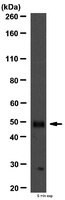
Enhanced structural and functional genome elucidation of the arsenite-oxidizing strain Herminiimonas arsenicoxydans by proteomics data.
Stéphanie Weiss,Christine Carapito,Jessica Cleiss,Sandrine Koechler,Evelyne Turlin,Jean-Yves Coppee,Michaël Heymann,Valérie Kugler,Magalie Stauffert,Stéphane Cruveiller,Claudine Médigue,Alain Van Dorsselaer,Philippe N Bertin,Florence Arsène-Ploetze
Biochimie
91
2009
Show Abstract
The arsenite-oxidizing strain Herminiimonas arsenicoxydans proteome was investigated with gel electrophoresis and tandem mass spectrometry analyses. The comparison of experimental and theoretical M(r) and pI, as well as that of peptide sequences identified by MS and predicted protein sequences, allowed the correction of five protein annotations. More importantly, the functional analysis of SDS- and 2D-PAGE proteome maps obtained in the presence of arsenic, combined with partial transcriptomic results indicate that H. arsenicoxydans expressed genes and proteins required not only for arsenic detoxification or stress response but also involved in motility, exopolysaccharide synthesis, phosphate import or energetic metabolism. This study provides therefore new insights into the adaptation processes of H. arsenicoxydans in response to arsenic. | 18852016
 |
Evaluation of the SELDI-TOF MS technique for protein profiling of pancreatic islets exposed to glucose and oleate.
Henrik Ortsäter,Tea Sundsten,Jian-Man Lin,Peter Bergsten
Proteomics
7
2007
Show Abstract
The aim of the study was to evaluate the SELDI-TOF MS technique for pancreatic islet research. Mouse islets were cultured at low or high glucose levels in the absence or presence of oleate and characterized by measuring insulin secretion and oxygen tension. Subsequently, the islets were protein profiled. Up to 200 different peaks could be detected in a single experiment with the majority of peaks corresponding to proteins with masses below 30 kDa. By combining different protein arrays, the number of detected peaks could be increased further. The optimal binding of islet proteins was achieved using the anionic exchange array and phosphate buffer (pH 6) when the binding of insulin was low, which allowed other less abundant proteins to be captured. When islets from different culture conditions were profiled and analyzed, in total 25 proteins were found to be oleate/glucose-regulated. An oleate-regulated protein was chosen for identification work, which was conducted by passive elution from SDS-PAGE gels and subsequent in-gel trypsin digestion and MALDI-TOF MS. The protein was identified as peptidyl-prolyl isomerase B (PPI-B). In conclusion, the study demonstrates that SELDI-technique can be used not only to obtain islet protein patterns but is also helpful in the subsequent identification of differentially expressed proteins. | 17661320
 |