanistic link between OGG1-BER and proinflammatory gene expression is OGG1's guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity, acquired after interaction with the 8-oxoG base and consequent activation of the small GTPase RAS. To test this hypothesis, we used BALB/c mice expressing or deficient in OGG1 in their airway epithelium and various molecular biological approaches, including active RAS pulldown, reporter and Comet assays, small interfering RNA-mediated depletion of gene expression, quantitative RT-PCR, and immunoblotting. We report that the OGG1-initiated repair of oxidatively damaged DNA is a prerequisite for GDP → GTP exchange, KRAS-GTP-driven signaling via MAP kinases and PI3 kinases and mitogen-stress-related kinase-1 for NF-κB activation, proinflammatory chemokine/cytokine expression, and inflammatory cell recruitment to the airways. Mice deficient in OGG1-BER showed significantly decreased immune responses, whereas a lack of other Nei-like DNA glycosylases (i.e., NEIL1 and NEIL2) had no significant effect. These data unveil a previously unidentified role of OGG1-driven DNA BER in the generation of endogenous signals for inflammation in the innate signaling pathway. | | 25267977
 |
Temporal dissection of K-ras(G12D) mutant in vitro and in vivo using a regulatable K-ras(G12D) mouse allele.
Wang, Z; Feng, Y; Bardeesy, N; Bardessy, N; Wong, KK; Liu, XY; Ji, H
PloS one
7
e37308
2012
Show Abstract
Animal models which allow the temporal regulation of gene activities are valuable for dissecting gene function in tumorigenesis. Here we have constructed a conditional inducible estrogen receptor-K-ras(G12D) (ER-K-ras(G12D)) knock-in mice allele that allows us to temporally switch on or off the activity of K-ras oncogenic mutant through tamoxifen administration. In vitro studies using mice embryonic fibroblast (MEF) showed that a dose of tamoxifen at 0.05 µM works optimally for activation of ER-K-ras(G12D) independent of the gender status. Furthermore, tamoxifen-inducible activation of K-ras(G12D) promotes cell proliferation, anchor-independent growth, transformation as well as invasion, potentially via activation of downstream MAPK pathway and cell cycle progression. Continuous activation of K-ras(G12D) in vivo by tamoxifen treatment is sufficient to drive the neoplastic transformation of normal lung epithelial cells in mice. Tamoxifen withdrawal after the tumor formation results in apoptosis and tumor regression in mouse lungs. Taken together, these data have convincingly demonstrated that K-ras mutant is essential for neoplastic transformation and this animal model may provide an ideal platform for further detailed characterization of the role of K-ras oncogenic mutant during different stages of lung tumorigenesis. | Western Blotting | 22606359
 |